Atmosphere | Geography - Precipitation | 11th Geography : Chapter 6 : Atmosphere
Chapter: 11th Geography : Chapter 6 : Atmosphere
Precipitation
Precipitation
Precipitation is the product of condensation of atmospheric water vapour that falls under gravity and reaches the surface of the earth.
In order to fall as rain drop or
snow, the tiny drop lets in a cloud must grow larger. The droplets accumulate
over the nuclei and combine to grow large enough to fall and reach the surface
of the earth due to gravity.
If the drop is smaller it falls
slowly so that it evaporates before it reaches the ground. Ice crystals in
cloud also cause precipitation. Each ice crystal grows by cooling so that they
become large in size and fall to the ground. They melt on the way due to
friction with the atmosphere and fall as rain.
Forms of Precipitation
The precipitation has various forms
based on the condition of occurrence (Figure 6.27). The various forms are;
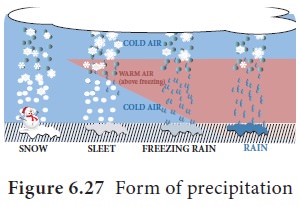
Rainfall: When water droplets of more than 0.5 mm diameter falls from the atmosphere to the ground it is called as ‘Rainfall’. If the diameter is less than 0.5mm, it is called as ‘Drizzle’.
Hail: When precipitation occurs at sub zero temperature, the water
droplets crystallise and fall as ice pellets with the size of 5 to 50 mm or
some times more. This is called as ‘Hail’.
Sleet :
Precipitation
occurs as falling of raindrop along with ice pellets less than 5 mm diameter or snow, called
as ‘Sleet’.
Snow: Precipitation occurs at below freezing point and falls as thin ice
flakes or powdery ice, called as ‘Snow’.
Dew: Condensation of water droplets on the objects at the surface of the
earth such as leaves and grasses are called as ‘Dew’.
Fact
File
Cloud Seeding or Artificial Rainfall
People have always wanted to create rain, so that they would not suffer
from drought. Modern science has been successful in causing rain in a limited
way through cloud seeding. This method is based on the knowledge of growing ice
crystals in clouds.
One method to cause rainfall from clouds is to introduce particles of
dry ice (solid CO2) into the cloud from an air plane. The dry ice causes ice
crystals to form in the cloud. These ice crystals coalesce, grow, melt and fall
as rain. Cloud seeding will not be successful unless the cloud is already
saturated with water vapour.
Types of Precipitation (Rainfall):
Precipitation can be classified based
on the causes for the rising up of air,
a.
Convectional rainfal
b.
Orographic or Relief rainfall
c.
Cyclonic or Frontal rainfall
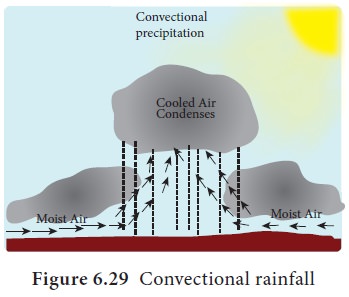
Convectional
Rainfall: As a result of heating of the surface air, the warm
moist air expands and is forced to rise to a great height. As the air rises, it
cools, reaches dew point and condenses to form clouds. This process influences
the upper tropospheric circulation. By further cooling, precipitation takes
place as rainfall. This rainfall occurs throughout the year near the equator in
the afternoon. It is called as 4 ‘O’ clock rainfall region. In middle
latitudes, convectional rainfall occurs in early summer in the continental
interiors (Figure 6.29).
Orographic or Relief Rainfall
It occurs when large mass of air is
forced to rise across land barriers, such as high mountain ranges, plateaus,
escarpments, or over high hills. On the windward side of the region the warm
moist air raises, temperature of the air falls below its dew point, forming
clouds which give subsequent rainfall. As the wind moves to the leeward side it
has emptied itself of moisture and thus descends the slope as warm dry winds.
The leeward side of the mountain therefore is called as the rain
shadow region (Figure
6.30).
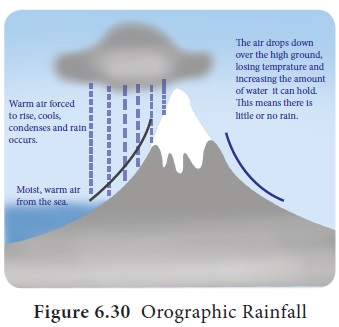
When altitude increases, the rainfall also
increases in
orographic pattern. But the rainfall decreases with altitude, once the amount
of moisture reduces in the air after a point where it reaches maximum rainfall
which is called as ‘Maximum Rainfall Line’. This condition where the rainfall
decreases with altitude is called ‘Inversion of Rainfall’.
Cyclonic or Frontal Rainfall
This type of precipitation is
associated with a cyclonic activity (Tropical and Temperate) and also occurs
along the frontal zone. Cyclonic rainfall is associated with Cumulo Nimbus
(CuNi) clouds. The rainfall is very heavy and accompanied with lightning and
thunder and high speed winds which has the potential to cause damage.
‘Frontal rainfall’ is associated with
fronts which form due to collision of different air masses. Warm front is
formed due to advent of warm air masses which leads to moderate rainfall. In
the same way cold front is formed due to advent
of cold air mass which leads to heavy rainfall with lightning and thunder.
An isohyets or
isohyetal line is a line joining
points of equal rainfall
on a map in a given period. A map with isohyets is called an isohyetal
map.
Cloud Burst
A ‘cloud burst’ is a sudden aggressive rainstorm
falling in a short period of time limited to a small geographical area.
Meteorologists say that the rain from a cloud burst is usually of the heavier
rain with a fall rate equal to or greater than 100 mm (3.94 inches) per hour.
Generally cloudbursts are associated with thunderstorms. The air currents
rushing up words in a rain storm hold up a large amount of water. For example
cloud bursts in the region of Uttarkhand (2013) and Chennai (2015).
Lightning and
Thunder are caused by differences in the electrical charge
of different parts of the cloud. The top of the cloud becomes positively
charged and the bottom is mostly negatively charged. When the difference is
great lightning occurs. Differences in the charge between cloud and the earth
surface also cause lightning.
Thunder is
caused by rapid expansion of the air
that is heated as the lightning passes through it.
Related Topics