Chapter: Civil : Railway Airport Harbour Engineering : Railway Engineering : Rails
Requirements for an Ideal Rail Section
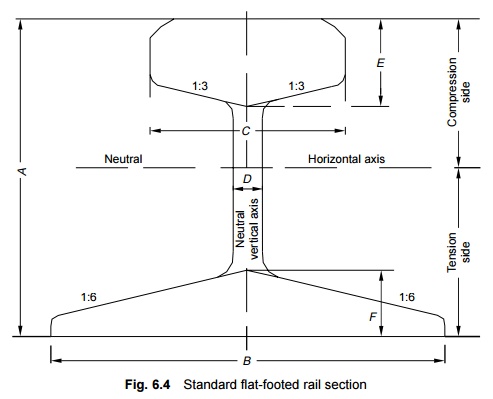
Requirements for an Ideal Rail Section
The requirements for an ideal rail section are as follows.
The rail
should have the most economical section consistent with strength, stiffness,
and durability.
(b) The
centre of gravity of the rail section should preferably be very close to the
mid-height of the rail so that the maximum tensile and compressive stresses are
equal.
(c) A rail
primarily consists of a head, a web, and a foot, and there should be an
economical and balanced distribution of metal in its various components so that
each of them can fulfil its requirements properly. The requirements, as well as
the main considerations, for the design of these rail components are as
follows.
Head: The head of the rail should
have adequate depth to allow for vertical wear. The rail head should
also be sufficiently wide so that not only is a wider running surface
available, but also the rail has the desired lateral stiffness. Web: The
web should be sufficiently thick so as to withstand the stresses arising
due to the loads bone by it, after allowing for normal corrosion.
Foot: The foot should be of
sufficient thickness to be able to withstand vertical and horizontal
forces after allowing for loss due to corrosion. The foot should be wide enough
for stability against overturning. The design of the foot should be such that
it can be economically and efficiently rolled.
Fishing angles: Fishing angles must
ensure proper transmission of loads from the rails to the fish plates.
The fishing angles should be such that the tightening of the plate does not
produce any excessive stress on the web of the rail.
Height of the rail: The height
of the rail should be adequate so that the rail has sufficient vertical
stiffness and strength as a beam.
Standard Rail Section
The rail is designated by its
weight per unit length. In FPS units, it is the weight in lbs per yard and in
metric units it is in kg per metre. A 52 kg/m rail denotes that it has a weight
of 52 kg per metre.
The weight of a rail and its
section is decided after considerations such as the following:
(a) Heaviest
axle load
(b) Maximum
permissible speed
(c) Depth of
ballast cushion
(d) Type and
spacing of sleepers
(e) Other
miscellaneous factors
The standard rail sections in use
on Indian Railways are 60 kg, 52 kg, 90 R, 75 R, 60 R and 50 R. The two heavier
rail sections, 60 kg and 52 kg, were recently introduced and are designated in
metric units. Other rails are designed as per the revised British Standard
specifications and are designated in FPS units though their dimensions and
weight are now in metric units. In the nomenclature 90 R, 75 R, etc., R stands
for revised British specifications.
Every rail rolled has a brand on
its web, which is repeated at intervals. As per IRS-T-12-88, the brand marks
are as follows:
IRS-52 kg
- 710 - TISCO - II 1991 ® OB
The
definitions for the various abbreviations are as follows:
(a) IRS-52-kg: Number
of IRS rail section, i.e., 52 kg
(b) 710: Grade
of rail section, i.e., 710 or 880
(c) TISCO: Manufacturer's
name, e.g., Tata Iron and Steel Co.
(d) II 1991: Month and year of manufacture
(February 1991)
(e) -> : An arrow showing the direction of
the top of the ingot
(f) OB: Process
of steel making, e.g., open hearth basic (OB)
The brand marks on the rails are
to be rolled in letters at least 20 mm in size and 1.5 mm in height at
intervals of 1.5 to 3.0 m.
The standard rail sections and
standard rail length prescribed on Indian Railways are given in Table 6.1.
Table
6.1 Standard rail
sections
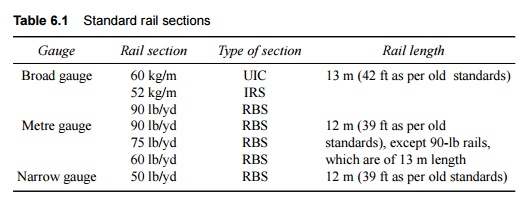
UIC-International Union of Railways, IRS-Indian Railway
Standard, RBS-Revised British
Standard.
Detailed
dimensions of standard rail sections are shown in Fig. 6.4 and Table 6.2.
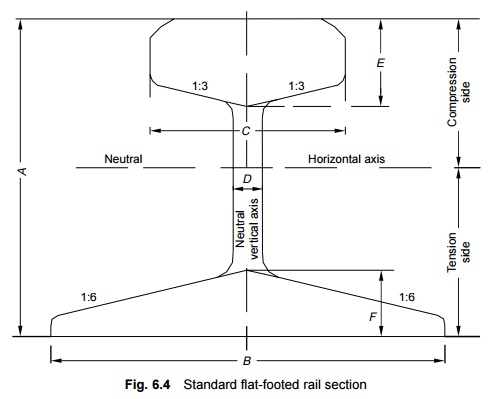
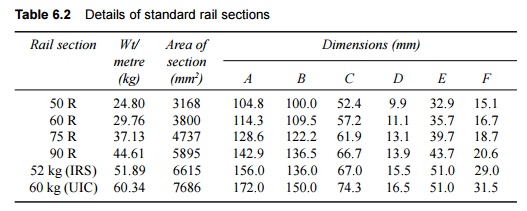
It may be
mentioned here that the 90 R rail section is adequate only for an annual
traffic density of about 10 GMT (gross million tonnes per km/annum), speeds of
up to 100 kmph, axle loads up to main line (ML) standard, and a service life of
about 20-25 years. Realizing to these limitations, the Indian Railways, in the
year 1959, designed a heavier rail section of 52 kg/m to meet the requirements
of heavier and faster traffic. This rail section was recommended for use on all
BG main line routes with future speeds of up to 130 kmph and traffic density of
20-25 GMT. The important dimensions of 52-kg and 60-kg rails are shown in Fig.
6.5.
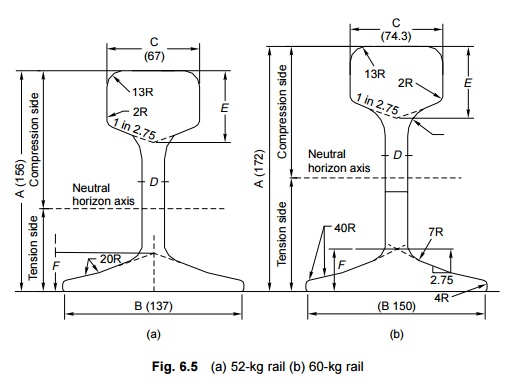
The
traffic density on the BG track routes of Indian Railways is increasing very
fast. Accordingly, to meet the future requirements of traffic, a new design has
been finalized for the 60-kg UIC section rail. The rail section has been
designed for speeds of up to 160 kmph and a traffic density of about 35 GMT.
Weight of rails
Though the weights of a rail and its section depend upon
various considerations, the heaviest axle load that the rail has to carry plays
the most important role. The following is the thumb rule for defining the
maximum axle load with relation to the rail section:
Maximum axle load = 560 × sectional
weight of rail in lbs per yard or kg per metre
For rails of 90 lbs per yard,
Maximum axle load = 560 × 90 lbs = 50,400 lbs or
22.5 t For rails of 52 kg per m,
Maximum
axle load = 560 × 52 kg = 29.12 t
Length of rails
Theoretically, the longer the
rail, the lesser the number of joints and fittings required and the lesser the
cost of construction and maintenance. Longer rails are economical and provide
smooth and comfortable rides. The length of a rail is, however, restricted due
to the following factors.
(a) Lack of
facilities for transport of longer rails, particularly on curves.
(b) Difficulties
in manufacturing very long rails.
(c) Difficulties
in acquiring bigger expansion joints for long rails.
(d) Heavy
internal thermal stresses in long rails.
Taking the above factors into consideration,
Indian Railways has standardized a rail length of 13 m (previously 42 ft) for
broad gauge and 12 m (previously 39 ft) for MG and NG tracks. Indian Railways
is also planning to use 26 m, and even longer, rails in its track system.
Related Topics