Advantages, Disadvantages | Conservation of Plants and Animals | Chapter 22 | 8th Science - Red Data Book | 8th Science : Chapter 22 : Conservation of Plants and Animals
Chapter: 8th Science : Chapter 22 : Conservation of Plants and Animals
Red Data Book
Red Data Book
The Red Data Book is the file for
recording rare and endangered species of animals, plants and fungi. Even some
local sub-species that exist within the territory of a state or country are
recorded in red data books. Red data book gives important data for
observational studies and monitoring programmes on habits and habitats of rare
and endangered species. This book is created to identify and protect the
species which are about to extinct.
Red Data Book is maintained by the
International Union for Conservation of Nature. It is an international
organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of
natural resources. It was founded in 1964 with the aim of maintaining a
complete record of every species that ever lived. The Red Data Book classifies
species mainly into three categories namely, threatened, not threatened and
unknown. This book also has information as to why a species has become extinct
along with the population trends and its distribution.
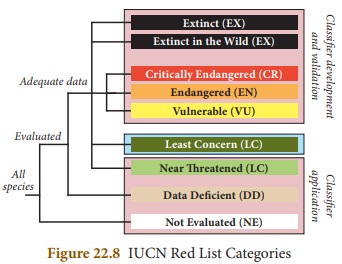
The Red Data Book contains
colour-coded information sheets like black for species which are extinct, red
for species that are endangered and so on. They are arranged according to the
extinction risk of many species and subspecies. The following figure gives the
colour coded information.
WWF – World Wildlife Fund
ZSI – Zoological Surveyof India
BRP – Biosphere Reserve Programme
CPCB – Central Pollution Control Board
IUCN – International Union for Conservation of Nature
Advantages of the Red Data Book
* It helps to evaluate the
population of a particular species.
* The data given in this book can be
used to evaluate the species at the global level.
* The risk of a species becoming
globally extinct can be estimated with the help of this book.
* It provides guidelines for
implementing measures for protecting endangered species.
Disadvantages of the Red Data Book
* The information available in the
Red Data Book is incomplete. Many extinct species are not updated in this book.
* The source of the book’s data has
been speculated.
* This book maintains the complete
record of all animals, plants, other species but it has no information about
the microbes.
World Wild life Day is
observed on March 3rd every year.
Red Data Book of India
India, a mega-diverse country with
only 2. 4% of the world’s land area, accounts for 7-8% of all recorded species,
including over 45,000 species of plants and 91,000 species of animals. The
country’s diverse physical features and climatic conditions have resulted in a
variety of ecosystems such as forests, wetlands, grasslands, deserts, coastal
and marine ecosystems which harbour and sustain high biodiversity and
contribute to human well being. Four out of 34 globally identified biodiversity
hotspots, the Himalayas, the Western Ghats, the North-East, and the Nicobar
Islands, can be found in India.
India became a state member of IUCN
in 1969, through the Ministry of environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC)
. The IUCN India country office was established in 2007 in New Delhi. Red Data
Book of India contains the conservation status of animals and plants which are
found in the Indian subcontinent. Surveys conducted by the Zoological Survey of
India and the Botanical Survey of India under the guidance of the Ministry of
Environment, Forest and Climate Change provide the data for this book.
Related Topics