Chapter: 11th Biochemistry : Chapter 7 : Nucleic Acids
Structure of DNA
Structure of DNA
In 1953,
J.D. Watson and F.H.C. Crick proposed a precise three dimensional model of DNA
structure based on model building studies, base composition and X-ray diffraction
studies carried out by Maurice Wilkins and Rosalind Franklin. This model is
popularly known as the DNA double helix (Figure7.6).
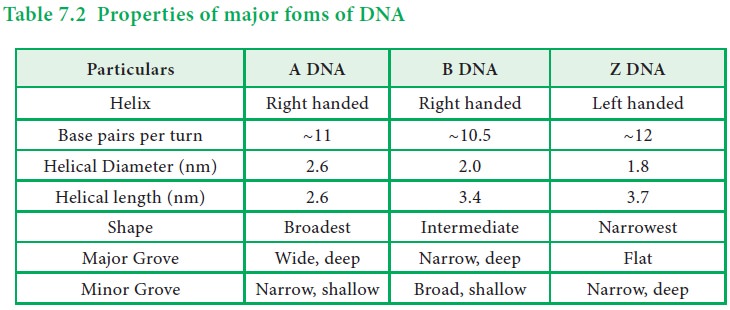
1. Different forms of DNA
There
are three forms of DNA – A, B and Z DNA. The characteristics of each form of
DNA is listed in the table given below.
Table
7.2 Properties of major foms of DNA
2. Salient features of the structure of DNA
The B
form DNA, also known as the Watson- Crick DNA is the most stable and prevalent
form of DNA. The important structural features of B- DNA are :
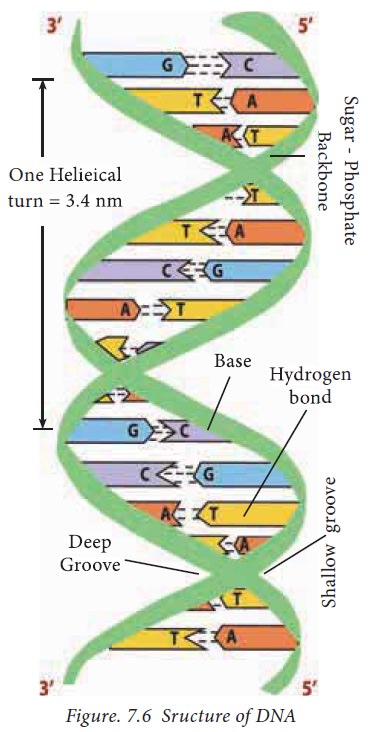
· Tvhere are two polynucleotide chains in the DNA
spirally twisted around each other to form a right handed double helix.
· The sugar-phosphate backbones remain on the
outside, while the core of the helix contains the purine and pyrimidine bases.
· The diameter of DNA is 2 nm or 20 A°. The length of
a complete turn of helix is 3.4 nm or 34 A° i.e. there are ~10.5bp per turn.
· The DNA helix has a shallow groove called minor
groove (-1.2nm) and a deep groove called major groove (-2.2nm). Proteins
interact with DNA through the minor and major grooves without disrupting the
DNA strands.
· Each polynucleotide chain is made up of four
different bases. The purine bases
present in DNA are adenine and guanine and the pyrimidine bases present are
thymine and cytosine. The sequence of purine and pyrimidine carry the genetic
information whereas the sugar and phosphate groups perform the structural role.
· Each polynucleotide chain has direction or
polarity. Further, each polynucleotide chain has 5΄phosphorylated and
3΄hydroxyl ends.
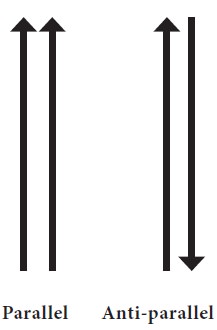
·
The two strands run
in opposite direction (i.e.) they are antiparallel.
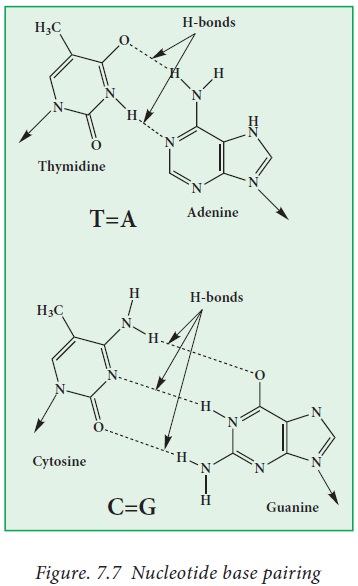
· The two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds
(base pairing) between the purine and pyrimidine bases of the opposite strands.
Watson and Crick deduced the rules of base pairing (Fig. 7.7). They are:
· The purine adenine (A) always pairs with the pyrimidine thymine
(T).
· The purine guanine (G) always pairs with the pyrimidine cytosine
(C).
Base pairing is achieved through
hydrogen bonding.
Therefore, if adenine appears in one
strand, thymine is found in the opposite strand and vice versa. When guanine is
found in one strand,
cytosine is present in the opposite strand
and vice versa. So, Base sequence of one strand is complementary to the
opposite strand. For example, If the sequence 5’ATGGACC3΄is present in one
strand, the complementary strand will be having the sequence, 3’TACCTGG5’.
There are two hydrogen bonds between
A and T and three hydrogen bonds between G and C.
·
Base composition of
DNA obeys Chargaff ’s rule.
Chargaff ’s rule
Erwin Chargaff, a scientist analyzed the chemical composition of DNA isolated from different
species and found that irrespective of the source, the molar concentration of Adenine
always equals Thymine and the molar concentration of Guanine always equals
Cytosine. A=T and G=C. Therefore, A + T = G + C and the ratio of A+T /G+C =
1.0,which means that the total number of purine bases = the total number of
pyrimidine bases.
Related Topics