Chapter: 11th Nutrition and Dietetics : Chapter 10 : Proteins and Lipids
Classification of fats
Classification of fats
Fats are classified
into 4 categories as follows:
1. On the basis of
chemical composition
2. On the basis of fatty
acids
3. On the basis of
requirement
4. On the basis of
sources
1. On the basis of chemical composition
Fats can be classified
into 3 main groups as follows:
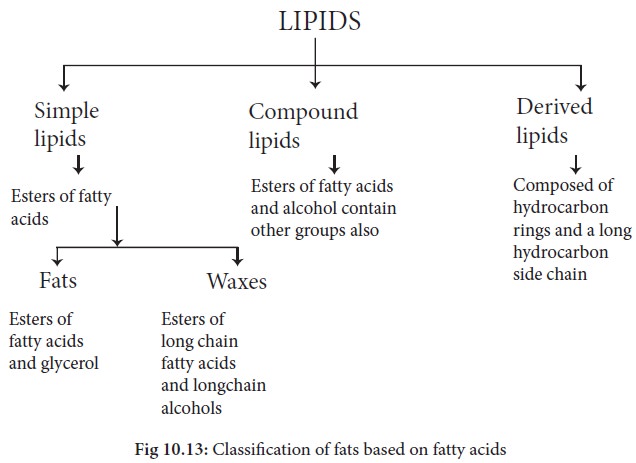
1. Simple lipids
These are esters of fatty acids and glycerol. They are also called as neutral fats or triglycerides. These neutral fats make up 98 -99% of food and body fats.(e.g) fats and oils
Waxes: A wax is a simple
lipid which is an ester of fatty acids and long chain aliphatic alcohols. The
alcohol may contain 12-32 carbon atoms. Waxes are found in nature as coatings
on leaves and stems. The wax prevents the plant from losing excessive amounts
of water.
2. Compound lipids
The compound lipids
contain, in addition to fatty acids and glycerol,some other organic compounds.
1. Phospholipids: These contain
phosphoric acid and a nitrogenous base in addition to fatty acids and
glycerol(e.g.)Lecithin and cephalin
2. Glycolipids: Complex lipids containing
carbohydrates in combination with fatty acids and glycerol(e.g) Cerebrosides
3. Lipoproteins: Lipoproteins are the
most important as they are the
carriers of lipids in
the blood and form cell membranes.
3. Derived lipids
These are substances
liberated during hydrolysis of simple and compound lipids which still retain
the properties of lipids. The important members of this group are sterols,
fatty acids and alcohol.
i. Sterols : Sterols are solid
alcohols and form esters with fatty acids. In nature they occur in the free
state in the form of esters. Based on their origin sterols are classified as
cholesterol (animal origin) and phytosterol (in plants).
Cholesterol is a waxy,
fat-like substance found in all cells of the body and has several important
functions in the body. It is synthesized in the body by the liver independent
of the dietary intake. The body normally synthesizes about 2 grams of
cholesterol. The dietary sources of cholesterol includes animal foods. It is used in the body for synthesizing
hormones, Vitamine D and substances which help digest foods. High blood
cholesterol is a risk factor for heart disease. Rich sources of dietary
cholesterol include meat, poultry(with skin), organ meats like brain, kidney,
liver and full fat dairy products.
ii. Fatty acids: They are the key,
refined fuel form of fat that the cell burns for energy. They are the basic
structural unit of fats and they may be saturated or unsaturated. (e.g) Oleic
acid, linoleic acid, linolenic acid, palmitic acid and myristic acid.
2. On the basis of fatty acids
Fats can be classified
based on the fatty acids present in them as follows:
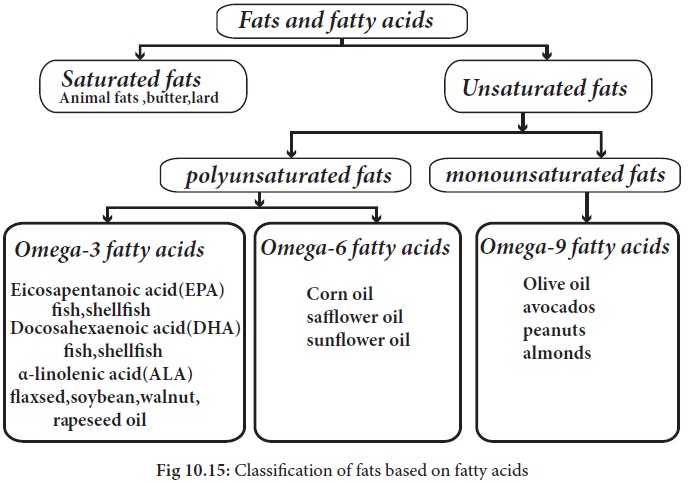
1. Saturated fatty acids
A saturated fat is a type of fat in which the
fatty acid chains have all or predominantly single bonds. Various fats contain
different

Saturated fatty acids, especially palmitic and stearic acids are
found in animal products such as cream, cheese, butter, other whole milk dairy
products and fatty meats which also contain dietary cholesterol. Certain
vegetable products have high saturated fat content, such as coconut oil and
palm kernel oil. Many prepared foods are high in saturated fat content, such as
pizza, dairy desserts and sausage.
2. Unsaturated fatty acids
An unsaturated fat is
a fat or fatty acid in which there is at least one double bond within the fatty
acid chain.
i. Monounsaturated fatty acid (MUFA): A fatty acid chain is monounsaturated if it contains one double bond. Monounsaturated fats are good fats. A diet high in MUFA can reduce blood cholesterol levels, lowers risk of heart disease, stroke and breast cancer, reduces pain in rheumatoid arthritis and helps in weight loss. Foods which contain MUFA (Oleic acid) are avocados, olives, olive oil, peanut butter and peanut oil. It is also known as omega-9 fatty acid.
(ii) Polyunsaturated
fatty acid (PUFA): A fatty acid is polyunsaturated if it contains more than
one double bond. They are of 2 types, namely Omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids.
a. Omega-3: It is also called ω−3
fatty acids or n−3 fatty acids with a double bond (C=C) at the third carbon
atom from the end of the carbon chain. The three types of omega−3 fatty acids
involved in human physiology are α-linolenic acid (ALA) [found in plant oils],
eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) [both commonly
found in marine oils]. Common sources of plant oils containing the omega−3
ALA fatty acid include
walnut, flaxseed, flaxseed oil,soybeans and chia seeds.The sources of animal
omega−3 EPA and DHA fatty acids include fish and fish oils.

The health benefits of
omega-3 fatty acids are immense and they have been proven effective in
the treatment and prevention of hundreds of medical conditions which includes
high cholesterol, depression, anxiety, cancer, diabetes mellitus,
inflammatory diseases, arthritis and cardiovascular diseases.
b. Omega-6: Omega-6 fatty acids
(also referred to as ω-6 fatty acids or n-6 fatty acids) are a family of pro-
inflammatory and anti-inflammatory polyunsaturated fatty acids that have in
common a final carbon-carbon double bond in the n-6 position, that is the sixth
bond, counting from

Omega-6 fats, also known as linoleic acid, are available only in food. The
human body cannot make them, so they are considered essential fats. They
support brain function, bone health, reproductive health, hair growth and
regulation of metabolism. Good sources of linoleic acid include vegetable oils.
3. On the basis of requirement
Fatty acids are of 2
types:
1. Essential fatty acids
Fatty acids which are
essential to be taken in our diet because they cannot be synthesized in our
body are known as essential fatty acids.(eg.) Linoleic, linolenic and
arachidonic acids.
2. Non-essential fatty acids
Non-essential fatty
acids are those which can be synthesized by the body and which need not be
supplied through the diet. Palmitic acid, oleic acid and butyric acid are
examples of non– essential fatty acids.
4. On the basis of sources
Fats are divided into
2 types based on their source, namely visible and invisible fats. Some fats and
oils added to food or used for
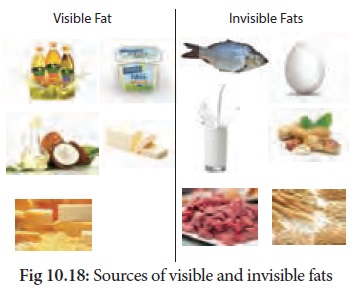
These are also known as pure fats. Many foods like milk, cream, egg yolk,
meat, fish and even cereals and legumes contribute substantial amount of
invisible fats (not visible in the food) to the diet.
Related Topics