Chapter: 11th Computer Technology : Chapter 15 : Internet and E-Mail
Structure and Working of E-Mail
Structure
and Working of E-Mail:
Electronic
Mail (email or e-mail) is a method of exchanging messages between people using
electronic devices. Email first entered limited use in the 1960s and by the
middle of 1970s had taken the form now recognized as email. Email operates
across computer networks, which is primarily called as Internet.
Earlier
email systems required the sender and the recipient to both be online at the
same time, in common with instant messaging. Today's email systems are based on
a store-and-forward model. Email servers accept, forward, deliver, and store
messages.
The
structure of the E-mail address is username@domain name
An
example of E-mail address is raman@gmail.com
An
E-mail address consists of two parts separated by @ symbol. The first part
Raman is the user name that identifies the address and the second part
gmail.com is the domain name of the E-mail server.
Sample E-mail Application
How Email works on the Internet :
To
send Internet e-mail, requires an Internet connection and access to a mail
server. The standard protocol used for sending Internet e-mail is called SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol). The SMTP protocol is used to
both send and receive email messages over the Internet.
When
a message is sent, the email client sends the message to the SMTP server. If
the recipient of the email is local the message is kept on the server for
accessing by the POP, IMAP or other
mail services for later retrieval.
If
the recipient is remote (i.e. at another domain), the SMTP server communicates
with a Domain Name Server (DNS) to find the corresponding IP address for the
domain being sent to. Once the IP address has been resolved, the SMTP server
connects with the remote SMTP server and the mail is delivered to this server
for handling.
If
the SMTP server sending the mail is unable to connect with the remote SMTP
server, then the message goes into a queue. Messages in this queue will be
retried periodically. If the message is still undelivered after a certain
amount of time (30 hours by default), the message will be returned to the
sender as undelivered.
Structure of an Email message:
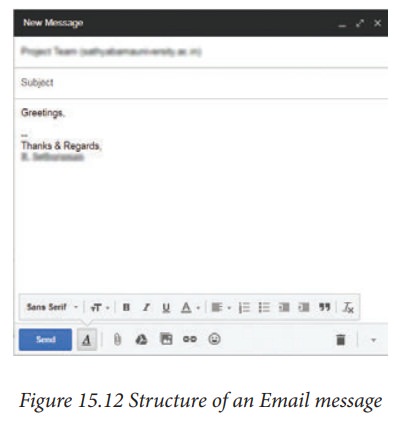
To: This field consists of the address to whom the message has to be sent. This is
mandatory.
CC:
Short for carbon copy. This is optional. The people who were mailed copies of
the message. The recepients of the message will know to whom all the copies
have been sent.
BCC: Its stands for Black Carbon Copy. It is used when we do not want one or
more of the recipients to know that someone else was copied on the message.
This is optional.
Subject : The Subject field indicates the purpose of e-mail.
Attachment: Attachment contains files that you are sending, linked documents,
pictures, etc. along with an e-mail.
Body: The email body is the main part of
an email message. It contains the
message’s text, images and other data (such as attachments). The email’s body
is distinct from its header, which contains control information and data about
the message (such as its sender, the recipient and the path an email took to
reach its destination).
Signature: Name of the sender
Advantages and Disadvantages of Email:
Advantages:
• Reliable: Because it notifies the sender if not delivered.
• Speed: E-mail is very fast delivered in fraction of seconds.
• Inexpensive: Its very cheap.
•
Waste Reduction: Helps in paperless communication thus eco-friendly.
Disadvantages:
• Forgery: Anyone who hacks the password of the sender can send a
message to anyone.
• Overload: Because it is cheap loads and loads of messages keeps coming.
• Junk: Junk emails are not intended mails and is inappropriate also. Junk
emails are sometimes referred to as spam.
Related Topics