Chapter: Object Oriented Programming(OOP) : Java Exception Handling
Exception Handling
EXCEPTION HANDLING
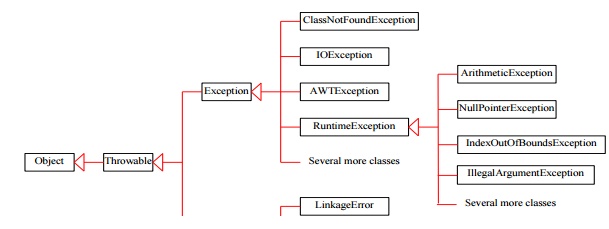

Throwing Exceptions
When the
program detects an error, the program can create an instance of an appropriate
exception type and throw it. This is known as throwing an exception. Here is an
example,
throw new
TheException();
TheException
ex = new TheException(); throw ex;
/** Set a
new radius */
public void setRadius(double newRadius) throws
IllegalArgumentException {
if (newRadius >= 0)
radius = newRadius;
else
throw new IllegalArgumentException( "Radius
cannot be negative");
}
Catching
Exceptions try {
statements; // Statements that may throw exceptions
}
catch (Exception1 exVar1) { handler for exception1;
}
catch (Exception2 exVar2) { handler for exception2;
}
...
catch (ExceptionN exVar3) { handler for exceptionN;
}
F An error
message appears on the console, but the GUI application continues running.
Write a
program that creates a user interface to perform integer divisions. The user
enters two numbers in the text fields Number 1 and Number 2. The division of
Number 1 and Number 2 is displayed in the Result field when the Divide button
is clicked.

Related Topics