Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Nursing Health Care Hospital Hygiene Higher secondary school College Notes
Purpose and Position of good body mechanics and posture
Definitions
Body mechanics means the co-oriented use of the body parts to produce motion and maintain equilibrium in relation to
both internal and external forces.
Posture is the relationship of the various parts of the body in activity or at rest.
Positioning a patient in correct
body alignment means to give proper support to the body in order to maintain muscle
tone and eliminate strain.
Purpose of good body mechanics and
posture
To provide maximum comfort and
relaxation
To aid in normal body functions
To prevent contractures and
neuromuscular deformities and complications
To conserve maximum possible energy
by preventing unnecessary strain
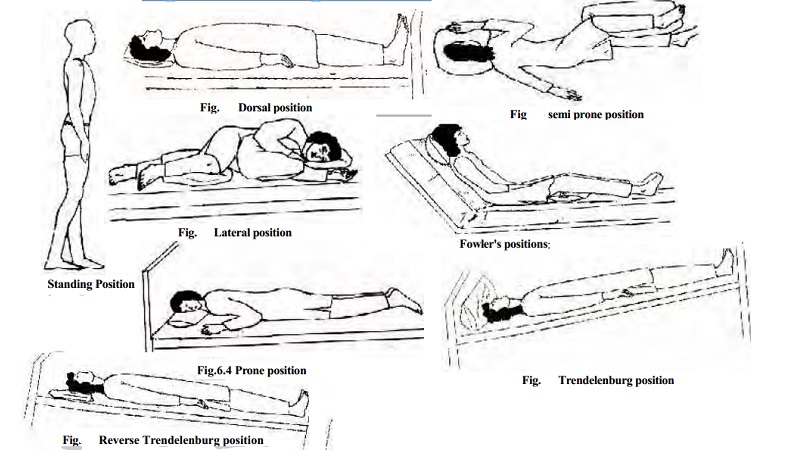
Standing position
In
correct standing position the head is held erect, back is kept straight as much
as possible, chest is put forward, shoulders are kept back, elbows are slightly
flexed, wrists are extended, fingers are slightly flexed, abdomen is drawn
inward and kept flat, knees are slightly flexed, and feet are pointing ahead
and parallel to each other about 3 inches apart.
Knowledge of correct standing
position is necessary because all other positions are modifications of standing
position.
When a nurse helps the patient to
sit or lie down in bed, she follows the principles of correct standing position
and keeps the patient's body in good alignment.
Sitting Position
In sitting position, the weight of
the body is balanced by ischial tuberosities, the buttocks and the thighs.
Elbows
are flexed and supported, hips are flexed at right angles to the trunk, knees
are flexed at right angles to the thighs, and angles are flexed to right angles
to the legs and are flat on floor. Back is held erect and the back and buttocks
are supported by the back of the chair.
Positions used for patients :
Dorsal position: Patient is flat on the bed with legs extended and arms at the sides of the body. This is not a
comfortable position, as the curves of the body are not supported.
Dorsal
recumbent position: This is called back lying position. This is a modification of
standing position. The only difference being, the patient is in horizontal
position instead of vertical.
Patient lies flat on his back with a
pillow under his head. A small pad is placed in the hollow of the back, and the
knees are slightly flexed. A soft pillow is arranged under the knees. A
footboard is provided to prevent foot drop. Arms are kept at the sides of the
body.
Most of the patients are nursed in this position.
Lateral
position: Patient lies on his side with spine straight. The knees are flexed; the
upper knee is more flexed than the lower one.
Pillows may be provided for the
head, in between the legs, and to support back and abdomen.
The lower arm is kept above the head
and the upper arm is placed on a pillow in front. The arms and legs do not bear
the weight of the body.
This
position is used for general comfort, rest and relaxation. During back care,
patient is placed in lateral position.
Left
lateral position is used for vaginal, perineal and rectal examinations, and the
post operative patients are kept in lateral position in order to maintain a
clear airway.
Jack knife position: Patient
lies on his back with his shoulders
slightly elevated. The hips and knees are flexed and brought up to the abdomen
and chest.
This position is useful to perform a
lumbar puncture.
Knee chest position:
The patient knees on the bed and then
lowers his head, shoulders and chest and rests them on the bed.
Head is turned to one side, and kept
on a pillow. The thighs are kept vertical. Arms are crossed above the head.
This position is useful for
performing vaginal and rectal examinations and for correcting displaced uterus
or other organs.
Lithotomy position:
The patient is kept on his back. Head and
shoulders rest on a small soft pillow. Knees are flexed well and buttocks are
brought over to the edge of the bed.
If it is used for a long period, the
legs are supported by stirrups, attached to the table.
The
position is used for examination or operations on rectum and genital organs.
Prone position:
Patient lies flat on his abdomen with head
kept on a pillow and turned to one side. Pillows are kept under the waist
and under the lower legs. The arms are flexed at the elbow and kept above the
head.
This
position is used when there is bedsore or burns or an injury at the back and as
a change of position for patients with fractured spine.
Sims position or semi prone position : This is a modified left
lateral position. The patient lies on the left side. Head, shoulders and chest
are turned forward so that her chest rests on the pillow.
The right knee is well flexed and
rests on the bed in front. The left knee is slightly flexed and is positioned
behind the right knee.
This
position is useful for performing vaginal examinations and for rest and
relaxation.
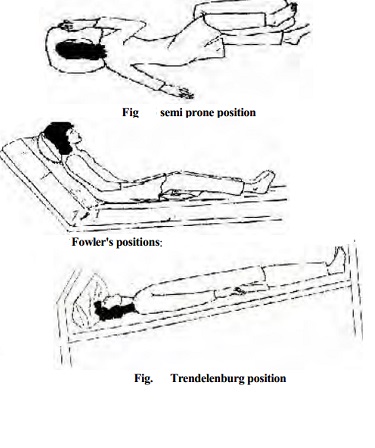
Fowler's positions:
Patient is in a partially sitting position.
The back of the bed is elevated to 45 degrees with the aid of a backrest
and pillows or by adjustment of the cot.
Patient's back, shoulder and head are
supported well. The knees are flexed and supported with a pillow or by cot
adjustment. A footrest is provided to prevent foot drop.
Patients are not kept in this
position for long time, since there is always the danger of thrombus formation.
This position is used for patients with dyspnoea (difficulty in breathing),
distended abdomen, abdominal surgery, cardio-thoracic disorders and ascites.
The position is also useful while
passing Ryle's tube and while performing tapping of ascites fluid.
Trendelenburg position :
The patient lies on his back with
the foot of the bed elevated on wooden blocks. Patient's head and trunk are
lower than the legs.
Reverse Trendelenburg position: The head and shoulders
are at a higher level than the hips, legs and feet.
This position is used for reducing
intracranial pressure and for other treatment measures.
Related Topics