Chapter: BIOLOGY (ZOOLOGY) Standard XII second year 12th text book Assignment topics question and answer Explanation Definition
Process of pulmonary respiration
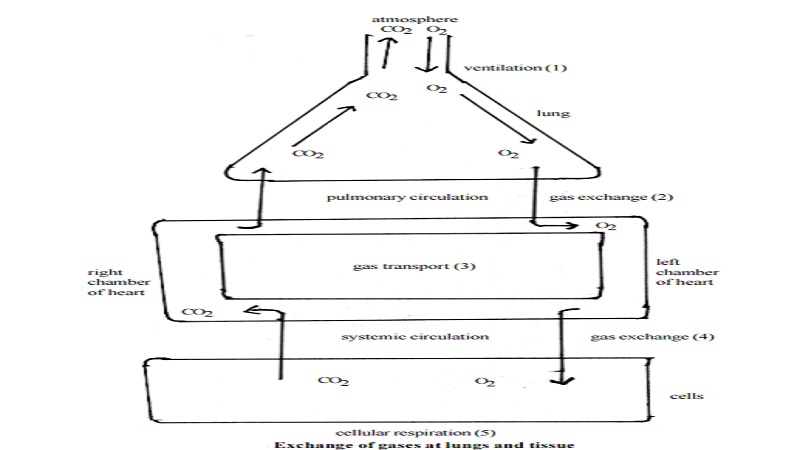
Process of pulmonary respiration
Respiration includes several processes which are listed below
(i).ventilation is the breathing in of air with more oxygen into the lungs (inspiration). It is followed by expulsion of air with more of carbon-di-oxide (expiration).
(ii) . Diffusion of oxygen from the alveoli into the blood inside surrounding capillaries.
(iii) . Transport of oxygen by the blood to the heart through the pulmonary vein.
(iv) . Distribution of oxygen by various arteries and their capillary network to all cells of the body. As the blood passes through tissue capillaries, it gives up oxygen (and nutrients such as glucose) to the body, tissues and picks up the waste products of cellular respiration (Carbon-di-oxide and water).
(v). Exchange of the oxygen and carbon-di-oxide between the blood and body cells. With in body cells glucose and oxygen take part in a complex series of reactions which provide energy to power the cells. During this cellular repiration glucose is converted to carbon-di-oxide and water. (Enzymatic oxidation).
(vi). Transporting blood with carbon-di-oxide. Carbon-di-oxide is carried back in the blood to the heart then to the lungs where it diffuses into the alveoli and is breathed out of the body (External respiration).
(vii) Exchanging of carbon-di-oxide with oxygen at the alveolar surface.
(viii) Expiration of air with carbon-di-oxide from the lungs.
Respiration
Respiration is a process by which oxygen reaches the body cells and is utilized by them in metabolism and carbon-di-oxide formed as a waste product gets eliminated. The real function of respiration is to provide the energy needed by body cells. Cells obtain energy by metabolizing glucose utilising oxygen. Hence they require a constant supply of oxygen. In addition, the waste products of the metabolic process, namely carbon-di-oxide must be carried away from the cells. The transport of oxygen and carbon-di-oxide between lungs and body cells takes place by an efficient cardio-vascular system.
Related Topics