Chapter: Object Oriented Programming(OOP) : Java Exception Handling
Packages - Java
PACKAGES
•
Packages enable grouping of functionally related
classes
•
Package names are dot separated, e.g., java.lang.
•
Package names have a correspondence with the
directory structure
•
Packages Avoid name space collision. There can not
be two classes with same name in a same Package But two packages can have a
class with same name.
•
Exact Name of the class is identifed by its package
structure. << Fully Qualified Name>> java.lang.String ;
java.util.Arrays; java.io.BufferedReader ; java.util.Date
•
Packages are mirrored through directory structure.
•
To create a package, First we have to create a
directory /directory structure that matches the package hierarchy.
•
Package structure should match the directory
structure also.
•
To make a class belongs to a particular package
include the package statement as the first statement of source file.
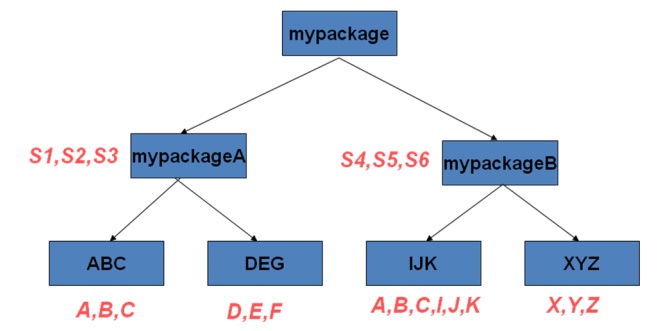
Package
ABC and IJK have classes with same name.
A class in
ABC has name mypackage.mypackageA.ABC.A
A class
in IJK has name mypackage.mypackageB.IJK.A
Include a
proper package statement as first line in source file
Make
class S1 belongs to mypackageA
package
mypackage.mypackageA;
public
class S1
{
public
S1( )
{
System.out.println("This
is Class S1");
}
}
Name the
source file as S1.java and compile it and store the S1.class file in mypackageA
directory
Make
class S2 belongs to mypackageA
package
mypackage.mypackageA;
public
class S2
{
public
S2( )
{
System.out.println("This
is Class S2");
}
}
Name the
source file as S2.java and compile it and store the S2.class file in mypackageA
directory
Make
class A belongs to IJK
package
mypackage.mypackageB.IJK;
public
class A
{
public A(
)
{
System.out.println("This
is Class A in IJK");
}
}
Name the
source file as A.java and compile it and store the A.class file in IJK
directory
1. Importing
the Package
import
statement allows the importing of package
Library
packages are automatically imported irrespective of the location of compiling
and executing program
JRE looks
at two places for user created packages
(i) Under the
current working directory
(ii) At the
location specified by CLASSPATH environment variable
•
Most ideal location for compiling/executing a
program is immediately above the package structure.
Example
importing
import
mypackage.mypackageA.ABC
import
mypackage.mypackageA.ABC.*;
class
packagetest
{
public
static void main(String args[])
{
B b1 =
new B(); C c1 = new C();
}
}
import
mypackage.mypackageA.ABC.*;
Import
mypackage.mypackageB.IJK.*;
class
packagetest
{
public
static void main(String args[])
{
A a1 =
new A();
}
}
mypackage.mypackageA.ABC.A
a1 = new mypackage.mypackageA.ABC.A();
OR
mypackage.mypackageB.IJK.A
a1 = new mypackage.mypackageB.IJK.A();
2. CLASSPATH Environmental
Variables
•
CLASSPATH Environmental Variable lets you define
path for the location of the root of the package hierarchy
•
Consider the following statement :
package
mypack;
What
should be true in order for the program to find mypack.
(i)
Program should be executed from the location immediately above mypack
OR
(ii)
mypack should be listed in the set of directories for CLASSPATH
Related Topics