Chapter: 9th Science : Sound
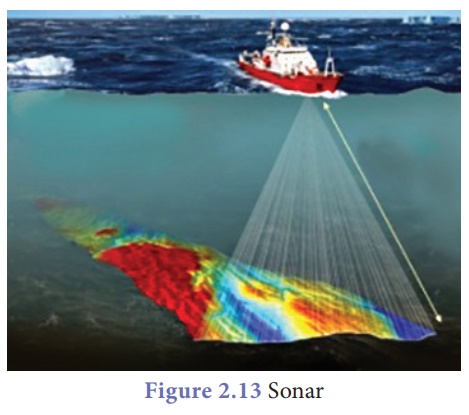
SONAR
SONAR
SONAR stands for Sound
Navigation And Ranging. Sonar is a device that uses ultrasonic waves to measure
the distance, direction and speed of underwater objects. Sonar consists of a
transmitter and a detector and is installed at the bottom of boats and ships.
The transmitter produces
and transmits ultrasonic waves. These waves travel through water and after
striking the object on the seabed, get reflected back and are sensed by the
detector. The detector converts the ultrasonic waves into electrical signals
which are appropriately interpreted. The distance of the object that reflected
the sound wave can be calculated by knowing the speed of sound in water and the
time interval between transmission and reception of the ultrasound.
Let the time interval
between transmission and reception of ultrasound signal be ‘t’ and
the speed of sound
through sea water be 2d = v × t. This method is called
echo-ranging. Sonar technique is used to determine the depth of the sea
and to locate underwater hills, valleys, submarine, icebergs etc.
Example 5
A ship sends out
ultrasound that returns from the seabed and is detected after 3.42 s. If the
speed of ultrasound through sea water is 1531m s-1, what is the
distance of the seabed from the ship?
Solution
Time between
transmission and detection, t = 3.42 s.
Speed of ultrasound in
sea water, v = 1531m s–1
Distance travelled by
the ultrasound = 2 × depth of the sea
We know, distance =
speed × time
2d = speed of
ultrasound × time
2d = 1531×3.42
∴d = 5236/2 m
d = 2618 m
Thus, the distance of
the seabed from the ship is 2618 m or 2.618 km
Related Topics