Organisation of Life | Chapter 18 | 8th Science - Questions Answers | 8th Science : Chapter 18 : Organisation of Life
Chapter: 8th Science : Chapter 18 : Organisation of Life
Questions Answers
TEXTBOOK EXERCISES
I. Choose the best
answer.
1.
_____________ is tough and thick white sheath that protects the inner parts of
the eye.
a) Sclera
b) Conjunctiva
c) Cornea
d) Iris
[Answer: (a) sclera]
2.
______________ cells are specialised cells that can be transformed into any
kind of cells.
a) Nerve
b) Stem
c) Heart
d) Bone
[Answer: (b) Stem]
3.
Maintenance of constant internal environment of the body is known as
a) homeostasis
b) homeophytes
c) homeokinesis
d) homeophilics
[Answer: (a) Homeostasis]
4.
In the absence of oxygen, glucose is broken down in to ______________.
a) lactic acid
b) citric acid
c) acetic acid
d) nitric acid
[Answer: (a) Lactic acid]
5.
The process of air passing in and out the lungs is called ______________.
a) inhalation
b) exhalation
c) breathing
d) None of these
[Answer: (c) Breathing]
6.
Osmosis isthe movement of water molecules from
a) higher concentration to a region
of lower concentration.
b) lower concentration to a region
of higher concentration.
c) Both of these
d) None of these
[Answer: (a) Higher concentration to a region of lower
concentration]
7.
The erythrocyte is placed in ______________solution which has lesser
concentration of solutes and greater concentration of water than in the
cytoplasm.
a) hypotonic
b) hypertonic
c) neutral
d) acidic
[Answer: (a) Hypotonic]
II. Fill in the
blanks.
1. Cell is the structural
and functional unit of living organisms.
2. The largest cell is egg of an
3. Fermentation is a good example
for anaerobic respiration.
4. Optic nerve is located
at the end of the eyes behind the retina.
5. The size of the cells are
measured in units of
III. Match the
following.
1. Carbohydrates- CO2,
Water and Heat
2. Glucose-Amino acid
3. Protein- Glucose
4. Amino acids-Cholesterol and other
steroid
5. Fatty acids- Enzymes, hormone,
protein
[Answer:
1 - c, 2 - a, 3 - b]
1. Carbohydrates - (c) glucose
2. Glucose - (a) CO2, water and heat
3. Protein - (b) amino acid
4. Amino acids
5. Fatty acids
IV. State true or
false. If false, correct the statement.
1. In hypotonic condition,
concentration of the external and the internal solution of the organism are
same .
Correct statement: The concentration of external solution is less compared to concentration of internal solution of the
organism.
2. Diffusion is the movement of
particles from an area of lower concentration to higher concentration .
Correct statement: Diffusion is the movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to lower concentration.
3. Human beings are warm blooded in
nature.
4. The larynx has fold of tissue
which vibrate with the passage of air to produce sound.
5. Aqueous humour plays an important
role in maintaining the shape of the eye.
V. Answer very
briefly.
1.
What is cell differentiation?
Answer: Our body develops from a single cell called zygote. The zygote
undergoes mitotic division to form many cells of different shape, size and
content. These cells attain change in structure and function which is called
differentiation. This form the foetus.
2.
State different types of tissues.
Answer: Depending on the basis of their structure and function, tissues
can be classified into four types.
(i) Epithelial (covering) tissue for protection.
(ii) Muscular (contractile) tissue for movements and locomotion.
(iii) Connective (supporting) tissue for binding different structures of body.
(iv) Nervous tissue for conduction of nerve impulses.
3.
Mention the function of ‘Alveoli’.
Answer:
(i) Alveoli are tiny air sacs in the lungs.
(ii) They are the workhouses of the respiratory system.
(iii) The exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide take place in
alveoli of the lungs.
4. Name the processes by which air enters and
comes out of our lungs.
Answer:
(i) The process of taxing air into the lungs is called
inspiration or inhalation.
(ii) The process of expelling air from the lungs is called
expiration or exhalation.
5. Differentiate osmoconformers and
osmoregulators.
Answer:
There are two major types of Osmoregulation :
Osmoconformers
These organisms try to maintain the osmolality of their body
matching with their surroundings. Most of the invertebrates, marine organisms
are osmoconformers.
Osmoregulators
These organisms maintain their internal osmolality, which can be
extremely different from that of the surrounding environment, through
physiological processes.
6. Define - Metabolism.
Answer:
(i) Metabolism is the sum of chemical reactions by which living
organisms sustain their life.
(ii) Metabolism consists of anabolism (the buildup of
substances) and catabolism (the breakdown of substances).
VI. Answer briefly.
1.
Define - Prokaryotic cell.
Answer: Organisms in which no true nucleus is seen are called prokaryotic. Ex :
Bacteria.
2.
Tabulate the differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
Answer:
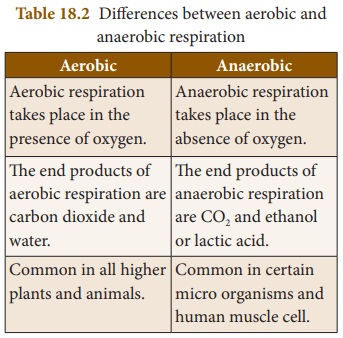
Aerobic
1. Aerobic respiration takes place in the presence of oxygen
2. The end products of aerobic respiration are carbon dioxide
and water
3 Common in all higher plants and animals
Anaerobic
1. Anaerobic respiration takes place in the absence of oxygen
2. The end products of anaerobic respiration are CO2 and
ethanol or lactic acid
3. Common in certain micro organisms and human muscle cell
3.
Why the human eye is compared with camera?
Answer: The human eye can be compared to a camera as both functions by
gathering, focusing, and transmitting the light through the lens for creating
an image of an object.
(i) The iris of the
eye controls the size of the pupil depending on the amount of light entering
it.
(ii) The pupil is
like the eyehole of a camera which allows light to come in.
(iii) Lens : It is a
transparent, biconvex, and an adjustable part of an eye, made up of protein.
The lens with the help of the cornea refracts light focused on the retina,
therefore creating images on it.
(iv) The retina consists of photoreceptors and converts light
rays into impulses to be sent to the brain. It is light sensitive.
The retina is compared to the film in a camera.
4.
Which organ and organ system help to maintain homeostasis?
Answer:
(i) Homeostasis is a property of a human biological system where
the self-regulating process tends to maintain the balance for the survival.
(ii) Behavioural and physiological responses are two important
regulating mechanisms that maintain the stability of homeostasis.
(iii) All the processes of integration and co-ordination of
function are mediated by nervous and hormonal system. The liver, kidneys, and
brain (hypothalamus), autonomic nervous system and the endocrine system help to
maintain homeostasis.
Define Eukaryotic cell?
Answer: Organisms in which true nucleus is seen (presence of nuclear
membrane) are called eukaryotic. Ex : Higher plants.
VII. Answer in detail.
1.
Draw the struture of human eye and label its parts.
Answer:
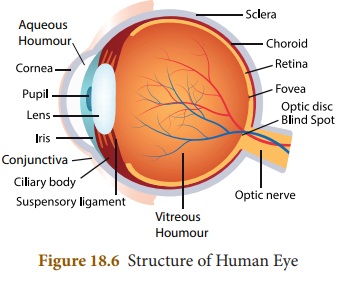
2.
Explain osmosis with an example.
Answer: Osmosis is the movement of solvent particles across a
semipermeable membrane from a dilute solution into a concentrated solution. The
solvent moves to dilute the concentrated solution and equalize the
concentration on both sides of the membrane.
The movement of liquids in and out cells is dependent on the
concentration of the solution surrounding it. There are 3 types of situations
in which this could vary:
(i) Isotonic : Here the concentration of external and internal solution of
the organism are the same.
(ii) Hypotonic: Here the external solution concentration is less compared to
the concentration of the inner solution of an organism. In this case water will
rush into the organism.
(iii) Hypertonic: Here the external solution concentration is greater than the
concentration of the inner solution of an organism. In this case the water will
rush out of the organism.
Ex : Red blood cells.
(1) When red blood cells are placed in hypertonic solution,
water flows out of the cell faster than it comes in. This results in
shrivelling of RBC.
(2) On the other hand if RBC is hypotonic, more water will flow
into the cell than out. This results in swelling of the cell and followed by
bursting.
(3) If the RBC is placed in an isotonic solutions, the flow of
water in and out of the cell will happen at the same rate.
3.
Differentiate between inhalation and exhalation.
Answer:
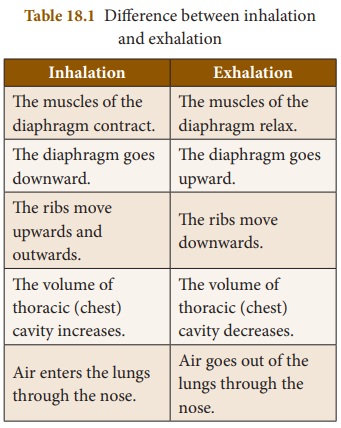
Inhalation
1. The muscles of the diaphragm contract.
2. The diaphragm goes downward.
3 The ribs move upwards and outwards.
4. The volume of thoracic (chest) cavity increases.
5. Air enters the lungs through the nose.
Exhalation
1. The muscles of the diaphragm relax.
2. The diaphragm goes upward.
3. The ribs move downwards.
4. The volume of thoracic (chest) cavity decreases.
5. Air goes out of the lungs through the nose.
4.
List out the different types of metabolism with an example.
Answer:
(i) Metabolism is the sum of chemical reactions by which living organisms
sustain their life.
(ii) Metabolism consists of anabolism (the buildup of
substances) and catabolism (the breakdown of substances).
Anabolism
:
Anabolism or constructive metabolism, is all about building and
storing: It supports the growth of new cells, the maintenance of body tissues,
and the storage of energy for use in the future. During anabolism, small
molecules are changed into larger, more complex molecules of carbohydrate,
protein and fat.
For
example,
Glucose → Glycogen and other sugars
Amino acids → Enzymes, hormones and proteins
Catabolism
:
Catabolism or destructive metabolism, is the process that
produces the energy required for all activity in the cells. In this process,
cells break down large molecules (mostly carbohydrates and fats) to release
energy. This energy release provides fuel for anabolism, heats the body, and
enables the muscles to contract and the body to move.
Carbohydrates → Glucose
Glucose → CO2, Water and heat
5.
Explain the mechanism of breathing.
Answer:
(i) The process of taking air into the lungs is called inspiration or inhalation.
(ii) During inspiration, the sternum is pushed up and outward
and the diaphragm is pulled down.
(iii) This increases the volume of the thoracic cavity and the
pressure decreases.
(iv) The air outside the body flows into the lungs. Here
exchange of gases takes place between the air and the blood.
(v) The process of expelling air from the lungs is called expiration or exhalation.
(vi) Upon exhalation, the lungs recoil to force the air out of
the lungs.
(vii) The intercostal muscles relax, returning the chest wall to
its original position. During exhalation, the diaphragm also relaxes, moving
higher into the thoracic cavity.
(viii) This increases the pressure within the thoracic cavity
relative to the environment.
(ix) Air rushes out of the lungs due to the pressure gradient.
This movement of air out of the lungs is a passive event.
VIII. Higher Order
Thinking Questions.
1.
Why do we need instant energy? Does glucose give that energy? Explain.
Answer:
(i) Energy is needed for performing day to day activities of the
body which is got through intake of food. This provides energy for all organ
systems.
(ii) Instant energy may be required in cases of extended
physical activities like running or physical ailments like tiredness or
giddiness.
(iii) Glucose is the simplest form of carbohydrate. Intake of
glucose help it to solubilise in the blood immediately, and is carried to
organs of the body thus helping to provide instant energy digestion of
carbohydrates also converts it to glucose finally.
2. How are we preparing pickles? What are the
steps involved in that?
Answer:
(i) Pickles are prepared usually by addition of excess salt. The
salty solution creates a high concentration (hypertonic) in the external medium
of the vegetable / fruit which is used for making pickles.
(ii) Therefore water comes out of the vegatable and it undergoes
plasmolysis and begins to shrink.
(iii) Thus when water content is lost the pickle is able to
retain its shelf life for a longer period.
IX. Value based
questions.
1. Dr.
Usha is a pulmonologist (Doctor for respiratory diseases). One day, a school
student named Arjun, met her with respiratory problems. After diagnosis, the
doctor advised him to go to playground daily and play football or basketball.
She also advised him to do pranayamam in the morning.
a)
Why did the doctor advise him to go to the playground?
b)
What is the use of pranayamam?
Answer:
(a) Playing is a good physical activity which helps to improve
breathing and blood circulation in the body. It also helps to relieve anxiety.
(b)
(1) Pranayamam teaches us the proper way of breathing, slowly
and deeply.
(2) It increases the capacity of the lungs and brings more
oxygen into the body.
(3) It is especially very useful when one has respiratory
problems and the breathing is irregular and unsteady.
(4) It improves blood circulation.
2.
Explain why you are not able to breathe normally when you are in closed and
crowded places?
Answer:
In a closed and crowded place, the number of people are more.
All of them breathe out carbon dioxide. Therefore the amount of CO2
in the air is much more than the amount of oxygen available for inhalation.
Therefore we find it difficult to breathe in a closed and crowded place.
3.
Shylesh is a school going kid studying standard VIII. He is crazy about playing
video games in mobile phones. After couple of months, his eyes turned red and
he felt severe pain in his eyes. His science teacher enquired about this and
advised his parents to take him to an eye doctor.
i)
How does excessive usage of mobile phone affect our eyes?
ii)
What are the values shown by the teacher?
Answer:
Impact of
excessive usage of mobile phones :
(i)
(1) Cell phone radiation can damage eyes and cause early
cataract.
(2) It can also lead to cataract in lens apart from affecting
retina, cornea etc.
(3) It strains the eye muscles.
(4) It also caused temporary problems like dry and itchy eyes,
blurry vision, pain in eyes etc.
(ii)
The teacher has shown values of
(1) Empathy
(2) Responsibility
(3) Personal care.
Related Topics