Chapter: Information Security : Physical Design
Security Technology
Security Technology
1. What is Security?
quality
or state of being secure—to be free from danger”
A
successful organization should have multiple layers of security in place:
Physical
security
Personal
security
Operations
security
Communications
security
Network
security
Information
security
Physical Design
Physical
design of an information security program is made up of two parts:
Security technologies
Physical security
Physical
design process:
-
Identifies complete technical solutions based on these technologies
(deployment, operations and maintenance elements)
- Design physical security measures to support
the technical solution.
2. Firewalls
- In buildings, a firewall is a fireproof wall
that restricts the spread of a fire.
- Network firewall prevents threats from spreading
from one network to another
Prevent
specific types of information from moving between the outside world (untrusted
networks) and the inside world (trusted networks)
ü The firewall may be a separate computer system, a software servic e
running on an existing router all serve r, or a
separate network containing a number of supporting devices.
Internet Firewalls
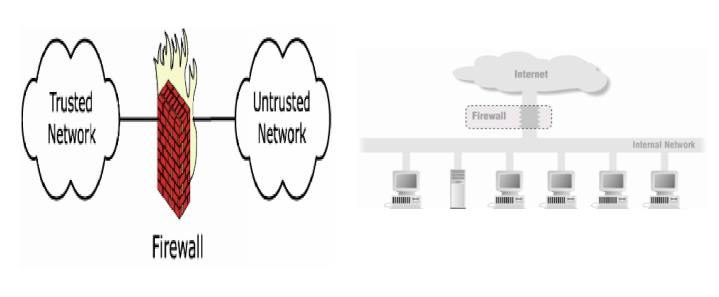
1 What Firewalls do
Protects
the resources of an internal network.
Restrict
external access.
Log
Network activities.
Intrusion detection
DoS
Act as
intermediary
Centralized
Security Management
Carefully
administer one firewall to control internet traffic of many machines.
Internal
machines can be administered with less care.
2 Types of Firewalls (General)
Firewalls types can be categorized depending on:
The Function or methodology the firewall use
Whether the communication is being done between a
single node and the network, or between two or more networks.
Whether
the communication state is being tracked at the firewall or not.
With regard to the scope of filtered communications
the done between a single node and the network, or between two or more networks
there exist :
Personal
Firewalls, a software application which normally filters traffic entering or
leaving a single computer.
Network
firewalls, normally running on a dedicated network device or computer
positioned on the boundary of two or more networks.
3 Firewall categorization methods
The Function or methodology the firewall use
Five
processing modes that firewalls can be categorized by are :
· packet
filtering
· application
gateways
· circuit
gateways
· MAC layer
firewalls
· hybrids
3.1.Packet filtering:
a packet filtering firewall installed on TCP/IP based network and
determine wether to drop a packet or forward it to the next network connection
based on the rules programmed in the firewall.
Packet filtering firewalls scan network data packets looking for violation
of the rules of the firewalls database.
Filtering firewall inspect packets on at the network layers.
If the device finds a packet that matches a restriction it stops the
packet from traveling from network to another.
filters packet-by-packet, decides to Accept/Deny/Discard
packet based on certain/configurable criteria – Filter Rule sets.
Typically stateless: do not keep a table of the connection state of the various traffic that
flows through them
Not dynamic enough to be considered true firewalls.
Usually located at the boundary of a network.
Their main strength points: Speed and Flexibility.
There are three subsets of packet filtering
firewalls:
dynamic filtering
stateful inspection
static filtering:
requires
that the filtering rules coverning how the firewall decides which packets are
allowed and which are denied.
ü This type of filtering is common
in network routers and gateways.
2. Dynamic
filtering
allows the firewall to create rules to deal with event.
This reaction could be positive as in allowing an internal user to
engage in a specific activity upon request or negative as in dropping all
packets from a particular address
3. Stateful inspection
keep track of each network connection between internal and external
systems using a state table.
A state table tracks the state and context of each packet in the conversation
by recording which station send , what packet and when.
More complex than their constituent component firewalls
Nearly all modern firewalls in the market today are staful
Stateful Inspection Firewalls
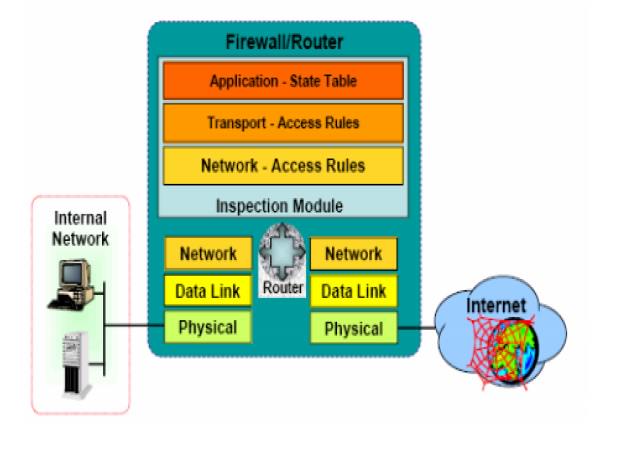
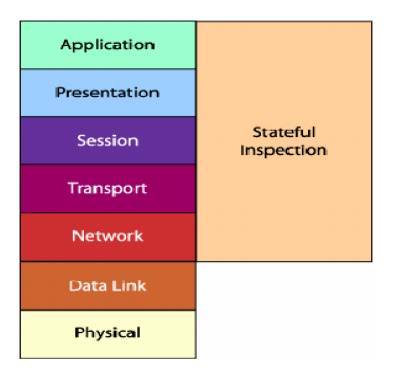
Basic Weaknesses Associated w ith Packet Filters\
Statful
They cannot pre vent attacks that employ
application-specific vulnerabilities or functions.
Logging function ality present in packet filter
firewalls is limited
-Most packet filter firewalls do not support advanced
user authent ication schemes.
Vulnerable to attacks and exploits that take
advantage of pro blems within the TCP/IP specification and protocol stack, such
as network layer ad dress spoofing.
Susceptible to sec urity breaches caused by
improper configurations.
Advantages:
One packet filter can protect an entire network
Efficient (require s little CPU)
Supported by mosst routers
Disadvantages:
Difficult to config ure correctly
Must consider rule set in its entirety
Difficult to test co mpletely
Performance penalty for complex rulesets
Stateful packet filtering much more expensive
Enforces ACLs at layer 3 + 4, without knowing any
application details
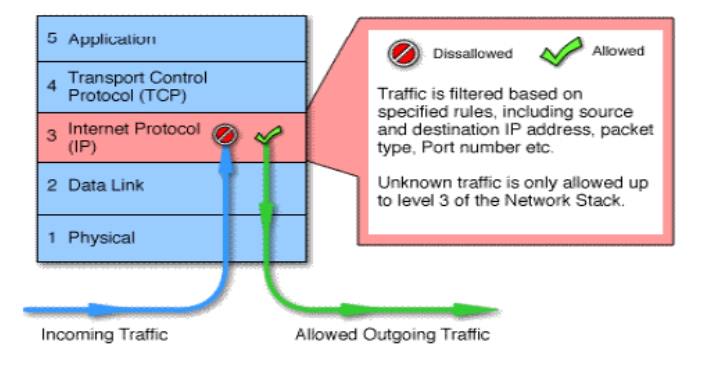
Packet Filtering Firewalls
The original firewall
Works at the network level of the OSI
model
Applies packet filters based on access
Rules:
Source IP address
Destination IP address
Application or protocol
Source port number
Destination port number
Packet Filtering Firewalls
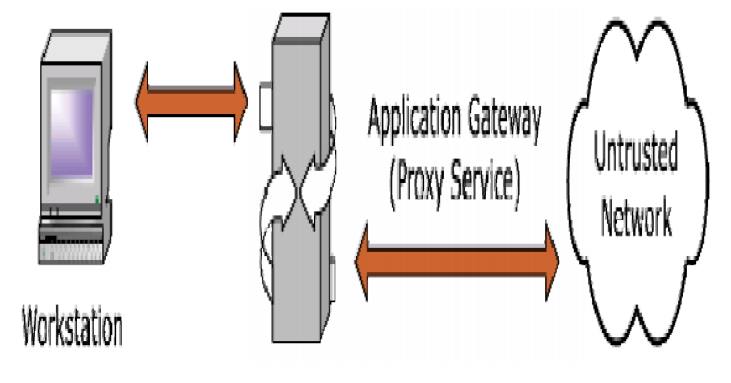
Application gateways:
is also known as proxy server since it runs special software that acts as a proxy for a service request.
One common example of proxy server is a firewall that blocks or requests for and responses to request for web pages and services from the internal computers of an organization.
The primary disadvantag e of application level firewalls is that they ar e designed for a specific protocols and c annot easily be reconfigured to protect against attacks in other protocols.
Application firewalls work at the application layer.
Filters packets on application data as well as on IP/TCP/UDP fields.
The interaction is controlled at the application layer
A proxy server is an application that mediates traffic between two network segments.
With the proxy acting a s mediator, the source and destination system s never actually“connect”.
Filtering Hostile Code: Proxies can analyze the payload of a packet o f data and make decision as to whether thiis packet should be passed or dropped.
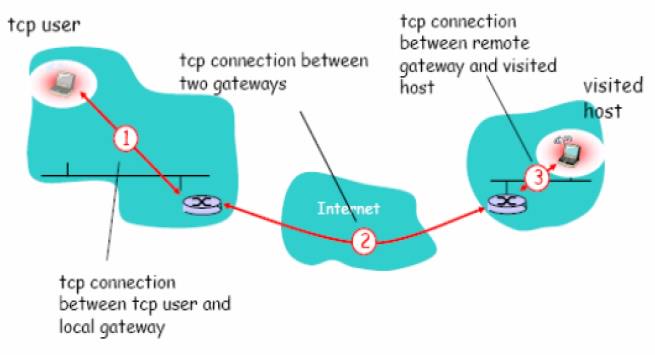
4.Circuit gateways:
operates
at the transport layer.
Connections
are authorized based on addresses , they prevent direct connections between
network and another.
They
accomplish this prevention by creating channels connecting specific systems on
each side of the firewall and then allow only authorized traffic.
relays
two TCP connections (session layer)
imposes
security by limiting which such connections are allowed
once
created usually relays traffic without examining contents
Monitor
handshaking between packets to decide whether the traffic is legitimate
typically
used when trust internal users by allowing general outbound connections
SOCKS
commonly used for this
Circuit Level Firewalls Example
4.MAC layer firewalls:
ü design to operate at the media access control layer.
Using
this approach the MAC addresses of specific host computers are linked to ACL
entries that identify the specific types of packets that can be send to each
host and all other traffic is blocked.
companied
the elements of other types of firewalls , example the elements of packet
filtering and proxy services, or a packet filtering and circuit gateways.
That
means a hybrids firewalls may actually of two separate firewall devices; each
is a separate firewall system, but they are connected so that they work
together.
Types of Firewalls
Finally,
Types depending on whether the firewalls keeps track of the state of network
connections or treats each packet in isolation, two additional categories of
firewalls exist:
Stateful firewall
Stateless firewall
Stateful firewall
keeps track of the state of network connections (such as TCP streams)
traveling across it.
Stateless firewall
Treats each network frame (Packet) in isolation. Such a firewall has no
way of knowing if any given packet is part of an existing connection, is trying
to establish a new connection, or is just a rogue packet.
The classic example is the File Transfer Protocol, because by design it
opens new connections to random ports.
Advantages of a Firewall
Stop incoming calls to insecure services
such as rlogin and NFS
Control access to other services
Control the spread of viruses
Cost Effective
More secure than securing every
system
Disadvantages of a Firewall
Central point of attack
Restrict legitimate use of the Internet
Bottleneck for performance
Does not protect the ‘back door’
Cannot always protect against
smuggling
Cannot prevent insider attacks
Related Topics