Force and Motion | Term 1 Unit 2 | 7th Science - Student Activities, Numerical Problems | 7th Science : Term 1 Unit 2 : Force and Motion
Chapter: 7th Science : Term 1 Unit 2 : Force and Motion
Student Activities, Numerical Problems
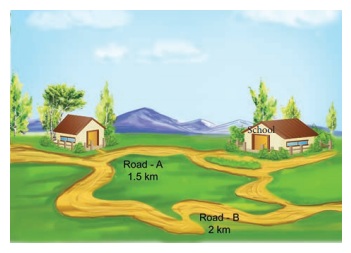
As shown in the above picture, Kavitha can reach her school in two ways. Can you tell, by choosing which path she could reach the school early.
Road A
Road B
Road A (1.5 km)
Road B (2 km)
Ōł┤ Road A is the answer
======== =========
Look at the nearby picture
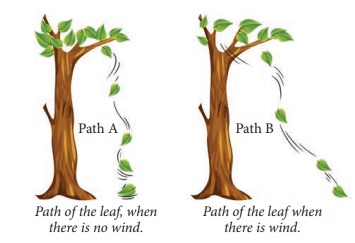
In which path the leaf will reach the ground first?
======== ======== ====== ======
Uma and Priya are friends studying in the same school. After school hours, they go to the nearby playground, play games and return back home. Oneday Uma told that she would reach the playground after visiting her grandmotherŌĆÖs house . The path in which they took reached the playground is shown here.
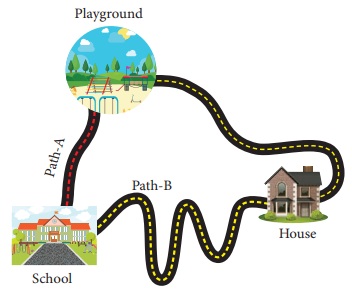
Take a twine and measure the length of the two paths (A & B). Which is the longest path among the two?
From the above examples, we could conclude that when an object travel from one place to another, it will reach faster if it travels along the straight line path. The straight line path is the shortest distance between two points.
======== ======== ====== ======
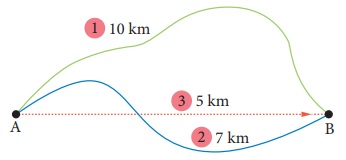
Figure shows the motion of a person between two places A and B.
He travels 10 km in first path. In the second path, he travels 7 km.
The distance between A and B via first path is 10 km. In the second path the distance is 7 km. The shortest distance between the two places is 5 km represented as 2. So the displacement is 5 km. (In east direction)
======== ======== ====== ======
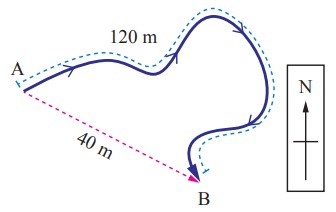
The path of an object travelling from A to B is shown in figure. Total distance travelled by the object is 120 m. The displacement of the object is 40 m (south-east direction)
======== ======== ====== ======
The path in which a rabbit ran is shown in figure. Find the distance and displacement of it in the two figures. Let us consider that each square is in an unit of one square meter. The rabbit starts from point A and reaches the point B.
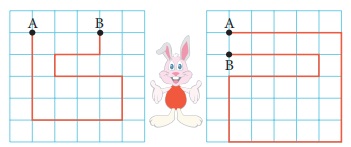
i) Distance - 17 m Displacement - 3m
ii) Distance - 27 m Displacement - 1m
When will the distance and displacement be equal. Explain. But the starting and finishing points should be different.
When travelling along the straight line path the distance and displacement be equal.
When we represent the displacement, we use a positive or negative sign depending on the direction with which it travels.

======== ======== ====== ======
Here we can consider the starting point as A and while the object moves from A to B the displacement is considered to be positive and from B to A it is negative.
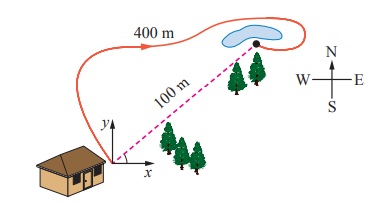
Answer the following questions:
* Subha goes to the nearby playground from her home.
1. What is the distance she travelled?
2. What is her displacement?
* The distance travelled by an object is 15 km and its displacement is 15 km. What do you infer from this?
The distance of a person = 30 km Displacement = 0 km.
* The distance of a person is 30 km and his displacement is 0 km. What do you inferfrom this?
(i.e.) The initial and the final position is same.
Nautical mile
Nautical mile is the unit for measuring the distance in the field of aviation and sea transportation. One nautical mile is 1.852 km.
The unit for measuring the speed of aeroplanes and ships is knot. One knot is the speed taken to travel one nautical mile in hour.
======== ======== ====== ======
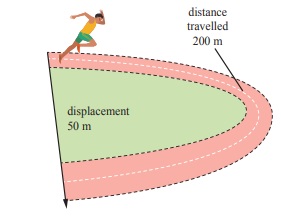
If an athlete in the diagram takes 25 s to complete a 200 m sprint event. Find her speed and velocity.
Speed = distance / time
=200 / 25
=8 m/s
velocity = displacement /time
=50/25
=2 m/s
E.g. Figure shows a car that travels 5 km due east and makes a U ŌĆō turn to travel another 7 km. If the time taken for the whole journey is 0.2 h. Calculate the average velocity of the car.
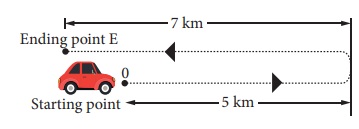
Average velocity = total displacement/time taken. (taking the direction due east of point O as positive)
= (5ŌĆō7)/0.2
= ŌĆō2 / 0.2
= ŌĆō10 km/h (or) ŌĆō10 ├Ś 5/18 = 25/9
= ŌĆō0.28 m / s
Answer the following questions:
* Calculate the velocity of a car travelling with a uniform velocity covering 100 m distance in 4 seconds.
Velocity = Sistance / time = 100/4 = 25 m/s
* Usain Bolt covers 100 m distance in 9.58 seconds. Calculate his speed. Who will be the winner if Usain Bolt comepetes with a Cheetah running at a speed of 30 m/s?
Speed of Usain Bolt = 10.43 m/s
Speed of cheetah = 30 m/s
Cheetah will be the winner.
* You are walking along east covering a distance of 4 m, then 2 m towards south,then 4 m towards west and at last 2 m towards north. You cover the total distancein 21 seconds, what is your average speed and average velocity?
Total distance covered = 12 m
Total time taken =21 seconds
Average speed = Total distance covered / total time = 12m / 21 = 0.571 m/s
Average velocity = 0 m/s
12m / 21 = 0.571 m/s
Average velocity = 0 m/s
Average velocity is zero because the starting point and the finishing point is same
Ōł┤Displacement is zero so, average velocity is also
Average velocity = Total distance / time
======== ======== ====== ======
In other words, the object undergoes acceleration when its speed and/or direction change(s).
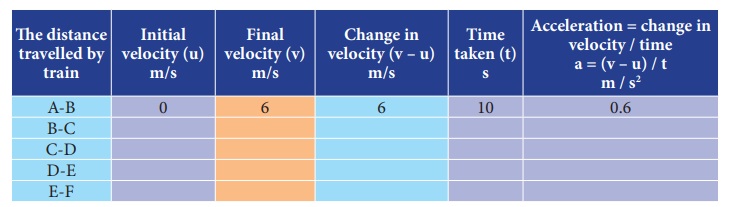
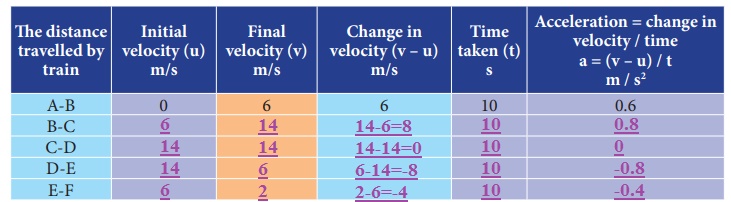
The velocity at different times of a train departing direction is given in the figure. Analyse this and complete the table .
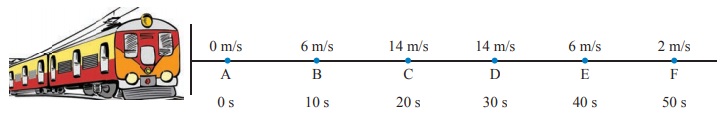
Answer:
Analysis:
When the train covers the distance A to B and B to C, it is accelerated motion.
When it covers the distance C-D, there is no acceleration (i.e) uniform velocity.
When it covers the distance D to E and E to F it has negative acceleration or deceleration or retardation, (i.e.) Its velocity decreases with respect to time.
Tell me
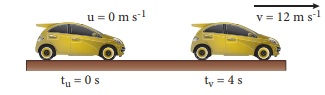
A car at rest starts to travel in a straight path. It reaches a velocity of 12 m/s in 4 s . What is its acceleration. Assuming that it accelerates uniformly?
Initial velocity u =0 m/s (since the car starts from rest)
Final velocity (v) =12 m /s
Time taken (t ) =4 s
acceleration ( a ) =(v ŌĆō u) / t
= (12ŌĆō0)/4
=3 m / s2
==== ======== =============
See how brisk I am !

My name is cheetah. I can run at a great speed. Do you know what my speed is? 25 m/s to 30 m/s. My speed changes from 0 to 20 m/s in 2 second. See how good my acceleration is !
Tell me
From the above information, can you calculate the acceleration of the cheetah?
Acceleration of the cheetah = [ Final velocity(v) - Initial velocity(u) ] / [time taken]
= [ v - u ] / t = 20-0 / 2 = 20/2 = 10 m/s2
Acceleration of the cheetah = 10 m/s2
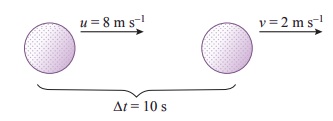
The velocity of a golf ball rolling in a straight line changes from 8 m/s to 2 m/s in 10 s. What is its deceleration, assuming that it is decelerating uniformly ?
Initial velocity (u) =8 m/s
Final velocity (v) =2 m/s
Time taken(t) =10 s
Acceleration (a) =(v ŌĆō u)/t
=(2 ŌĆō 8)/10
= ŌĆō0.6 m/s2
The deceleration is ŌĆō0.6 m/s2
Table shows a moving bus with uniform acceleration.
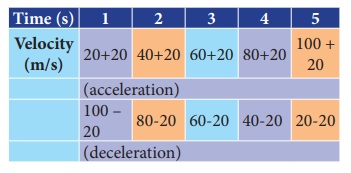
When the velocity of the object is increasing by 20 m/s the acceleration is 20 m/s2 When the velocity of the object is decreasing by 20 m/s the deceleration is 20 m/s2.
When the velocity of the object is decreasing by 20m/s the deceleration is 20 m/s2.
Deceleration = Decrease in velocity / Deceleration = t = 20/20 = 1s
The velocity of the object is decreasing by 20m/s in one second.
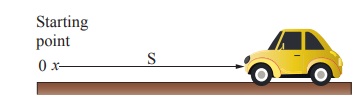
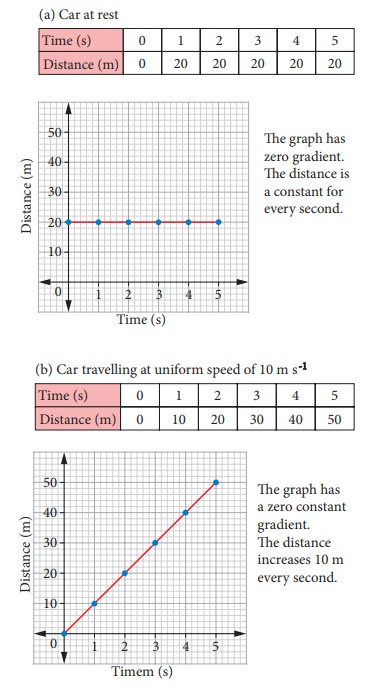
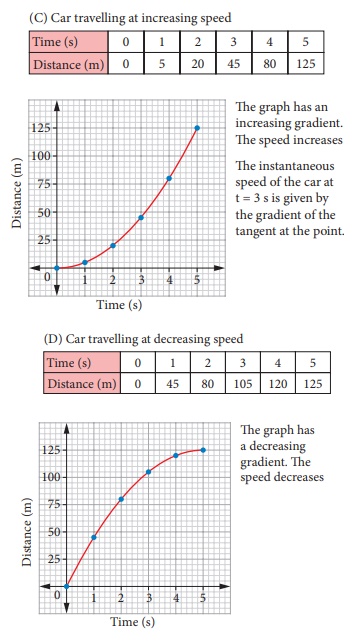
Figure shows a car travelling along a straight line away from the starting point O. The distance of the car is measured for every second. The distance and time are recorded and a graph is plotted using the data. The results for four possible journeys are shown below.
= ==== ======== =============
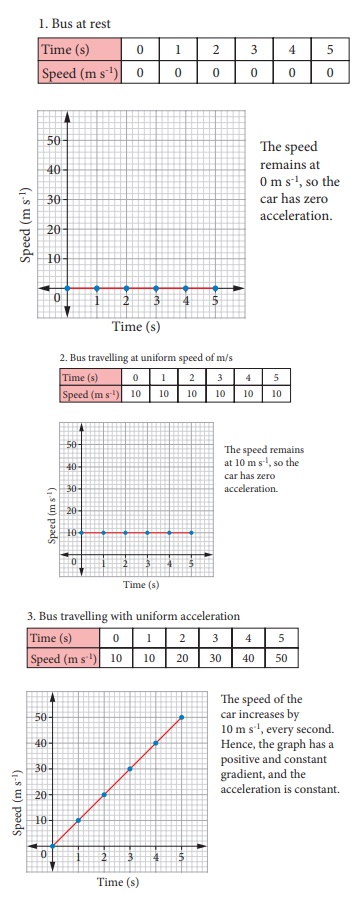
Let us consider a bus travelling from Thanjavur to Trichy. The speed of the bus is measured for every second. The speed and time are recordedand a graph is plotted using the data. The results for four possible journeys are shown.
=========== ==============

Related Topics