Chapter: 11th 12th standard bio zoology Human Body higher secondary school
Poultry Farming methods
Poultry
The term poultry refers to the rearing and breeding of avian species such as chickens, ducks, turkeys, geese and guinea-fowls which have been domesticated. They are the best converters of feed into animal protein compared to other livestock. Chickens are the most common poultry enterprises. Chickens alone occupy 90% of the total poultry.
Breeds
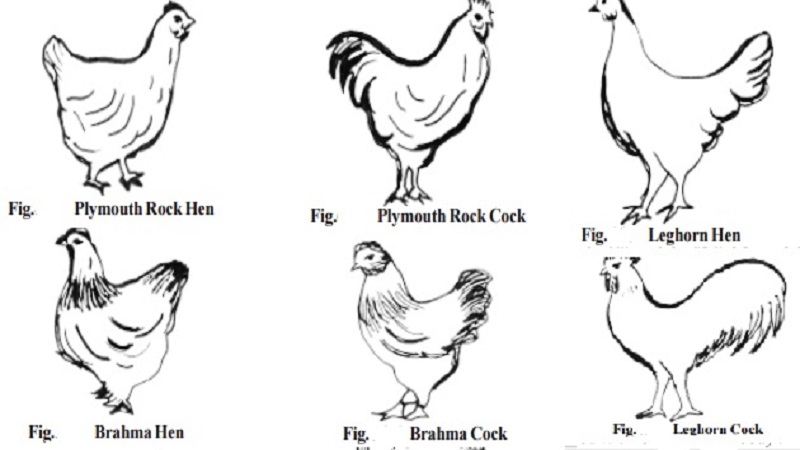
There are more than hundred breeds and more varieties of fowls. The fowls are classified based on their utility to man. They are meat type, egg type, dual type and games and ornamental type. Based on their origin there are four major exotic breeds of fowls. They are American breeds, Asiatic breeds, English breeds and Mediterranean breeds. In addition to the above many of the indigenous breeds are also reared.
Farming methods
Poultry farming has now become very popular. It is recoginzed as an organised and scientifically based industry with tremendous employment potential. It plays an important part in the rural economy of India. It provides a ready source of income to the cultivator. Besides meat and eggs, poultry supplies feathers and rich manure.The following factors are being taken into consideration for the growth of poultry farming 1) small initial investment 2) availability of quality chicks 3) short generation interval 4) quick, assured and better returns compared to other livestock species 5) availability of trained man power 6) better understanding and knowledge of the improved and scientific methods of feeding 7) management and health control.
Rearing involves the following stages:- Selection of eggs, incubation and hatching of eggs, brooding or care of new borns, housing of poultry, feeding of poultry are the important steps in rearing of chickens.
1. Selection of eggs:- Eggs meant for hatching and rearing must be selected very carefully. The following points should be considered during selection of eggs.
(1)The egg should be fertile (2) Over-sized and small sized eggs should not be selected instead medium sized should be preferred (3) Dark-brown shelled eggs hatch earlier than light-brown shelled eggs (4) Freshly laid eggs are preferred for rearing.
2. Incubation and hatching:
The fertilized hen's egg undergoes development during incubation and hatching processes. The fully formed bird emerges out of egg after a hatching period of 21-22 days. During this period the egg must obtain optimum temperature, humidity and ventilation etc. The maintanance of newly laid eggs in optimum condition till hatching is called incubation.
The incubation is of two types namely natural incubation and artificial incubation. In the natural incubation method, the eggs are subjected to the care of mother. Only a limited number of eggs can be incubated by a mother hen. In artificial incubation the eggs are maintained in a chamber(incubator) which stimulates the optimum environmental condition. In artificial incubation more number of eggs can be incubated than natural incubation.
3. Brooding :- Brooding is the care and management of young chickens for four to six weeks immediately after hatching. Like incubation, brooding also has the natural and artificial methods. In the former, day-old chickens are left to the care of mother and in the latter temperature controlled artificial brooder is used.
Factors involved in brooding :
1. Temperature :- The hatched chicks are kept inside the incubator for about 36 hours and then transfered to artificial brooder. The optimum temperature is 330c during the first 3 days. During the subsequent weeks of brooding the temperature is reduced by 30c each week till it reaches 210c.
2. Ventilation :- Fresh air movement is important for good health and proper growth of the chicks. Poor ventilation results in the accumulation of carbon monoxide, ammonia and water vapour which may lead to microbial infection.
3. Floor space :- Adequate floor space is to be provided for the proper development of chicken. Minimum 500sq.cm of floor space per chickens is to be provided. Crowding of chickens leads to poor growth and induces cannibalistic tendencies amongst the birds.
Litter :- The floor of the brood house is layered by beds of hay, rice husk or saw dust and this is called litter. The litter bed should be 5 to 7.5cm thick and it must be kept dry.
Light :- To keep the brood house free from infectious germs, the brood house must be well ventilated. Evenly distributed sunlight promotes proper growth of the birds and formation of vitamin D.
4. Housing of poultry :- Open sided poultry is popular in our country. The primary objective of providing housing to poultry is to protect them from sun, rain and predators and to provide comfort. Poultry house should be well ventilated. It should be kept cool in summer and warm in winter. The floor of the poultry house should be moisture-proof, rat proof, free from cracks, easily cleanable and durable.
5. Poultry feeding :- Feeding of poultry bird is an important part of rearing. The diet of chickens must contain adequate amount of water, carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins and minerals. The food stuffs such as maize, barley, sorghums, wheat, oil cake, rice etc are to be given in standard requirements.
Poultry byproducts
Poultry and poultry products are highly perishable. Hence, due attention has to be paid to the problems relating to processing, preservation and marketing of poultry and poultry products for the benefit of producers, processors and consumers. In a poultry processing unit, raw materials go as waste in the form of blood, feathers, heads and feet. Hatchery waste includes infertile eggs, dead embryos, and hatchery unstable chicken. Large quantity of wet droppings are also available. Processing and using of this byproducts will not only reduce the cost of poultry production, but also solve the disposal problem and minimize pollution hazard. A great deal of work has been done for processing this by-products into feather-meal, poultry byproducts meal, hatchery byproducts meal, egg shell meal, albumin flake, dried and poultry manure.
Poultry diseases : These birds are commonly affected by diseases such as ranikhet, coccidiosis, fowl pox and tick fever.
Related Topics