Chapter: Object Oriented Programming(OOP) : Java Exception Handling
Multithreaded Programming
MULTITHREADED PROGRAMMING
A single
threaded program class ABC
{
….
public
void main(..)
{
…
..
}
}
A
Multithreaded Program
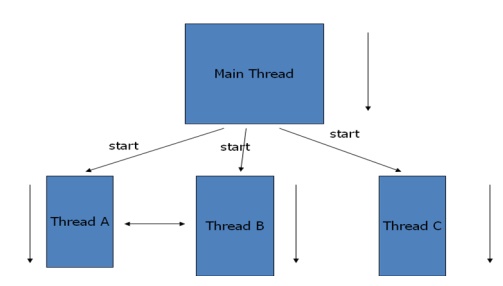
Multithreading
– Multiprocessors
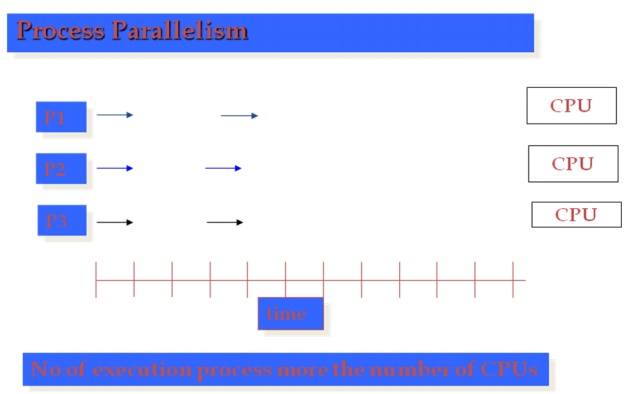
An
example
class MyThread extends Thread { // the thread
public void run() {
System.out.println("
this thread is running ... ");
}
} // end
class MyThread
class ThreadEx1 { // a program that utilizes the
thread
public static void main(String [] args ) {
MyThread
t = new MyThread();
// due to
extending the Thread class (above)
// I can
call start(), and this will call
// run(). start()
is a method in class Thread.
t.start();
} // end
main()
}// end
class ThreadEx1
class
MyThread implements Runnable
{
.....
public
void run()
{
// thread
body of execution
}
}
Creating Object:
MyThread myObject = new MyThread();
n Creating
Thread Object:
Thread thr1 = new Thread( myObject );
n Start
Execution:
thr1.start();
class MyThread implements Runnable { public void
run() {
System.out.println("
this thread is running ... ");
}
} // end
class MyThread
class
ThreadEx2 {
public static void main(String [] args ) { Thread t
= new Thread(new MyThread());
// due to
implementing the Runnable interface
// I can
call start(), and this will call run().
t.start(); } // end main()
}// end
class ThreadEx2
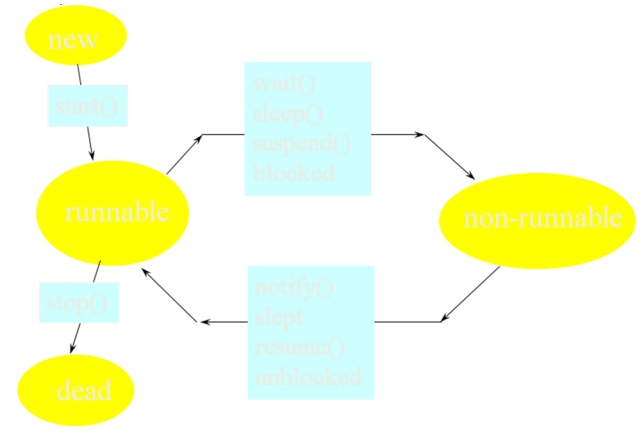
Life Cycle of Thread
Three
threads example
class A
extends Thread
{
public
void run()
{
for(int
i=1;i<=5;i++)
{
System.out.println("\t
From ThreadA: i= "+i);
}
System.out.println("Exit
from A");
}
}
class B
extends Thread
{
public
void run()
{
for(int
j=1;j<=5;j++)
{
System.out.println("\t
From ThreadB: j= "+j);
}
System.out.println("Exit
from B");
}
}
class C
extends Thread
{
public
void run()
{
for(int
k=1;k<=5;k++)
{
System.out.println("\t
From ThreadC: k= "+k);
}
System.out.println("Exit
from C");
}
}
class
ThreadTest
{
public
static void main(String args[])
{
new
A().start(); new B().start(); new C().start();
}
}
[raj@mundroo] threads [1:76] java ThreadTest From
ThreadA: i= 1
From
ThreadA: i= 2 From ThreadA: i= 3
From
ThreadA: i= 4
From
ThreadA: i= 5
Exit from
A
From ThreadC:
k= 1
From
ThreadC: k= 2
From
ThreadC: k= 3
From
ThreadC: k= 4
From
ThreadC: k= 5
Exit from
C
From
ThreadB: j= 1
From
ThreadB: j= 2
From
ThreadB: j= 3
From
ThreadB: j= 4
From
ThreadB: j= 5
Exit from
B
Related Topics