Conservation of Plants and Animals | Chapter 22 | 8th Science - Endangered Species | 8th Science : Chapter 22 : Conservation of Plants and Animals
Chapter: 8th Science : Chapter 22 : Conservation of Plants and Animals
Endangered Species
Endangered Species
Our country is a home for variety of
species with rich flora and fauna. Flora is the plant life occurring in a
particular area. Fauna is the animal life occurring in a particular area. The
Royal Bengal Tigers, the Asiatic Cheetah and several other birds are found in
India. But due to various reasons like environmental pollution, deforestation,
loss of habitat, human interference, poaching and hunting many animals in India
are extinct and many are endangered. Species which no longer exist on earth are
called extinct species. E.g. Dinosaurs, Dodo. An endangered species is an
animal or a plant that is considered to be at the risk of extinction. It means
that there are only few of them left on the earth and soon they might extinct.

Activity 4
Observe the following
days in your school
World Forest Day - March
21
World Water Day - March
22
Environmental Day - June
5
World Nature
Conservation Day -July 28
Ozone Day - September
16
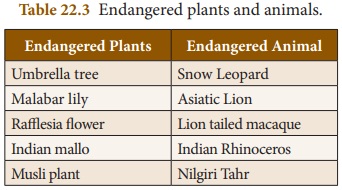
It is reported that nearly 132
species of plants and animals are critically endangered in India. Snow leopard,
Bengal tiger, Asiatic lion, Purple frog and Indian giant squirrel are some of
the endangered animals in India.
Each year, 22nd May is
celebrated as World Biodiversity Day. Biodiversity is a term used to describe
the different plants, animals,marine life, microorganisms, insects, habitats,
ecosystem etc. that make our planet so unique and so fascinating.
Many algae, fungi, bryophytes, ferns
and gymnosperms are disappearing with the destruction of forests. And, each
disappearing species may take away with it many species of animals and microbes
which depend on them for food and shelter. Similarly, list of animals on the verge
of being lost is endless. Prawns, oysters, lobsters, crabs, squid, octopus,
cuttlefish, beetles, dragonfly, grasshoppers, fish and even frogs are dying by
absorbing poisonous gases through their skin. Locust is one insect which has
almost disappeared from India. Following animals are getting rare these days.
* Reptiles: Some lizards, turtles,
crocodiles and gharials.
* Birds: Falcon, eagle, hawk,
vulture, peacock-peahen, pigeon, duck.
* Mammals: Wild cats such as tigers,
lions, deer such as chinkara and blackbuck, chiru (Tibetan goat), musk deer,
rhino, elephants, blue whale, flying squirrel.

Activity 5
Collect as many
pictures of wild plants and wild animals as possible. Prepare a poster showing
the endangered species separately.
1. Determination of Endangerment
Whether a particular species is
endangered or not is determined by the following ways.
* When the geographical range of the
species is limited.
* The population of the species is
limited i.e., less than 50 adult individuals.
* When the population has decreased
or will decrease by more than 80% in 10 years.
* If the population is less than 250
individuals and is continuously declining at 25% for the past three years.
* There is a high possibility of
extinction in the wild.
Yeoman Butterfly has been
declared state butterflyof Tamil Nadu. This species is endemic to WesternGhats.
It is among 32 butterfly species found in Western Ghats.

2. Causes for Endangerment
There are various reasons why a species
may become endangered or extinct. Some of them are explained below.
a.
Loss of habitat
Trees that provide food and shelter
to so many species are destroyed due to human intervention.
b.
Over hunting and poaching
Large number of animals are hunted
for their horns, skin, teeth and many other valuable products.
c.
Pollution
Number of animals are affected by
pollutions like air pollution and water pollution. In the recent years more
number of animals is affected by wastes in the form of plastic.
d.
New habitat
Sometimes animals are taken by
people to new habitat where they do not naturally live. Some of them may
extinct and some may survive. The new ones may also get attacked by the species
already living there and cause their extinction.
e. Chemicals
We use pesticides and other
chemicals to get rid of damaging insects, pests or weeds. But they can also
poison desired plants and animals if we do not use them correctly.
At one time Dinosaur, ferns and some
gymnosperms were wide spread on the earth. They disappeared from the earth, may
be due to shortage of space and food or due to climatic change

f.ŌĆéDiseases
Diseases due to various unknown
reasons may affect the animals and make them extinct.
g.ŌĆéNatural
calamities
Animals may also be destroyed due to
natural disasters like flood and fire.
3. Saving Endangered Species
Nature is beautiful and it is filled
with different plants and animals. For maintaining healthy ecological balance
on the earth, animal and plant species are important. They have medicinal,
scientific, ecological and commercial value. Each organism on the earth has a
unique place in food chain that contributes to the ecosystem. But they are
endangered mainly due to human activity. We need to take certain measures to
protect them and preserve them.
* Some of the animal species are
endangered mainly because of hunting and poaching. If it is controlled there
can be a significant change in the number of endangered animals.
* Controlling pollution can have a
positive impact on animals, fish and birds all over the world.
* When we consume more, more
pollutants are put into the environment. By consuming less, we can protect the
ecosystems.
* Animals often mistake plastic for
food and hence plastics harm and cause endangerment of many species. Limiting
the amount of plastic and recycling it can save the endangered animals.
* Recycling things and buying eco
friendly products will preserve the environment resources and hence the
animals.
* Pesticides and chemicals which cause
damage to the environment should be avoided.
* Planting native trees will provide
food to the animals.
Planting the native
trees like Neem tree, Umbrella tree and Banyan tree in our surrounding will be
helpful for the animals. Many birds and animals find shelter in those trees.
4. Government Initiatives
In order to preserve the plants and
animals, government has taken lot of initiatives and some acts have also been
passed to protect them. For example, Project Tiger is a wildlife conservation
project initiated in India in 1972 to protect the Bengal Tiger. It was launched
on 1st April 1973 and has become one of the most successful wildlife
conservation ventures. Corbett National Park was the first National Park in
India to be covered under project Tiger. Due to ŌĆśProject TigerŌĆÖ the population
of Tiger has increased in India from 1400 in 2006 to 2967 in 2018. Apart from
this, government has enacted the following Acts.
1. Madras Wildlife Act, 1873.
2. All India Elephant Preservation
Act, 1879.
3. The Wild Bird and Animal
Protection Act, 1912.
4. Bengal Rhinoceros Preservation
Act, 1932.
5. All India Wildlife Protection
Act, 1972.
6. Environmental Protection Act,
1986.
Related Topics