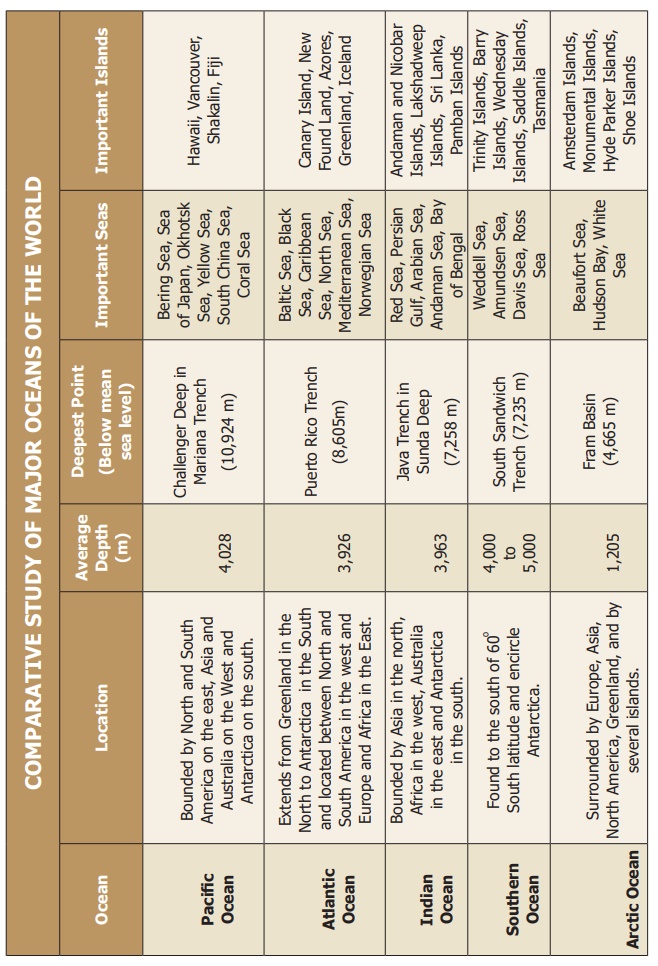
Hydrosphere | Geography - Relief Of The Ocean Floor | 9th Social Science : Geography: Hydrosphere
Chapter: 9th Social Science : Geography: Hydrosphere
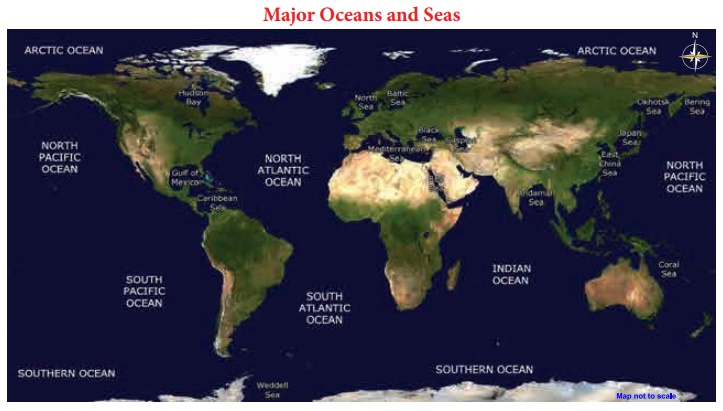
Relief Of The Ocean Floor
Relief Of The Ocean Floor
The ocean floor is not
flat as it was believed to be in the earlier days. It comprises of many complex
and varied relief as observed on the earth’s surface. The ocean floor also has
high mountains, deep trenches and large flat plains. These features are formed
due to the tectonic, volcanic and depositional activities.
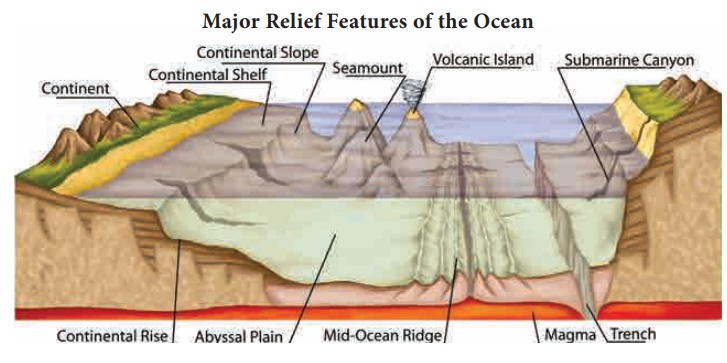
The ocean basins are
characterised by the following major relief features:
·
Continental shelf
·
Continental slope
·
Continental rise
·
Deep sea plain or Abyssal plain
·
Oceanic deep
·
Oceanic ridge
(A) Continental Shelf
A shallow and gently
sloping platform extending out from the adjoining continental land mass into
the sea is called Continental Shelf. It is almost a uniform zone of sea bed
with a gentle gradient.
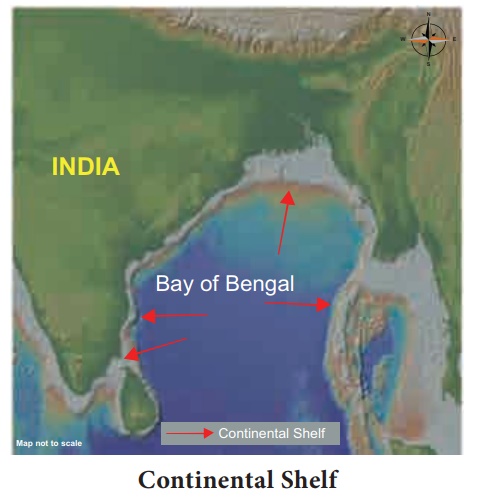
The continental shelf is
of great significance for the following reasons:
·
They are shallower, thus enables sunlight to penetrate through the
water. This encourages abundant growth of grass, sea weeds and plankton. Hence
these zones become the richest fishing grounds in the world. Eg. The
Grand Banks of Newfoundland.
·
The continental shelves have extensive deposits of minerals and
mineral fuels. Hence, this zone becomes accessible for oil drilling and mining
activities. E.g. Mumbai High in Arabian Sea.
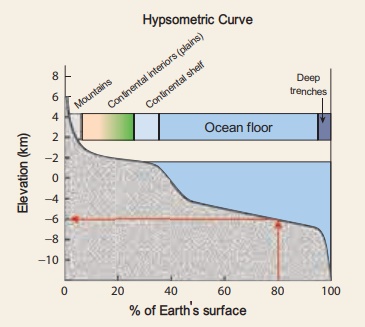
(C) Continental Slope
A steep slope which
descends from the edge of the continental shelf to the deep ocean-bed is called
continental slope. It forms a boundary between the Continental Crust and the
oceanic crust. This zone is free from deposits as they are steep. The most
important characteristic of continental slope is the presence of deep canyons
and trenches. Due to the low penetration of sunlight, the slope has
nearly freezing temperature. Hence aquatic life has very slow rate of
metabolism.
(C) Continental Rise
At the base of the
continental slope is a gently sloping layer of sediments which merge into the
deep-sea floor. This underwater feature found between continental slope and
abyssal plains is called the continental rise. It consists of submarine
fans which are similar to the alluvial fans found on land.
(D) Deep Sea Plains or
Abyssal Plains The deep sea plains or abyssal plains are underwater plains found
on the deep ocean floor. These plains extend from continental rise to the mid
oceanic ridges. The gradient of the slope is very gentle and it appears as a
uniform flat and featureless plain. These plains are usually covered by the
thick layer of sediments composed of clay, silt and sand, brought by the
rivers. These are often characterized by features like abyssal hills, sea
mounts, guyots, coral, atoll etc.
(E) Oceanic Deeps
Trenches are the deepest
part of the oceans and occupy about 7% of the total relief of the ocean floor.
The ocean temperature in the trench is slightly cooler than the freezing
temperature. As they are sediment free, most trenches are V-shaped with
steep sides. Epicentre of the great earthquakes are all found in
the trenches.

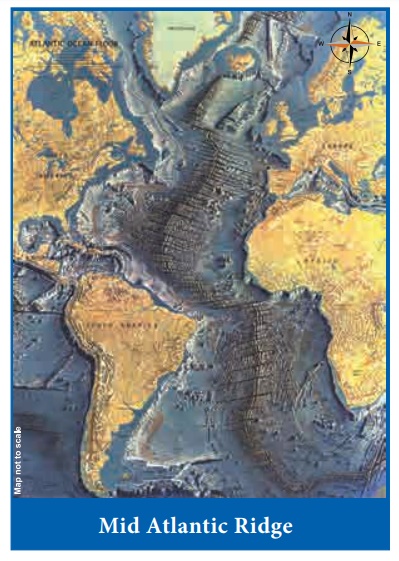
(F) Oceanic Ridge
Oceanic ridge is a
continuous submarine mountain chain. They are made of young basaltic rock
formed when two tectonic plates moves apart. The mid-ocean ridge is probably
the most extensive single feature of the earth’s topography. Two of the most
well known mid ocean ridges are the Mid-Atlantic Ridge and the East Pacific
Ridge. The Mid -Atlantic Ridge is the largest unbroken oceanic ridge.
Related Topics