Chapter: Medical Surgical Nursing: Critical Thinking,Ethical Decision Making, and the Nursing Process
Steps of the Nursing Process
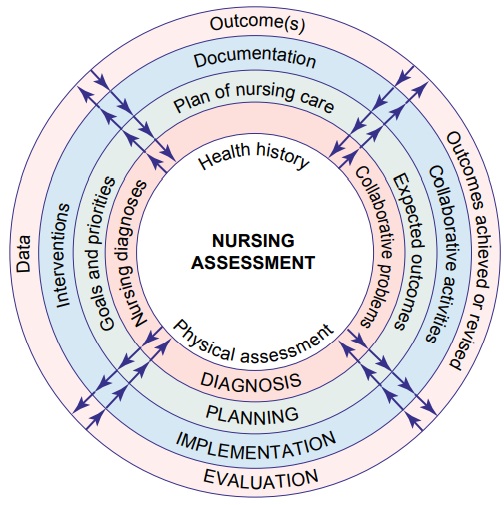
Steps of the Nursing Process
The nursing process is a
deliberate problem-solving approach for meeting a person’s health care and
nursing needs. Although the steps of the nursing process have been stated in
various ways by different writers, the common components cited are assessment,
diagnosis, planning, implementation, and evaluation. The ANA’s Standards of Clinical Nursing Practice (1998)
include an addi-tional component entitled “outcome identification” and
establish the sequence of steps in the following order: assessment, diagno-sis,
outcome identification, planning, implementation, and eval-uation. For the
purposes of this text, the nursing process will be based on the traditional
five steps and will delineate two compo-nents in the diagnosis step: nursing
diagnoses and collaborative problems. After the diagnoses or problems have been
determined, the desired outcomes are often evident. The traditional steps are
defined as follows:
1) Assessment: The systematic collection of data to
determinethe patient’s health status and identify any actual or po-tential
health problems. (Analysis of data is included as part of the assessment. For
those who wish to emphasize its im-portance, analysis may be identified as a
separate step of the nursing process.)
2) Diagnosis: Identification of the following two types
ofpatient problems:
a) Nursing diagnoses: Actual or potential health problemsthat can
be managed by independent nursing inter-ventions
b) Collaborative problems: “Certain physiologic
complica-tions that nurses monitor to detect onset or changes in status. Nurses
manage collaborative problems using physician-prescribed and nursing-prescribed
interven-tions to minimize the complications of the events”.
3) Planning: Development of goals and outcomes, as well as
aplan of care designed to assist the patient in resolving the diagnosed
problems and achieving the identified goals and desired outcomes.
4) Implementation: Actualization of the plan of care
throughnursing interventions.
5) Evaluation: Determination of the patient’s responses to
thenursing interventions and the extent to which the out-comes have been
achieved.
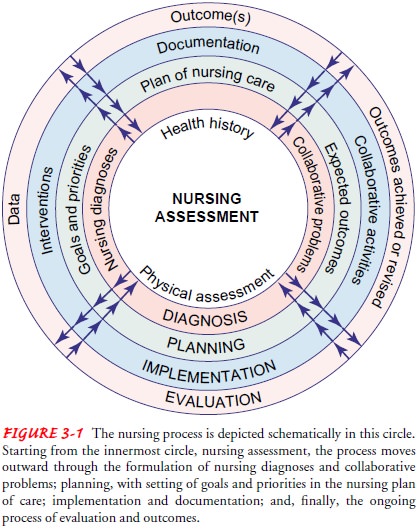
Dividing the nursing
process into distinct steps serves to em-phasize the essential nursing actions
that must be taken to resolve the patient’s nursing diagnoses and manage any
collaborative prob-lems or complications. Dividing the process into separate
steps is, however, artificial: the process functions as an integrated whole,
with the steps being interrelated, interdependent, and recurrent (Fig. 3-1).
Chart 3-6 presents an overview of the nursing activities involved in applying
the nursing process.

Related Topics