Chapter: Plant Biochemistry: Polysaccharides are storage and transport forms of carbohydrates produced by photosynthesis
Cellulose is synthesized by enzymes located in the plasma membrane
Cellulose is synthesized by enzymes located in the plasma membrane
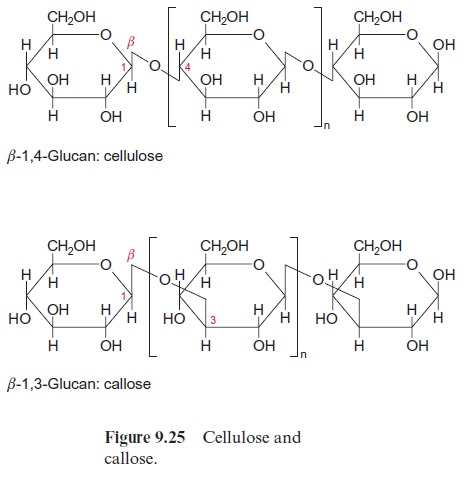
Cellulose, an important cell constituent , is a glucan in which the glucose residues are linked by ( β1→4)-glycosidic bonds forming a very long chain (Fig. 9.25). The synthesis of cellulose is catalyzed by cellulose synthase located in the plasma membrane. The required glucose molecules are delivered as UDP-glucose from the cytosol, and the newly synthesized cellulose chain is excreted into the extracellular compartment (Fig. 9.26). It has been shown in cotton-producing cells—a useful system for studying cellulose synthesis—that UDP-glucose is supplied from cytosolic sucrose by the action of a membrane-bound sucrose synthase. The UDP-glucose released is transferred directly to the cellulose synthase.
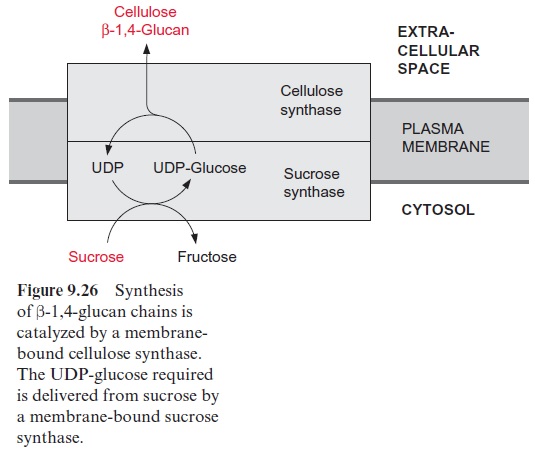
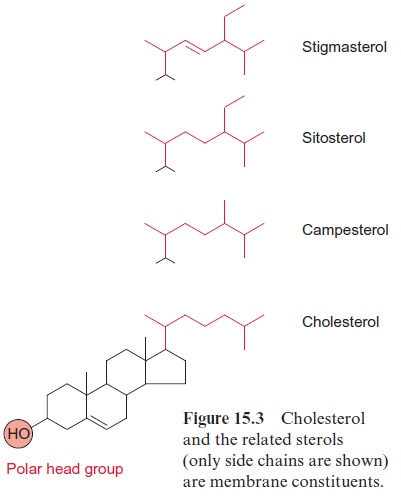
Alternatively UDP-glucose is synthesized from glucose 1-phosphate and UTP, catalyzed by UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase. The synthesis of cellulose starts with the transfer of a glucose residue from UDP-glucose to sitosterol (Fig. 15.3), a plasma membrane lipid. The glu-cose residue is bound to the hydroxyl group of the membrane lipid via a glycosidic linkage and acts as a primer for the cellulose synthesis, thus anchoring the growing cellulose chain to the membrane. Cellulose never occurs in single chains but always in a crystalline array of many chains called a microfibril . It is assumed that, due to the many neigh-boring cellulose synthases in the membrane, allβ-1,4-glucan chains of a microfibril are synthesized simultaneously and spontaneously assemble to a microfibril.
Synthesis of callose is often induced by wounding
Callose is a β-1,3-glucan (Fig. 9.25) with a long unbranched helical chain. Callose forms very compact structures and functions as a universal insula-tion material in the plant. In response to wounding of a cell, large amounts of callose can be synthesized very rapidly at the plasma membrane. According to present knowledge, its synthesis proceeds like the synthesis of cellulose (shown in Fig. 9.26). Membrane-bound sucrose synthase pro-vides UDP-glucose for callose synthesis. Callose synthesis is stimulated by an increase in the cytosolic Ca++ concentration. Wounding is accompanied by a Ca++ influx and an increase of the cytosolic Ca++ concentration, thus inducing the synthesis of callose for insulation. Plasmodesmata of injured cells are closed by callose formation in order to prevent damage to other cells of the symplast . Moreover, callose serves as a filling mate-rial to close defective sieve tubes.
Cell wall polysaccharides are also synthesized in the Golgi apparatus
In contrast to the synthesis of cellulose and callose localized outside of the plasma membrane, the synthesis of the cell wall polysaccharides hemicel-lulose and pectin takes place in the Golgi apparatus. In the synthesis GDP activated hexoses (e.g., GDP-mannose and GDP-fucose) are involved. The transfer of the polysaccharides synthesized in the Golgi apparatus to the cell wall proceeds via exocytotic vesicle transport.
Related Topics