Chapter: Object Oriented Programming(OOP) : Java Exception Handling
Strings - Java
STRINGS
— string:
An object storing a sequence of text characters.
— Unlike
most other objects, a String is not created with new. String name =
"text";
String
name = expression;
— Examples:
String name = "Marla Singer";
int x = 3;
int y = 5;
String
point = "(" + x + ", " + y + ")";
Indexes
— Characters
of a string are numbered with 0-based indexes: String name = "P.
Diddy";
— The first
character's index is always 0
— The last
character's index is 1 less than the string's length
— The
individual characters are values of type char (seen later)
String methods
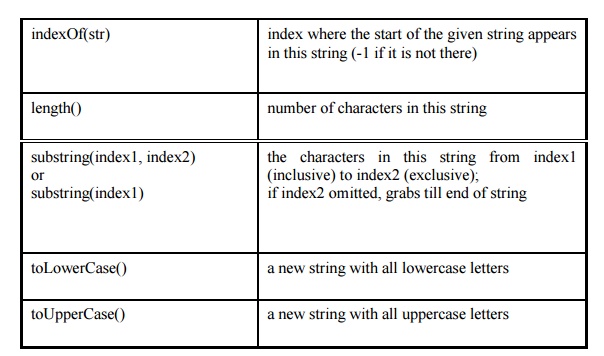
// index 012345678901
String s1 = "Stuart Reges";
String s2 = "Marty Stepp";
System.out.println(s1.length()); // 12
System.out.println(s1.indexOf("e")); // 8
System.out.println(s1.substring(7,
10)) // "Reg"
String s3 = s2.substring(2, 8);
System.out.println(s3.toLowerCase()); // "rty st"
ď‚— Given
the following string:
// index 0123456789012345678901 String book
= "Building Java Programs";
ď‚— How
would you extract the word "Java" ?
ď‚— How
would you extract the first word from any string?
Modifying strings
— Methods
like substring, toLowerCase, etc. create/return
a new
string, rather than modifying the current string.
String s
= "lil bow wow";
s.toUpperCase();
System.out.println(s); // lil bow wow
— To modify
a variable, you must reassign it: String s = "lil bow wow";
s =
s.toUpperCase();
System.out.println(s);
// LIL BOW WOW
Strings
as parameters
public
class StringParameters {
public static void main(String[] args) {
sayHello("Marty");
String
teacher = "Helene"; sayHello(teacher);
}
public static void sayHello(String name) {
System.out.println("Welcome, " + name);
}
}
Output:
Welcome,
Marty
Welcome,
Helene
Strings
as user input
— Scanner's
next method reads a word of input as a String. Scanner console = new
Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("What is your name? ");
String
name = console.next(); name = name.toUpperCase();
System.out.println(name
+ " has " + name.length() +
" letters
and starts with " + name.substring(0, 1)); Output:
What is
your name? Madonna MADONNA has 7 letters and starts with M
— The
nextLine method reads a line of input as a String.
System.out.print("What
is your address? ");
String
address = console.nextLine();
Comparing
strings
— Relational
operators such as < and == fail on objects. Scanner console = new
Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("What is your name? ");
String
name = console.next(); if (name == "Barney") {
System.out.println("I
love you, you love me,"); System.out.println("We're a happy
family!");
}
— This code
will compile, but it will not print the song.
— ==
compares objects by references (seen later), so it often gives false even when
two Strings have the same letters.
The
equals method
— Objects
are compared using a method named equals. Scanner console = new
Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("What is your name? ");
String
name = console.next(); if (name.equals("Barney")) {
System.out.println("I
love you, you love me,"); System.out.println("We're a happy
family!");
}
— Technically this is a method that returns a
value of type boolean, the type used in logical tests.
Related Topics