Chapter: Nutrition and Diet Therapy: Minerals
Phosphorus (P) - Nutrition Minerals
Phosphorus (P)
Phosphorus, together
with calcium, is necessary for the formation of strong, rigid bones and teeth.
Phosphorus is also important in the metabolism of car-bohydrates, fats, and
proteins. Phosphorus is a constituent of all body cells. It is necessary for a
proper acid-base balance of the blood and is essential for the effective action
of several B vitamins. Like calcium, phosphorus is stored in bones, and its
absorption is increased in the presence of vitamin D.
Sources.Although phosphorus is widely distributed in
foods, its bestsources are protein-rich foods such as milk, cheese, meats,
poultry, and fish. Cereals, legumes, nuts, and soft drinks also contain
substantial amounts of this mineral.
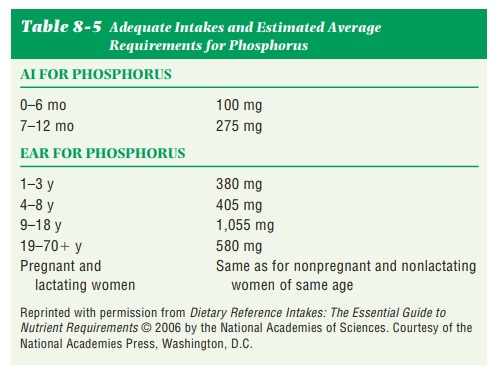
Requirements.The requirement for phosphorus is provided as
AI forthe first 12 months and as EAR (Estimated Average Requirements) after
that (Table 8-5). Phosphorus is measured in milligrams.
Deficiency.Because phosphorus is found in so many foods,
its deficiency israre. Excessive use of antacids can cause it, however, because
they affect its ab-sorption. Symptoms of phosphorus deficiency include bone demineralization (loss of minerals),
fatigue, and anorexia.
Related Topics