Chapter: 12th Computer Science : Chapter 13 : Database concepts and MySql : Python and CSV Files
Python and CSV Files: Book Back Questions and Answers
Computer Science : Database concepts and MySql : Python and CSV Files
Evaluation
Part – I
Choose the best answer (1 Marks)
1.A CSV file is also known as a ….
(A) Flat File
(B) 3D File
(C) String File
(D) Random File
2.The expansion of CRLF is
(A) Control Return and Line Feed
(B) Carriage Return and Form Feed
(C) Control Router and Line Feed
(D) Carriage Return and Line Feed
3.Which of the following module is provided by Python to do several operations on the CSV files?
(A) py
(B) xls
(C) csv
(D) os
4.Which of the following mode is used when dealing with non-text files like image or exe files?
(A) Text mode
(B) Binary mode
(C) xls mode
(D) csv mode
5.The command used to skip a row in a CSV file is
(A) next()
(B) skip()
(C) omit()
(D) bounce()
6.Which of the following is a string used to terminate lines produced by writer()method of csv module?
(A) Line Terminator
(B) Enter key
(C) Form feed
(D) Data Terminator
7.What is the output of the following program? import csv d=csv.reader(open('c:\PYPRG\ch13\city.csv'))
next(d)
for row in d: print(row)
if the file called “city.csv” contain the following details
chennai,mylapore
mumbai,andheri
A) chennai,mylapore
(B) mumbai,andheri
(C) chennai
(D) chennai,mylapore
mumba mumbai,andheri
8.Which of the following creates an object which maps data to a dictionary?
(A) listreader()
(B) reader()
(C) tuplereader()
(D) DicReader ()
9.Making some changes in the data of the existing file or adding more data is called
(A)Editing
(B) Appending
(C) Modification
(D) Alteration
10.What will be written inside the file test.csv using the following program import csv
D = [['Exam'],['Quarterly'],['Halfyearly']]
csv.register_dialect('M',lineterminator = '\n')
with open('c:\pyprg\ch13\line2.csv', 'w') as f:
wr = csv.writer(f,dialect='M')
wr.writerows(D)
f.close()

(A) Exam Quarterly Halfyearly
(B) Exam Quarterly Halfyearly
(C)
E
Q
H
(D)
Exam,
Quarterly,
Halfyearly
Part – II
Answer the following questions (2 Marks)
1. What is CSV File?
Ans. A CSV file is a human readable text file where each line has a
number of fields, separated by commas or some other delimiter.
2. Mention the two ways to read a CSV file using Python.
Ans. (i) CSV files have been used extensively in e-commerce
applications because they are considered very easy to process.
(ii) There are two ways to read a CSV file.
(a) Use the csv modules reader function
(b) Use the DictReader class.
3. Mention the default modes of the File.
Ans.
The default mode of csv file in reading and writing is text mode.
4. What is use of next() function?
Ans. next() function is used to skip the first row while sorting a
CSV file or a selected column.
5. How will you sort more than one column from a csv file?Give an example statement.
Ans. To sort by more than one column you can use itemgetter with
multiple indices, operator .itemgetter (1,2).
Syntax :
sortedlist = sorted(data, key=operator.itemget
ter(Col_number),reverse=True)
Part – III
Answer the following questions (3 Marks)
1. Write a note on open() function of python. What is the difference between the two methods?
Ans. Python has a built-in function open() to open a file. This
function returns a file object, also
called a handle, as it is used to
read or modify the file accordingly.
2. Write a Python program to modify an existing file.
Ans. import csv
row = [‘3’, ‘Meena’,’Bangalore’]
with open(‘student.csv’, r’) as readFile:
reader = csv.reader(readFile)
lines = list(reader) # list()- to
store each row of data as a list
lines [3] = row
with open( student.csv’, ‘w’) as writeFile:
# returns the writer object
which converts the user data with delimiter
writer = csv.writer(writeFile) #writerows()method writes multiple rows to a csv file
writer.writerows(lines)
readFile.close()
writeFile.close()
3. Write a Python program to read a CSV file with default delimiter comma (,).
Ans. import csv
csv.register_dialect('myDialect',delimiter
=',',quoting=csv.QUOTE_ALL,
skipinitialspace=True)
f=open('c:\\pyprg\\quotes.csv',,r')
reader = csv.reader(f, dialect='myDialect')
for row in reader:
print(row)
4. What is the difference between the write mode and append mode.
Ans. The ‘w’ write mode creates a new file. If the file is already
existing ‘w’ mode overwrites it. Where as ‘a’ append mode is used to add the
data at the end of the file if the file already exists otherwise creates a new
one.
5. What is the difference between reader() and DictReader() function?
Ans. The main difference between the csv.reader() and DictReader()
is in simple terms csv.reader and csv.writer work with list/tuple, while csv.
DictReader and csv.DictWriter work with dictionary.
Part – IV
Answer the following questions (5 Marks)
1. Differentiate Excel file and CSV file.
Ans.
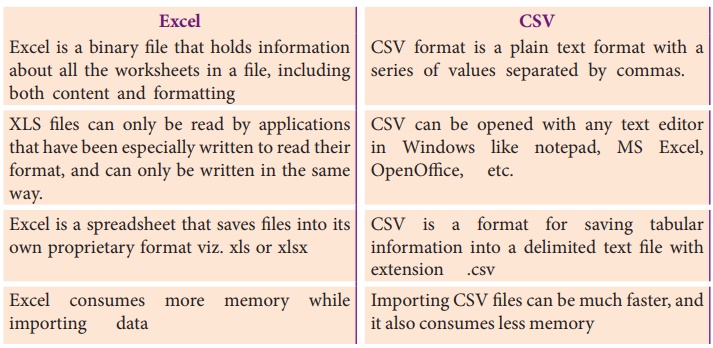
Excel
• Excel is a binary file that holds information about all the
worksheets in a file, including both content and formatting
• XLS files can only be read by applications that have been
especially written to read their format, and can only be written in the same
way.
• Excel is a spreadsheet that saves files into its own
proprietary format viz. xls or xlsx
• Excel consumes more memory while importing data
CSV
• CSV format is a plain text format with a series of values
separated by commas.
• CSV can be opened with any text editor in Windows like
notepad, MS Excel, OpenOffice, etc.
• CSV is a format for saving tabular information into a
delimited text file with extension. CSV
• Importing CSV files can be much faster, and it also consumes less memory
2. Tabulate the different mode with its meaning.
Ans.
Mode : Description
r' : Open a file for
reading, (default)
'w' : Open a file for
writing. Creates a new file if it does not exist or truncates the file if it
exists.
‘x’ : Open a file for exclusive creation. If the file already
exists, the operation fails.
‘a' : Open for appending at the end of the file
without truncating it. Creates a new file if it does not exist.
't’ : Opren in text mode,
(default)
’b’ : Open in binary mode.
‘+’ : Open a file for updating (reading and writing)
3. Write the different methods to read a File in Python.
Ans. Read a CSV File Lsing
Python :
There are two ways to read a CSV file.
(i) Use the csv modules reader function
(ii) Use the DictReader
class.
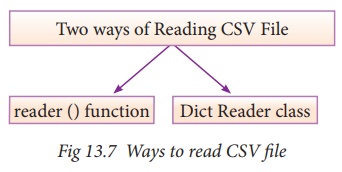
CSV Module’s Reader Function:
(i) You can read the contents of CSV file with the help of
csv.reader() method. The reader function is designed to take each line of the
file and make a list of all columns.
(ii) Then, you just choose the column you want the variable data
for. Using this method one can read data from csv files of different formats
like quotes (""), pipe (|) and comma (,).
The syntax for csv.readerf) is
csv.reader(fileobject,delimiter,fmtparams)
where
(iii) file object :
passes the path and the mode of the file
(iv) delimiter:an
optional parameter containing the standard dilects like , | etc can be omitted.
(v) fmtparams :
optional parameter which help to override the default values of the dialects
like skipinitialspace,quoting etc. can be omitted.
* CSV file - data with default delimiter comma (,)
* CSV file - data with Space at the beginning
* CSV file - data with quotes
* CSV file - data with custom Delimiters
CSV file with default delimiter
comma (,): The following program read a file called
“sample 1. csv” with default delimiter comma (,) and print row by row.
Program:
#importing csv
import csv
#opening the csv file which is in different location with read
mode
with open('c:\\pyprg\\samplel.csv', 'r') as F:
#other way to open the file is f= ('c:\\pyprg\\sample1.csv',
'r')
reader = csv.reader(F)
# printing each line of the Data row by row print(row)
F.close()
Output:
['SNO', 'NAME', 'CITY']
['12101', 'RAM', 'CHENNAI']
['12102', 'LAVANYA', 'TIRUCHY']
['12103', 'LAKSHMAN', 'MADURAI']
Reading CSV File Into A
Dictionary:
(i) To read a CSV file into a dictionary can be done by using
DictReader class of csv module which works similar to the reader() class but
creates an object which maps data to a dictionary.
(ii) The keys are given by the fieldnames as parameter.
DictReader works by reading the first line of the CSV and using each comma
separated value in this line as a dictionary key.
(iii) The columns in each subsequent row then behave like
dictionary values and can be accessed with the appropriate key (i.e.
fieldname).
(iv) If the first row of your CSV does not contain your column
names, you can pass a fieldnames parameter into the DictReader s constructor to
assign the dictionary keys manually.
(v) The main difference between the csv. reader() and
DictReader() is in simple terms csv.reader and csv.writer work with list/tuple,
while csv.DictReader and csv. DictWriter work with dictionary, csv. DictReader
and csv. DictWriter take additional argument fieldnames that are used as
dictionary keys.
(vi) For Example Reading “sample8.csv” file into a dictionary
Program:
import csv
filename = c:\\pyprg\\sample8.csv’
input_file =csv.DictReader(open(filename,’r’)) for row in
input_file:
print(dict(row) ) #dict() to print data
Output:
{‘ItemName ‘: ‘Keyboard ‘, ‘Quantity’: ‘48’}
{‘ItemName ‘: ‘Monitor’ ‘Quantity’: ‘52’}
{‘ItemName ‘: ‘Mouse ‘, ‘Quantity’: ‘20’}
In the above program, DictReader() is used to read “sample8.csv”
file and map into a dictionary. Then, the function dict() is used to print the
data in dictionary format without order. Remove the dict() function from the
above program and use print(row).Check you are getting the following output
OrderedDict([(‘ItemName ‘, ‘Keyboard ‘), (‘Quantity’, ‘48’)])
OrderedDict([(‘ItemName ‘, ‘Monitor’), (‘Quantity’, ‘52’)])
OrderedDict( [(‘ItemName ‘, ‘Mouse ‘), (‘Quantity’, ‘20’)])
4. Write a Python program to write a CSV File with custom quotes.
Ans. import csv
info = [[‘SNO’, ‘Person, ‘DOB’],
[T’,‘Madhu’,‘18/12/2001’],
[‘2’, ‘Sowmya’,’19/2/1998’],
[‘3’, ‘Sangeetha’,’20/3/1999’],
[‘4’, ‘Eshwar’, ‘21/4/2000’],
[‘5’, ‘Anand’, ‘22/5/2001’]]
csv.register_dialect(‘myDialect’,quoting=csv.QUOTE_ALL)
with open(‘c:\\pyprg\\chl3\\person.csv’, ‘w’) as f:
writer - csv.writer(f, dialect=’myDialect’)
for row in info:
writer, writero w( row)
f.close()
5. Write the rules to be followed to format the data in a CSV file.
Ans. Rules to be followed to
format data in a CSV file:
(i) Each record (row of data) is to be located on a separate
line, delimited by a line break by pressing enter key.
Example: ←|
xxx,yyy ←|
←| denotes enter Key to be pressed
(ii) The last record in the file may or may not have an ending
line break.
Example:
ppp, qqq←|
yyy, xxx
(iii) There may be an optional header line appearing as the
first line of the file with the same format as normal record lines. The header
will contain names corresponding to the fields in the file and should contain
the same number of fields as the records in the rest of the file.
Example:
field_namel,field_name2,field_name3←|
aaa,bbb,ccc ←|
zzz,yyy,xxx CRLF(Carriage Return and Line Feed)
(iv) Within the header and each record, there may be one or more
fields, separated by commas. Spaces are considered part of a field and should
not be ignored. The last field in the record must not be followed by a comma.
For example: Red , Blue
(v) Each field may or may not be enclosed in double quotes. If
fields are not enclosed with double quotes, then double quotes may not appear
inside the fields.
Example:
"Red","Blue","Green"←| #Field data with double quotes
Black,White,Yellow #Field data
without double quotes
(vi) Fields containing line breaks (CRLF), double quotes, and
commas should be enclosed in double-quotes.
Example:
Red, “,”, Blue CRLF # comma itself is a field value.so it is
enclosed with double quotes Red, Blue, Green
(vii) If double-quotes are used to enclose fields, then a
double-quote appearing inside a field must be preceded with another double
quote.
Example:
“Red, ” “Blue”, “Green”, # since double quotes is a field value
it is enclosed with another double quotes ,, White
Related Topics