Chapter: Essential Microbiology: Industrial and Food Microbiology
Products derived from genetically engineered microorganisms
Products
derived from genetically engineered microorganisms
Recombinant DNA technology can be used to
genetically modify microorganisms so that they produce commercially important
proteins such as human insulin. This is done by incorporating the gene for the
desired protein into an
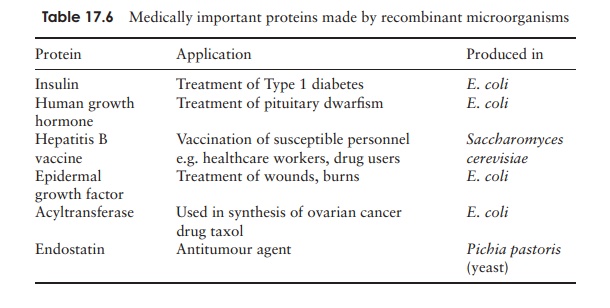
The initial
application of this technology was in the micro-bial production of medically
important proteins such as insulin and epidermal growth factor (Table 17.6),
however other proteins may also be produced by these means. These include
enzymes used in diagnostic and analytical applications, where a higher purity
of preparation is required than, for example, the enzymes used in detergents.
These are often derived originally from other microorganisms; for example the
thermostable DNA polymerase from Thermus
aquaticus used in PCR is now commonly made by recombinant E. coli cells that have been transformed
with the T. aquaticus gene. Many of
the more recent recombinant human proteins to be developed for therapeutic use
have been too complex for expression in a microbial system (e.g. Factor VIII),
so it has been necessary to employ cultured mammalian cells.
Related Topics