Chapter: 11th Biochemistry : Chapter 7 : Nucleic Acids
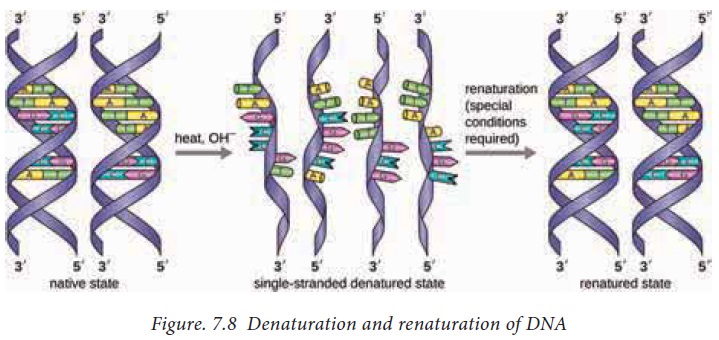
Denaturation of DNA
Denaturation of DNA
At high temperatures (950C),
the double helical structure of DNA melts due to disruption of base pairing
that results in two single strands. This is called as Denaturation of DNA. The
temperature at which it does so is called as Melting temperature (Tm). AT rich
regions melt faster than GC rich regions. Therefore, Tm is dependent upon the
composition of DNA. During denaturation, the absorption of DNA at 260nm
increases. This property of DNA is called as hyperchromicity. If the
temperature is brought down, the single strands rejoin to form double stranded
regions. This is called as annealing of DNA (Fig. 7.8). This property of DNA is
exploited in Polymerase Chain Reaction.
Related Topics