Force and Motion | Term 1 Unit 2 | 7th Science - Stability and three types of stability, Condition for Stability | 7th Science : Term 1 Unit 2 : Force and Motion
Chapter: 7th Science : Term 1 Unit 2 : Force and Motion
Stability and three types of stability, Condition for Stability
Stability
Stability is a measure of the bodyŌĆÖs
ability to maintain its original position.
The three types of stability are
a. Stable equilibrium
b. Unstable equilibrium
c. Neutral equilibrium
a. Stable Equilibrium
The frustum can be tilted through
quite a big angle without toppling.
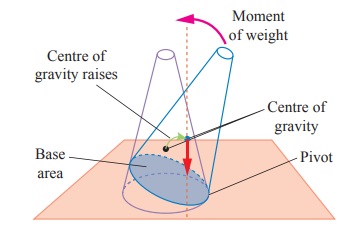
Its centre of gravity is raised when
it is displaced.
The vertical line through its centre
of gravity still falls within its base.
So it can return to its
orginalpositionl.
b. Unstable Equilibrium
The frustum will topple with the
slightest tilting. Its centre of gravity is lowered when it is displaced.
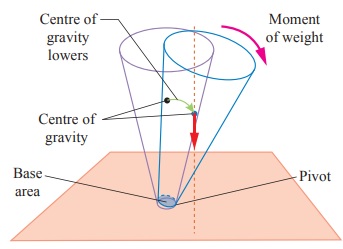
The vertical line through its centre
of gravity falls outside its base.
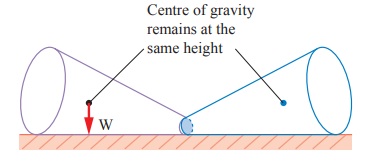
c. Neutral Equilibrium
d. It causes frustum to topple.
e. The frustum will rolls about but
does not topple.
f. Its centre of gravity remains at
the same height when it is displaced.
g. The body will stay in any
position to which it has been displaced.
Condition for Stability
* To make a body more stable
* Lower its centre of gravity
Increase the area of its base
* This box is at the point of
tipping over
* A heavy base lowers at the centre
of gravity So the box does not tip over
* A brode base makes the box more di’¼ācult to tip over
The Thanjavur Doll
It is s type of traditional Indian
toy made of terracotta material. The centre of gravity and the total weight of the
doll is concentrated at its bottom most point, generating a dance-like
continuous movement with slow oscillations.

Real Life Applications
of Centre of Gravity
It is for the reasons of stability
that the luggage compartment of a tour bus is located at the bottom and not on
the roof. Extra passengers are not allowed on the upper deck of a crowded
double decker bus. Racing cars are built low and broad for stability. Table
lamps and fans are designed with large heavy bases to make them stable.
Related Topics