Chapter: Object Oriented Programming(OOP) : Java Exception Handling
Java I/O ŌĆō The Basics
JAVA I/O ŌĆō THE BASICS
ŌĆó
Java I/O is based around the concept of a stream
ŌĆō Ordered sequence of information (bytes)
coming from a source, or going to a
ŌĆśsinkŌĆÖ
ŌĆō Simplest stream reads/writes only a single
byte, or an array of bytes at a time
ŌĆó
Designed to be platform-independent
ŌĆó
The stream concept is very generic
ŌĆō Can be applied to many different types of
I/O
ŌĆō Files, Network, Memory, Processes, etc
ŌĆó
The java.io package contains all of the I/O
classes.
ŌĆō Many classes specialised for particular
kinds of stream operations, e.g. file I/O
ŌĆó
Reading/writing single bytes is quite limited
ŌĆō So, it includes classes which provide extra
functionality
ŌĆō e.g. buffering, reading numbers and Strings
(not bytes), etc.
ŌĆó
Results in large inheritance hierarchy, with
separate trees for input and output stream classes
Java I/O ŌĆō InputStream

Java I/O
ŌĆō InputStreams
ŌĆó
I/O in Java:
InputStream
in = new FileInputStream(ŌĆ£c:\\temp\\myfile.txtŌĆØ); int b = in.read();
//EOF is
signalled by read() returning -1 while (b != -1)
{
//do
somethingŌĆ” b = in.read();
}
in.close();
ŌĆó But
using buffering is more efficient, therefore we always nest our streamsŌĆ”
InputStream inner = new FileInputStream(ŌĆ£c:\\temp\\myfile.txtŌĆØ);
InputStream
in = new BufferedInputStream(inner); int b = in.read();
//EOF is
signalled by read() returning -1
while (b
!= -1)
{
//do
somethingŌĆ” b = in.read();
}
in.close();
ŌĆó
WeŌĆÖve omitted exception handling in the previous
examples
ŌĆó
Almost all methods on the I/O classes (including
constructors) can throw an IOException or a subclass.
ŌĆó
Always wrap I/O code in tryŌĆ”catch blocks to handle
errors.
I/O ŌĆō OutputStream
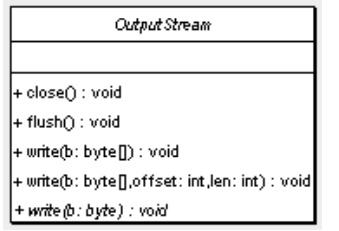
OutputStream
out = null; try
{
OutputStream
inner = new FileOutputStream(ŌĆ£c:\\temp\\myfile.txtŌĆØ); out = new
BufferedOutputStream(inner);
//write
data to the file } catch (IOException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally
{
try {
out.close(); } catch (Exception e) {}
}
Related Topics