Chapter: 11th Nutrition and Dietetics : Chapter 10 : Proteins and Lipids
Structure of proteins
Structure
of proteins
About 20 different
amino acids may appear in proteins. All amino acids share a common chemical
‘backbone’ and it is these backbones that are linked together to form proteins.
Each amino acid also carries a side chain, which varies from one amino acid to
another. The side chains make the amino acids differ in sizes, shape and
electrical charge. The side chains on amino acids are what makes proteins so
varied in comparison with either carbohydrate (or) lipids.
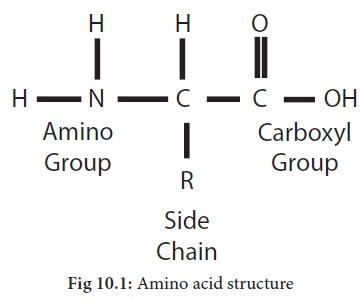
Each amino acid
contains a carboxyl (COOH) or acidic group and an amino
(NH2) or
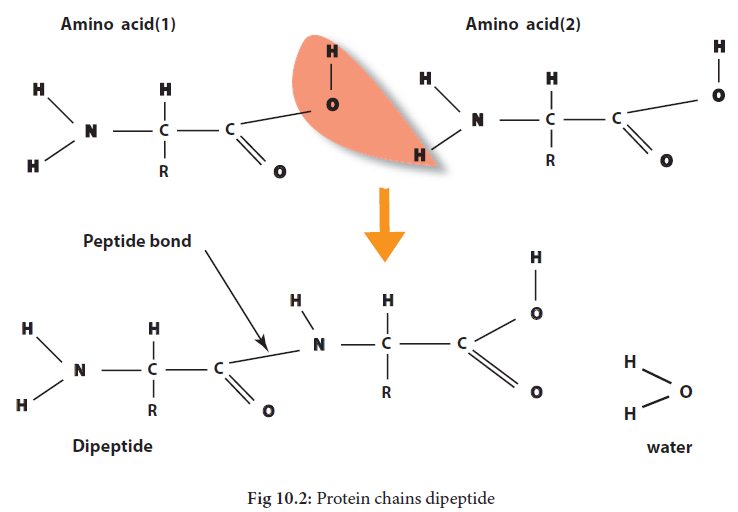
basic group. The amino acids are mostly linked together in forming a protein
molecule through NH2 group of one amino acid condensing with COOH
group of another amino acid with the elimination of one molecule of water, and
a compound thus
formed is called a
peptide and the linkage is called ‘peptide linkage’.
Protein chains
The 20 amino acids can be linked end-to-end in a virtually infinite variety of sequences to form proteins. When two amino acids bond together, the resulting structure is known as dipeptide.
Three amino acids bonded together to form a tripeptide. As
additional amino acids join the chain, the structure becomes a polypeptide.
Most proteins are polypeptides that are 100 to 300 amino acids long.
Related Topics