Atmosphere | Geography - Humidity, Condensation and Clouds | 11th Geography : Chapter 6 : Atmosphere
Chapter: 11th Geography : Chapter 6 : Atmosphere
Humidity, Condensation and Clouds
Humidity,
Condensation and Clouds
Humidity is the amount of water
vapour in the atmosphere. Temperature of the air controls the capacity of the
air to hold moisture. The maximum amount of moisture that can be hold by the
air in the particular temperature is called as Humidity Capacity. As the volume
increases with the temperature of the air, it can hold more moisture. So,
humidity capacity increases with temperature. It is measured as weight of
humidity or volume of the air.
Humidity of the air can be expressed
in the following ways.
a. Absolute
Humidity: This measures the total amount of water vapour
present in the air at particular time. It is highly variable based on the
surface on which the air moves. It is measured as weight of humidity/ volume of
the air.
Hygrometer is used to measure the
relative humidity of a region.
b. Relative
Humidity (RH %): This is the ratio
of Absolute humidity and humidity capacity in term of percentage. It reveals
the condition of air to get saturated. This is controlled by both temperature
and moisture content of the air. The condition is that when the temperature
increases RH% decreases. But when absolute humidity increases RH% increases.
Process of Condensation
Condensation is the change of the
physical state of water vapour (gas state) into water (liquid state). The
following process explains mechanism of condensation in the atmosphere.
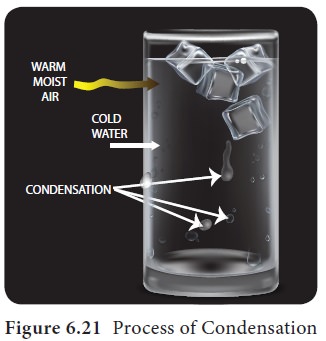
If an air reaches 100% relative
humidity, it means that the air is completely filled with moisture content. It
indicates that both the absolute humidity and the humidity capacity of the air
are in same level. This condition is called ‘saturation of air’ which can be
attained by reducing the temperature of the air or increasing the moisture
content. The temperature at which the air gets saturated is called as ‘dew
point’. The RH crosses the 100% when the temperature of the air drops below its
dew point. This condition is called as ‘super saturation’ of the air. In this
condition the air releases the excess moisture out of it in the form of tiny
water droplets which floats and form clouds in the atmosphere.
If the same process occurs on the
surface of the earth, it is called as ‘fog’ or cloud on the ground.
Clouds and its Types
Clouds are tiny water droplets
suspended in the air formed due to the condensation.
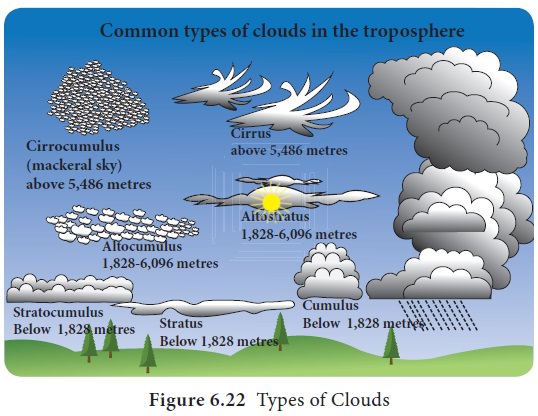
The clouds can be classified based on
their form, height and appearance as follows: (Figure 6.22)
a. High clouds: Mainly cirrus (Ci) which are feathery form at 6 km above the ground.
i. Cirrus (Ci) – This looks fibrous
and appears as wisps cotton in the blue sky. It indicates fair weather and
gives brilliant sun set.
ii. Cirro Cumulus (Cc) – This appears
as white globular masses, forming a mackerel sky.
iii. Cirro Stratus (Cs) – This
resembles a thin white sheet. The sky looks milky and the sun and moon shines
through this clouds and form a ‘halo’.
b. Middle
Clouds: Mainly Alto (Alt) clouds at 2 km to 6 km above the
ground.
•
Altocumulus (Alt-Cu): These are woolly, bumpy clouds arranged in layers
appearing like waves in the blue sky. They indicate fine weather.
•
Altostratus (Alt-St): These are denser and have watery look.
c. Low
Clouds: Mainly Stratus or
sheet clouds below 2 km height.
Stratocumulus (St-Cu): This is rough
and bumpy clouds with wavy structure.
•
Stratus (St): This is very low cloud, uniformly grey and thick, appears like
highland fog. It brings dull weather and light drizzle. It reduces the
visibility and is a hindrance to air transportation.
•
viii. Nimbostratus (Ni-St): This is dark dull cloud, clearly layered, as
it brings rain, snow and sleet and it is called as rainy cloud.
d. Clouds
with vertical extent: These are mainly cumulus clouds whose
•
Cumulus (Cu): This is vertical cloud with rounded top and horizontal
base, associated with convectional process in the tropical region. It also
called as ‘fair weather cloud’.
•
Cumulonimbus (Cu-Ni): This is over grown cumulus cloud with great
vertical extent, with black and white globular mass. The cauliflower top
spreads like an anvil. This is formed due to heavy convection in the tropical
regions. It is accompanied by lightning, thunder and heavy rainfall.

Fog, Mist and Smog
‘Fog’ is defined as almost microscopic droplets of water condensed from
super saturated air and suspended over or near the surface of the earth. Fogs
reduce the visibility to less than 1 km. Fog occurs during calm or light wind
conditions. It is more common in the areas near to the ocean due to the supply
of more moisture by sea breeze. In the interior of the continents fog is formed
due to reduction of temperature to extreme low during the winter nights.
If the fog has higher visibility due
to lesser water drops near the surface it is termed as ‘mist’.
In large industrial areas the air is
more polluted. If the fog forms in that area it mixes with the pollutants and
turns into smog (smoke 1 fog 5 smog)
which is more hazardous to the health of the people.
Hydrological Cycle
Continuous movement of water among
the three spheres is known as Hydrological Cycle. Hydrological cycle involves evaporation, condensation, precipitation, advection, interception,
evapo-transpiration, infiltration, percolation and runoff to the ocean (Figure
6.24).
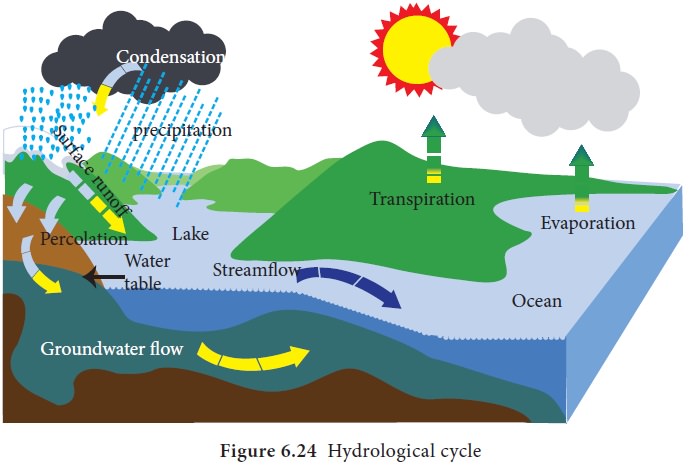
Evaporation
is the process by which water in liquid state changes
into vapour state using heat energy from Sun. Evaporation is maximum when the
temperature is high, on the large expanse of water and when dry winds blow over
water surface.
Condensation is the process by which water vapour cools to form water droplet by loosing temperature. The condensation occurs when dew point is reached in the atmosphere.
Precipitation is the process by which all forms of water particles fall from the atmosphere and reach the ground.
The rain drop that falls may get evaporated before
it reaches the ground in an extremely arid region.
Student Activity
The cup filled with ice cubes has tiny water droplets on its outer surface (Figure 6.21). Identify why.

The moisture in the atmosphere is based on the following processes:
Evaporation – Water changes from liquid state to gaseous (vapour) state.
Transpiration – Water state changes from liquid in to (gas) vapour state due to the activity of plants.
Evapotranspiration – This denotes that the total amount of (liquid) water state changed in to (gas) vapour state due to evaporation and the activity of plants transpiration.
Isonephs – The imaginary line connecting the places having equal amount of cloudiness.
Related Topics