Chapter: BIOLOGY (ZOOLOGY) Standard XII second year 12th text book Assignment topics question and answer Explanation Definition
Mechanism and Types of muscle contraction
Mechanism and Types of muscle contraction
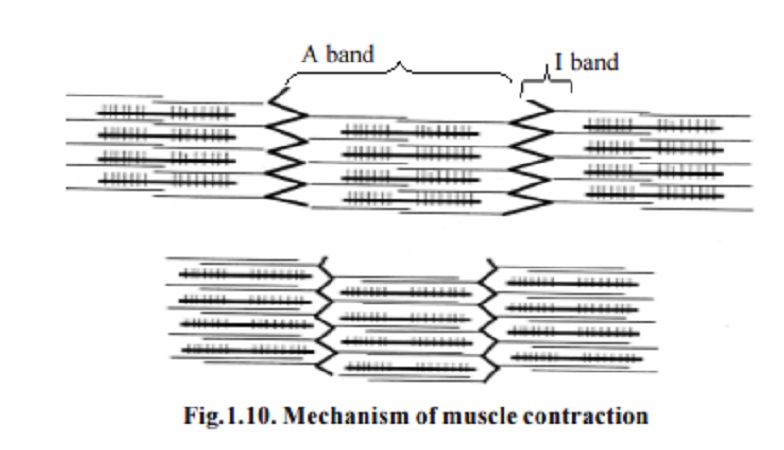
Mechanism of muscle contraction.
I. Sliding - filament hypothesis.
Hanson and Huxley proposed this hypothesis (1955). According to this hypothesis, the contractile unit of muscle is made up of two types of filaments i.e., myosin and actin. These filaments during contraction slide over one another. It has been observed that both at the time of contraction and stretching, the length of the 'A band' remains constant. The length of the 'I band', on the other hand, changes in accordance with the length of the muscle.
Due to this, the Z discs are pulled together. Thus successive sarcomeres are pulled. This leads to the contraction of the muscle.
ATP as the source of Energy for contraction :- For a muscle in action, energy is required. This energy is released by cleaving ATP molecules to ADP+ Pi. Greater amount of work is performed by the muscle, with greater amount of ATP that is cleaved. This energy binds with active site of actin filament to contract.
Neuro muscular Transmission :- The muscles are innervated by myelinated nerve fibres that originate from the spinal cord. The nerve ending makes a junction, called neuromuscular junction. The nerve is connected at the midpoint of muscle fibre so that action potential in the fibre travels in both directions. When a nerve impulse reaches the neuro-muscular junction, a substance called acetylcholine is released. The acetylcholine induces muscle fibre for contraction.
Initiation of muscle contraction :- Initiation of contraction of skeletal muscle begins with action potentials in the muscle fibres. These elicit electrical currents that spread to the interior of the fibre, where Ca ions are released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. The Ca ions inturn initiate the chemical events of the contractile process. This overall process of controlling muscle contraction is called excitation.
Maximum strength of contraction : The maximum strength of contraction of a muscle operating at a normal muscle length is about 3.5 Kg / Sq.cm. of muscle.
Changes in muscle strength : When a muscle begins to contract after a long period of rest, its initial strength of contraction may be as little as one half of its maximum strength. It gains strength after 30-50 muscle twitches. Weight lifters apply this to reach maximum capacity.
Muscle Tone
When the muscles are at rest, a certain amount of contraction usually remains. This residual degree of contraction in skeletal muscles is calledmuscle tone. The skeletal muscle tone is the result of nerve impulses from the spinal cord . These in turn are partially controlled by impulses transmitted from the brain. To some extent, the muscle tone is due to the muscle fibres itself.
Muscle Fatigue :- ( muscle contraction is diminished)
Prolonged and strong contraction of muscle leads to the state of muscle fatigue. This is due to muscle glycogen depletion and lactic acid accumulation. Fatigue probably results from inability of the contractile process and deficient metabolic process of the muscle fibre.
However, experiments show, that transmission of nerve signals through the neuromuscular junction can occasionally diminish the prolonged muscle activity, thus further reducing the power of muscle contraction. It is a well known fact that non-supply of blood to the muscles leads to almost complete fatigue within a minute. This is due to non-supply of O2 and nutrients to the muscles.
Rigor Mortis :- Several hours after death all the muscles of the body attain a state of contracture called Rigor mortis. This is due to complete depletion of ATP in muscle fibres. The muscle remains in rigor, until the lysosome enzymes completely destroy all muscle proteins. This will take place within 15-25 hours after death.
Muscle Pull
Muscle pull is actually a muscle tear. A traumatic pulling of the fibres produces tear known as strain. This injury can occur due to sudden stretching of muscle beyond their point of elasticity. While some strains are the result of high velocity impacts, other types of pull can be due to repetitive
movements. When the muscles are being exerted over a long period of time, they become vulnerable to tearing from a simple change in the position of muscles.
Back pain is a common problem, caused by muscle pull. This may be due to improper posture at the chairs. In these cases, the muscles are tightened over a long time, but the muscles may not tear until something as simple as reaching for a glass of water occurs.
Types of muscle contraction :
There are 2 types of muscle contractions.
1. Isotonic contraction: It involves muscle shortening as the myofilaments slide. This contraction produces normal movements, such as bending the knee, rotating the arms and smiling.
2. Isometric contraction: It occurs when the myofilaments 'spin their wheels' without moving, causing tension in the muscle. This is due to the muscles that are pitted against some more or less immovable object.
Isometric and aerobic exercises
In isometric exercise, muscles are moved through a short distance against a high resistance, as in pushing or pulling an immovable object. Isometric exercise is best for developing large muscles, whereas isotonic exercise has beneficial effects on the cardiovascular system. Isometric exercise-increases the thickness of the muscle fibres and their ability to store glycogen.
Exercise :
The muscle inactivity always leads to weakness and wasting of muscles. Muscles are no exception to the saying 'use it or lose it'. Regular exercise increases muscle size, strength and endurance. There are several exercises according to the needs and benefits. For example jogging or biking results in stronger, more flexible muscles with greater resistance to fatigue. Stamina formation is mainly carried out through aerobic activities, such as running and swimming.
Related Topics