Physics Laboratory Practical Experiment - Study of Relation Between Frequency and Length of a Given Wire Under Constant Tension Using Sonometer | 11th Physics : Practical Experiment
Chapter: 11th Physics : Practical Experiment
Study of Relation Between Frequency and Length of a Given Wire Under Constant Tension Using Sonometer
STUDY OF RELATION BETWEEN
FREQUENCY AND LENGTH OF A GIVEN WIRE UNDER CONSTANT TENSION USING SONOMETER
AIM
To study
the relation between frequency and length of a given wire under constant
tension using a sonometer.
APPARATUS REQUIRED
Sonometer,
six tuning forks of known frequencies, Metre scale, rubber pad, paper rider,
hanger with half ŌĆō kilogram masses, wooden bridges
FORMULA
The
frequency n of the fundamental mode of vibration of a string is given by n
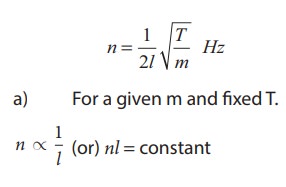
Where
n ŌåÆ
Frequency of the fundamental mode of vibration of the string (Hz)
m ŌåÆ Mass
per unit length of the string ( kg mŌĆō1 )
l ŌåÆ Length
of the string between the wedges (m)
T ŌåÆ
Tension in the string (including the mass of the hanger) = Mg ( N )
M ŌåÆ Mass
suspended, including the mass of the hanger (Kg)
DIAGRAM
SONOMETER - STUDY OF RELATION BETWEEN FREQUENCY AND LENGTH OF A GIVEN WIRE UNDER CONSTANT TENSION USING SONOMETER
PROCEDURE
┬Ę
Set up the
sonometer on the table and clean the groove on the pulley to ensure minimum
friction
┬Ę
Stretch
the wire by placing suitable mass in the hanger
┬Ę
Set the
tuning fork into vibrations by striking it against the rubber pad. Plug the
sonometer wire and compare the two sounds.
┬Ę
Adjust the
vibrating length of the wire by sliding the bridge B till the sounds appear
alike.
┬Ę
For the
final adjustment, place a small paper rider R in the middle of the wire AB.
┬Ę
Sound the
tuning fork and place its shank stem on the bridge A or on the sonometer box
and slowly adjust the position of bridge B until the paper rider is agitated
violently indicating resonance.
┬Ę
The length
of the wire between the wedges A and B is measured using meter scale. It is the
resonant length. Now the frequency of vibration of the fundamental mode equals
the fre-quency of the tuning fork.
┬Ę
Repeat the
above procedure for other tuning forks by keeping the same load in the hanger.
OBSERVATIONS
Tension
(constant) on the wire (mass suspended from the hanger including its own mass)
T = _______ N
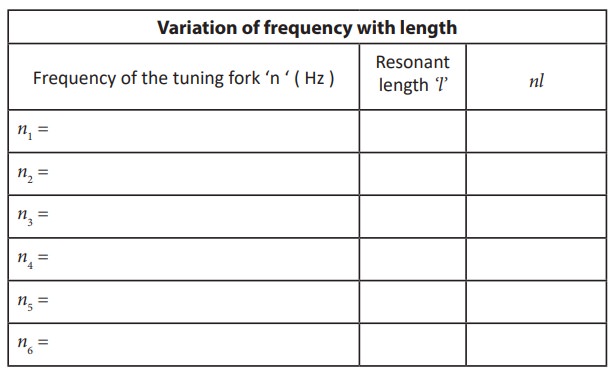
GRAPH:
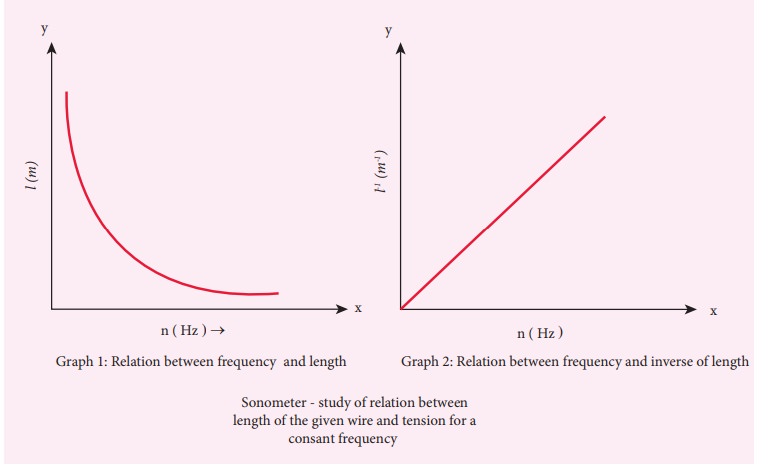
CALCULATION
The
product nl for all
the tuning forks remain constant (last column in the table)
RESULT
┬Ę
For a
given tension, the resonant length of a given stretched string varies as
reciprocal of the frequency (i.e., n ŌłØ 1/l)
┬Ę
The
product nl is a
constant and found to be ______ (Hz m)
Related Topics