Chapter: Basic Electrical and electronics : Semiconductor Devices And Applications
Rectifiers and Types of rectifiers
RECTIFIERS
The
“rectifier” is a circuit that converts AC voltages and currents into pulsating
DC voltages and currents. It consists of DC components and the unwanted ac
ripple or harmonic components which can be removed by using filter circuit.
Thus the output obtained will be steady DC voltage and magnitude of DC voltage
can be varied by varying the magnitude of AC voltage.
Filters: A circuit that removes ripples
(unwanted ac components) present in the pulsating dc voltage.
Regulator: A circuit that maintains the
terminal voltage as constant even if the input voltage or load current varying.
Types of rectifiers:
Rectifiers
are grouped into two categories depending on the period of conduction.
(a)Half wave rectifier (b) Full wave rectifier
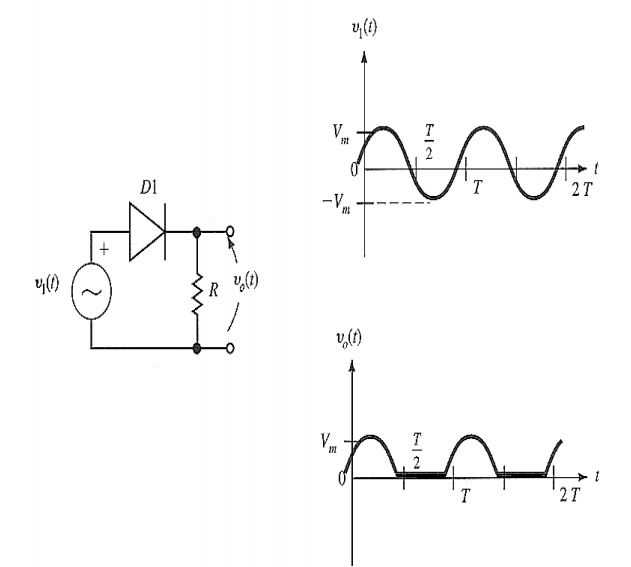
Half wave Rectifier:
Principle
It is a
circuit that converts alternating voltage or current into pulsating voltage or
current for half the period of input cycle hence it is named as “half wave rectifier”.
Construction
Ø It
consists of step-down transformer, semiconductor diode and the load resistance.
Ø The step-down
transformer – reduce the available ac voltage into required level of smaller ac
voltage.
Ø The diode
can be used to convert the ac into pulsating dc.
Operation
Ø During
the positive half cycle of input, the diode D is forward biased, it offers very
small resistance and it acts as closed switch and hence conducts the current
through the load resistor.
Ø During
the negative half cycle of the input diode D is heavily reverse biased, it
offers very high resistance and it acts as open switch hence it does not
conduct any current. The rectified output voltage will be in phase with AC
input voltage for completely resistive load.
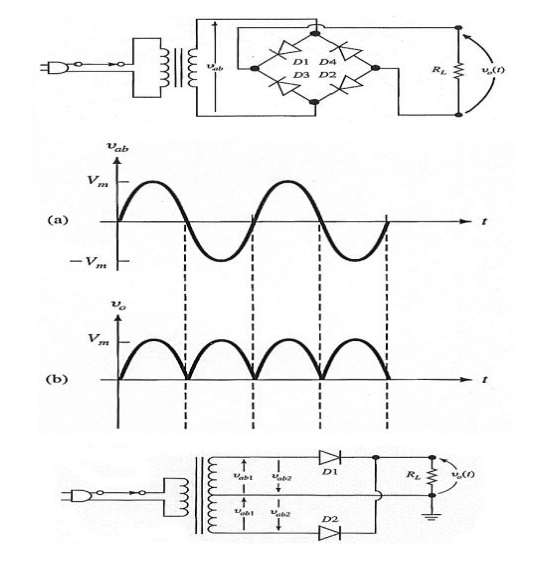
Full wave Rectifier:
Principle
A circuit
that converts the ac voltage or current into pulsating voltage or current
during both half cycle of input is known as “full wave rectifier”.
Operation
Ø During
positive half cycle of ac input, diode D1 becomes forward biased,
provides very small resistance and acts as closed switch, resulting in the flow
of current.
Ø During
negative half cycle, diode D1 reverse biased, offers high resistance
and it acts as open circuit.
Voltage Regulation:
Ratio of Difference of secondary voltage to Primary voltage to secondary voltage.
Related Topics