Organisation of Life | Chapter 18 | 8th Science - Organ | 8th Science : Chapter 18 : Organisation of Life
Chapter: 8th Science : Chapter 18 : Organisation of Life
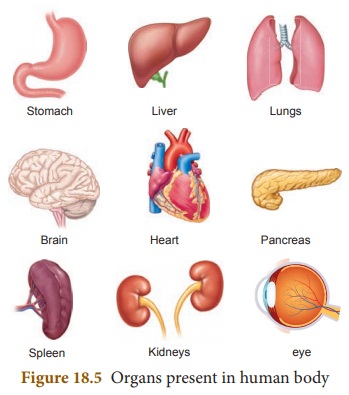
Organ
Organ
Organs are the structures made up of two or
more types of tissues, organized to carry outa particular function. Example:
Brain, heart,lungs, kidneys, liver etc. , Each of them has specific functions.
Most organs are made up of four
types of tissues. For example, the intestine, is made of epithelial tissue as
the inner lining, which helps in enzyme secretion and nutrient absorption.
Epithelial tissue is covered by layers of muscle tissue, which help in
peristaltic movements to move the food. The intestine is also supplied by blood
tissue (connective tissue) which helps in transporting nutrients absorbed by
the intestine, and is connected to the brain through the nerve tissue, which
conveys instructions from the brain.
Now let us study in detail about the structure of an eye.
The eyes -
Photoreceptor
The eye is one of the important
sensory organs in the human body. It is composed of muscular tissue, connective
tissue and neural tissue. It is mainly responsible for vision, differentiation of color (the human eye
can differentiate approximately 10 – 12 million colors) and maintaining the biological clock of the
human body. The human eye can be compared to a camera as both functions by
gathering, focusing, and transmitting the light through the lens for creating
an image of an object.
To understand more about our eye and
how our eye functions, we need to look into the structure of the human eye.The
human eyes are the most complicated sense organ in the human body, with several
parts fixed together forming a spherical structure. Every part of the human eye
is mainly responsible for a certain action. The structure of a human eye can be
broadly classified into external structure and internal structure.
a. External structure
of an Eye
The parts of the eye that are
visible externally comprise of the external structure of the eye.
Sclera
It is a tough and thick white sheath
that protects the inner parts of the eye. We know it as the ‘white of the eye’.
Conjunctiva
It is a thin transparent membrane
that is spread across the sclera. It keeps the eyes moist and clear by
secreting small amounts of mucus and tears.
Cornea
It is the transparent layer of
membrane that is spread over the pupil and the iris. The main role of the
cornea is to refract the light that enters the eyes.
Iris
It is a pigmented layer of tissues
that make up the colored portion of the eye. Its primary function is to control
the size of the pupil, depending on the amount of light entering it.
Pupil
It is the small opening located at
the middle of the iris. It allows light to come in.
b. Internal structure
of an Eye
The internal structure of the eye
includes the following parts.
Lens
It is a transparent, biconvex, and
an adjustable part of an eye, made up of protein. The lens with the help of the
cornea refracts light which converges on the retina and creates images on it.
Retina
It is the layer present at the back
of the eye where all the images are formed. The retina functions by converting
the light rays into impulses and sending the signals to the brain through the
optic nerve.
Optic
nerve
It is located at the end of the
eyes, behind the retina. The optic nerve is mainly responsible for carrying all
the nerve impulses from the retina to the human brain.
Aqueous
Humour
It is a watery fluid that is present
in the area between the lens and the cornea. It is
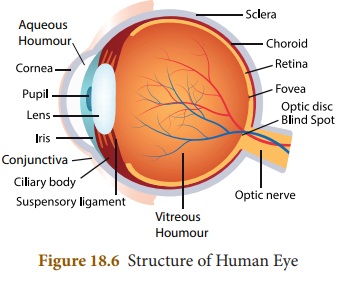
Vitreous
Humour
It is a semi-solid, transparent,
jelly-like substance that covers the interior portion of the eyes. It plays an
important role in maintaining the shape of the eye and also causes refraction
of light before it reaches the retina.
Related Topics