Conservation of Plants and Animals | Chapter 22 | 8th Science - Conservation | 8th Science : Chapter 22 : Conservation of Plants and Animals
Chapter: 8th Science : Chapter 22 : Conservation of Plants and Animals
Conservation
Conservation
According to WWF (World Wildlife Fund)
there has been 60% decrease in the size of population of animals, birds, fish,
reptiles and amphibians over the past 40 years. In order to leave something for
the future generation, we need to conserve it now. Conservation is the
protection, preservation, management of wildlife and natural resource such as
forest and water. Conservation of biodiversity helps us to protect, maintain
and recover endangered animals and plant species. Conservation is of two types.
They are:
• In-situ conservation (within
habitat)
• Ex-situ conservation (outside the
habitat)
1. In-situ conservation
It is nothing but conservation of
living resources within the natural ecosystem in which they occur. This is
achieved by protection of natural habitat and maintenance of endangered species
in certain protected areas such as national parks, wildlife or bird sanctuaries
and biosphere reserves. In India, there are about 73 national parks, 416
sanctuaries and 12 biosphere reserves.
a.
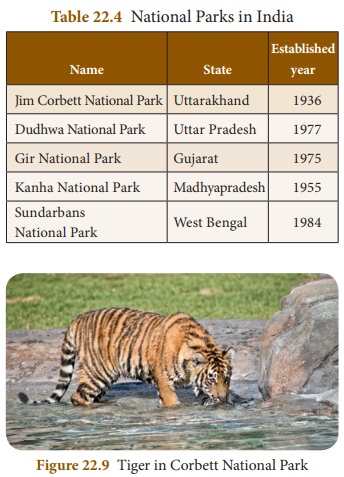
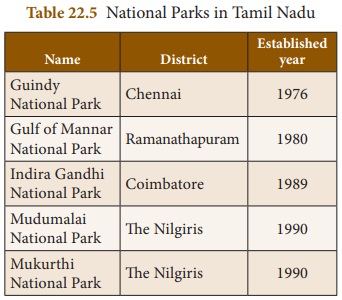
National Parks
National park is an area which is
strictly reserved for the betterment of the wildlife. Here, activities like
forestry, grazing or cultivation are not permitted. Even private ownership
rights are not allowed in these areas. The national parks cover an area of 100
– 500 square kilometers. In these parks a single plant or animal species are
preserved.
b.
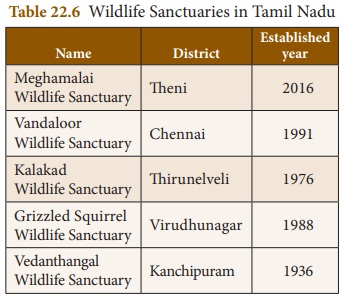
Wildlife sanctuaries
Sanctuary is a protected area which
is reserved for the conservation of animals only. Human activities like
harvesting of timber, collection of forest products and private ownership
rights are allowed here. Controlled interference like tourist activity is also
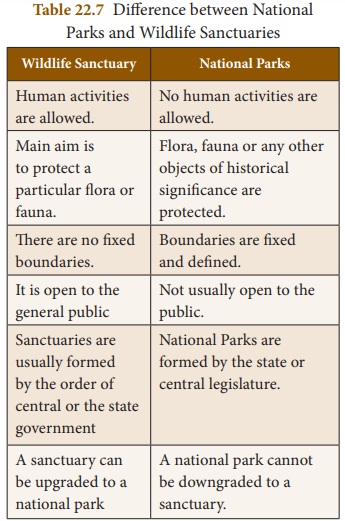
allowed. The differences between national parks and wildlife sanctuaries are
given in Table 22. 6

c.
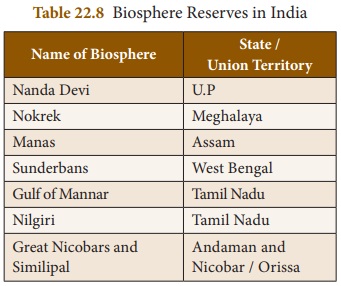
Biosphere reserves
Biosphere is a protected area where
human population also forms the part of the system. The area of these places
will be around 5000 square kilometers. They conserve the eco system, species
and genetic resources. These areas are set up mainly for economic development.
Activity 6
Find out the national
parks and wildlife santuaries in Tamil Nadu. Visit those places and collect
more information about them.
Advantages of In-situ conservation
* Species can be adapted to their
habitat.
* Species can interact with each
other.
* Natural habitat is maintained.
* It is less expensive and easy to
manage.
* Needs of indigenous people are
protected.
2. Ex-situ Conservation
It is the conservation of wildlife
outside their habitat. Establishing zoos and botanical gardens, conservation of
genes, seedling and tissue culture are some of the strategies followed in this
method.
a.
Botanical gardens
It is a place where flowers, fruits
and vegetables are grown. These places provide a healthy and calm environment.
b.
Zoological parks
Zoological parks are the areas where
wild animals are conserved. In India there are about 800 zoological parks.
The oldest zoo is
Schoenbrunn Zoo in Vienna, established in the year 1759. In India the first Zoo
was established in Barrachpur in the year 1800.
c.
Tissue Culture
It is a technique of growing plant
cells, tissues, organs, seeds or other plant parts in a sterile environment on
a nutrient medium.
d.
Seed bank
The seed bank preserves dried seeds
by storing them in a very low temperature. The largest seed bank in the world
is the Millennium Seed Bank in England.
e.
Cryo Bank
It is a technique by which a seed or
embryo is preserved at a very low temperature. It is usually preserved in
liquid nitrogen at –1960C. This is helpful for the conservation of species
facing extinction.
Advantages of Ex-situ conservation
* It prevents the decline of
species.
* Endangered animals can be breeded in
these ways.
* Threatened species are breeded and
released in natural environment.
* It is useful for conducting
research and scientific work.
Related Topics