Organisation of Life | Chapter 18 | 8th Science - Organ System | 8th Science : Chapter 18 : Organisation of Life
Chapter: 8th Science : Chapter 18 : Organisation of Life
Organ System
Organ System
A group of organs form the organ
system, and together they perform a particular function. The heart and the
blood vessels together make the cardiovascular system.
Organs suchasnose, pharynx, trachea, lungs and diaphragm work to get her as the respiratory
system. The mouth, oesophagus, stomach, duodenum, and the intestines together
form the digestive system. Other examples of organ system include the endocrine
system, integumentary system, muscular system, reproductive system, skeletal
system, urinary system, immune system, etc. Let us see the respiratory system
as an example for organ system elaborately.
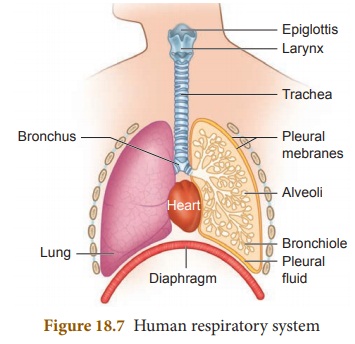
The Respiratory System
Our respiratory system consists of
organs like trachea, bronchus and lungs which are responsible for exchange of
air between the atmosphere and the blood. Let us see the organs of the
respiratory system in detail.
The
nose
We inhale air through the nostrils,
which lead to the nasal cavity. The inner surface of this cavity is lined with
cilia and mucous producing cells, which make it sticky and moist. The cilia and
mucous trap dust and germs to prevent them from going deeper into the
respiratory tract. The blood vessels in the nose help to warm the inhaled air.
The
windpipe
After passing through the nasal
cavity, the air enters the pharynx. Then it goes into the trachea or the
windpipe which is an elastic tube extending down the length of the neck and
partly into the chest cavity. Between the pharynx and the trachea lies a small
air passage called the larynx commonly known as the voice box. The larynx has fold of tissue which vibrate with the
passage of air to produce sound.
Bronchi
The trachea divides into two
branches called bronchi (Singular:
bronchus). Each bronchus leads to a lung, where it divides and redivides to
finally form air passages called bronchioles.
Lungs
The lungs are the organs present in
the chest cavity that allow our body to exchange gases (oxygen and carbon
dioxide). The lungs are two spongy elastic bags, on each side of the thoracic
cavity. The thoracic cavity is bound dorsally by the vertebral column and
ventrally by the sternum, laterally by the ribs and on the lower side by the
dome shaped diaphragm. The left lung is slightly smaller than the right lung
(allows room for the heart). Within the lungs, each bronchiole leads to a bunch
of air sacs called alveoli (Singular: Alveolus).
On an average, an
adult humanbeing at rest breathes in andout 15 – 18 times in a minute. During
heavy exercise, breathing rate can increase upto 25 times per minute.
Smoking damages lungs.
Smoking is also linked to cancer. It must be avoided.
When you sneeze, you
should cover your nose so that the foreign particles you expel are not inhaled
by others.
Alveoli
Alveoli are tiny air sacs in the
lungs that are located at the end of bronchial tubes, which is microscopic in
nature. It is meant for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Mechanism of Breathing
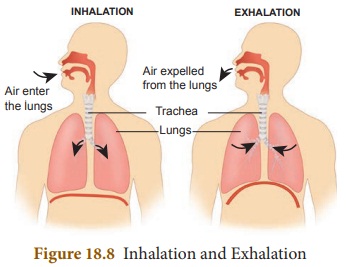
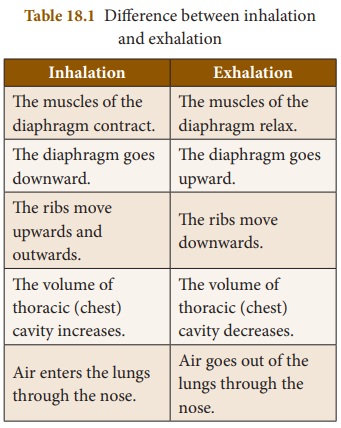
Inspiration
(Inhalation)
The process of taking air into the
lungs is called inspiration or
inhalation. During inspiration, the sternum is pushed up and outward and the
diaphragm is pulled down. This increases the volume of the thoracic cavity and
thus the pressure decreases. The air outside the body flows into the lungs.
Here exchange of gases takes place between the air and the blood.
Expiration
(Exhalation)
The process of expelling air from
the lungs is called expiration or
exhalation. Upon exhalation, the lungs recoil to force the air out of the
lungs. The inter costal muscles relax, returning the chest wall to its original
position. During exhalation, the diaphragm also relaxes, moving higher into the
thoracic cavity. This increases the pressure within the thoracic cavity
relative to the environment. Air rushes out of the lungs due to the pressure
gradient. This movement of air out of the lungs is a passive event.
Exchange
of gases in the Alveoli
The content of oxygen in the inhaled
air in alveoli is more than the blood flowing through the capillaries. So, the
oxygen moves into the blood by simple diffusion.
Haemoglobin in the blood combines
with oxygen to form oxyhaemoglobin.
The blood carrying oxygen reaches the heart through blood vessels. The heart
pumps it to all the tissues in the body. The tissues release carbon dioxide
which is carried back to alveoli by the blood. Carbon dioxide diffuses from the
blood to the air in the alveoli and is sent out of the body when the air is
exhaled.
Activity 2
Stand erect and wave
your hands in side wards. Take a deep breath and feel your rib movements. Then
run some 100 metres and observe the rib movements. Discuss in the class room
about what you observed.
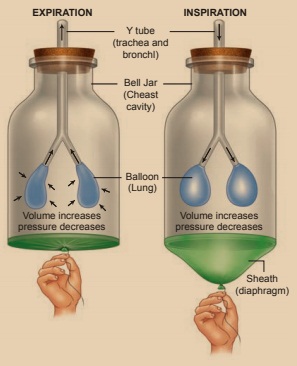
Activity 3
Constructing a model
of lungs.
Materials required
Y shaped tube, a large
balloon, two small balloons, a one litre plastic bottle, cork.
Method of Construction
Cut off the plastic
bottle in the middle. Fix two small balloons in both the ends of the Y-tube.
Make a hole in the cork and fix the y-tube. Make a small hole in the cork and
fix the y-tube through the hole as shown in the picture. Cut a large balloon
into two halves and fix one half tightly around the open part of the bottle.
Method of Working
Hold the large balloon
in the middle and pull it slowly downwards as shown in the picture. Observe the
change in the balloons inside the bottle. Now leave the balloon free.
Related Topics