Chapter: Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology: Integumentary System
Subcutaneous Tissue
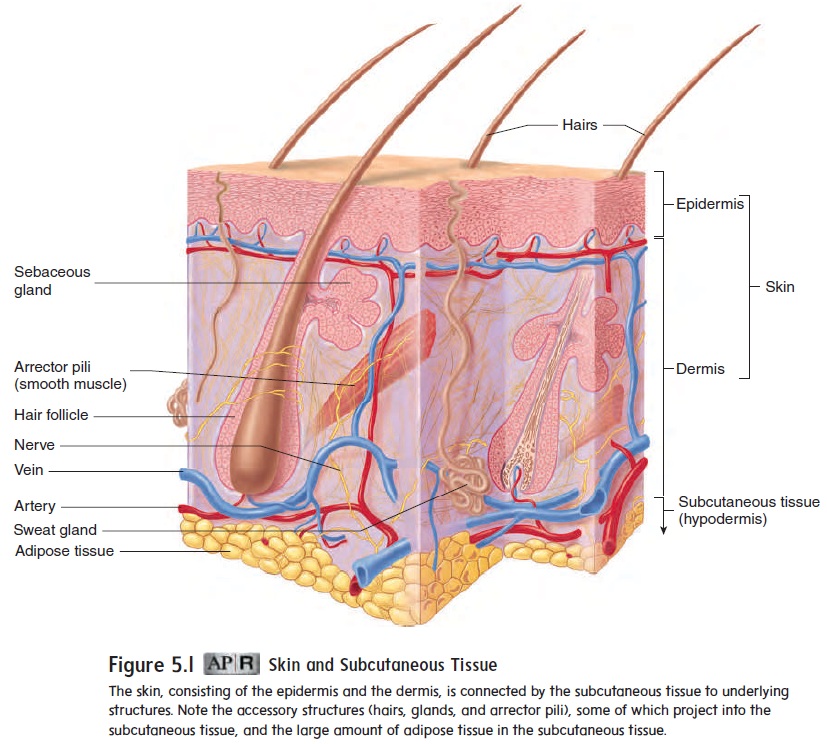
SUBCUTANEOUS TISSUE
Just as a house rests on a foundation, the skin rests on the subcu-taneous tissue, which attaches it to underlying bone and muscleand supplies it with blood vessels and nerves (see figure 5.1). The subcutaneous (s̆u b-koo-t̄a ′n̄e -̆u s; under the skin) tissue, which is not part of the skin, is sometimes called hypodermis (h -p̄o - der′mis; under the dermis). The subcutaneous tissue is loose con-nective tissue, including adipose tissue that contains about half the body’s stored lipids, although the amount and location vary with age, sex, and diet. Adipose tissue in the subcutaneous tissue functions as padding and insulation, and it is responsible for some of the differences in appearance between men and women as well as between individuals of the same sex.
The subcutaneous tissue can be used to estimate total body fat. The skin and subcutaneous tissue are pinched at selected locations, and the thickness of the fold is measured. The thicker the fold, the greater the amount of total body fat. The percentage of body fat var-ies in the population, but on average women have higher total body fat than do males. The acceptable percentage of body fat varies from 21% to 30% for females and from 13% to 25% for males. A body fat percentage above the acceptable range is an indicator of obesity.
Related Topics