Chapter: Plant Biochemistry: Polysaccharides are storage and transport forms of carbohydrates produced by photosynthesis
Sucrose synthesis takes place in the cytosol
Sucrose synthesis takes place in the cytosol
The synthesis of sucrose, a disaccharide of glucose and fructose (Fig. 9.13), takes place in the cytosol of the mesophyll cells. As in starch synthesis, the glucose residue is activated as nucleoside diphosphate-glucose, although in this case via UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase:
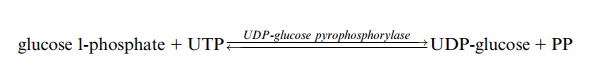
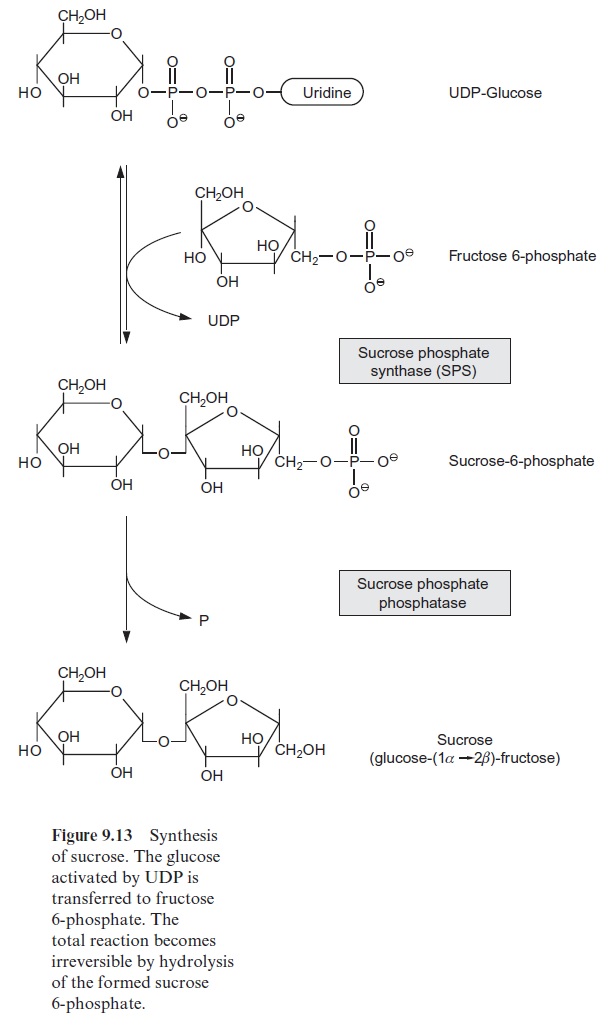
In contrast to the chloroplast stroma, a pyrophosphatase is not present in the cytosol of mesophyll cells. Since pyrophosphate cannot be with-drawn from the equilibrium, the UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase reac-tion is reversible. Sucrose phosphate synthase(abbreviated SPS, Fig. 9.13) catalyzes the transfer of the glucose residue from UDP-glucose to fructose 6-phosphate forming sucrose 6-phosphate. Sucrose phosphate phosphatase, forming an enzyme complex together with SPS, hydrolyzes sucrose 6-phos-phate, thus withdrawing it from the sucrose phosphate synthase reaction equilibrium. Therefore, the overall reaction of sucrose synthesis is an irre-versible process.
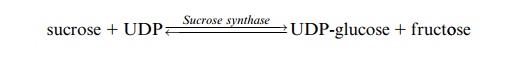
In addition to sucrose phosphate synthase, plants also contain a sucrose synthase:
This reaction is reversible. It is not primarily involved in sucrose synthesis but in the utilization of sucrose by catalyzing the formation of UDP-glucose and fructose from UDP and sucrose. This enzyme occurs mostly in nonphotosynthetic tissues. It is for instance involved in sucrose breakdown in amyloplasts of storage tissue such as potato tubers to sup-port starch synthesis . It also plays a role in the synthesis of cellulose and callose, where the sucrose synthase, otherwise soluble, is membrane-bound.
Related Topics