Chapter: Modern Pharmacology with Clinical Applications: Antiinflammatory and Antirheumatic Drugs
Sulfasalazine
Sulfasalazine
Sulfasalazine (Azulfidine) is approved for the
treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and ulcerative colitis. It is also used to
treat ankylosing spondylitis and Crohn’s disease. Comparisons of sulfasalazine
with other DMARDs sug-gest that it is more effective than hydroxychloroquine,
azathioprine, and oral gold compounds. It is at least as effective as
intramuscular gold and penicillamine. It has a greater degree of toxicity than
hydroxychloroquine but less than gold compounds and penicillamine. After 5
years, approximately 75% of patients have discontinued sulfasalazine therapy,
primarily because of a lack of effi-cacy as opposed to intolerable side
effects.
Basic Pharmacology
Sulfasalazine is a prodrug of which 70% is
converted by colon bacteria to two active metabolites, sulfapyri-dine and
5-aminosalicylic acid (mesalamine). Sulfa-pyridine has antibacterial activities,
and 5-aminosali- cylic acid is antiinflammatory; however, these effects do not
account for the ability of this drug to slow the processes of rheumatoid
arthritis. Recent research sug-gests additional activities of sulfasalazine
that may be relevant to these effects: its ability to increase adeno-sine
levels, its inhibitory effects on IL-1 and TNF-αrelease, and its inhibition of
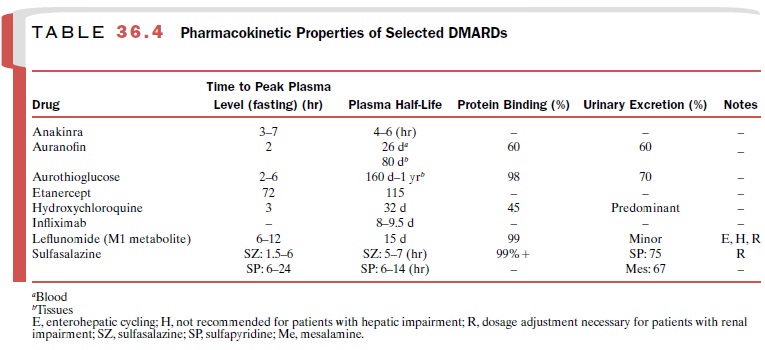
NF- B. The pharmacoki-netic data for this and other DMARDs are provided in
Table 36.4.
Adverse Effects
Mild to moderate side
effects, including nausea, vomit-ing, abdominal pain, diarrhea, anorexia, and
headache, occur in up to 33% of patients taking this drug. Skin rash and
discoloration, fever, reversible male infertility, and liver enzyme elevation
occur less frequently. Rare hematological abnormalities, such as
agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia, hemolytic anemia, neutropenia, or other blood
dyscrasias, can be fatal. Hypersensitivity re-actions occur rarely.
Contraindications and Drug Interactions
Sulfasalazine is contraindicated in individuals
with hy-persensitivity to salicylates, sulfonamides, sulfony-lureas, and
certain diuretics (furosemide, thiazides, and carbonic anhydrase inhibitors).
Because it can cause kernicterus, sulfasalazine is contraindicated in infants
and children under 2 years of age. Sulfasalazine passes into breast milk and is
therefore contraindicated for nursing mothers. Similarly, pregnant women near
term should not use this drug, although it appears to be the safest of the
DMARDs during early pregnancy.
Sulfasalazine can precipitate
attacks of porphyria and should not be used by individuals with bowel or
urinary obstruction.
Sulfasalazine can inhibit the absorption of
cardiac glycosides and folic acid. It may displace certain drugs, including
warfarin, phenytoin, methotrexate, tolbu-tamide, chlorpropamide, and oral
sulfonylureas, from their protein binding sites. Sulfasalazine can diminish the
effectiveness of penicillins and estrogen-containing oral contraceptives.
Related Topics