Chapter: Nutrition and Diet Therapy: Minerals
Iodine (I) - Nutrition Trace Minerals
Iodine (I)
Iodine is a component
of the thyroid hormones, thyroxine (T4) and triiodothy-ronine (T3).
It is necessary for the normal functioning of the thyroid gland, which
determines the rate of metabolism.
Sources.The primary sources of iodine areiodized salt,seafood, andsome plant
foods grown in soil bordering the sea. Iodized salt is common table salt to
which iodine has been added in an amount that, if used in normal cook-ing,
provides sufficient iodine.
Requirements.The DRI for adults is 150 mg a day. Additional
amountsare needed during pregnancy and lactation.
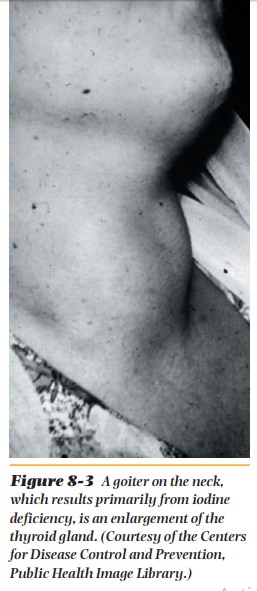
Deficiency.When the thyroid gland lacks sufficient
iodine, the manu-facture of thyroxine and triiodothyronine is retarded. In its
attempt to take up more iodine, the gland grows, forming a lump on the neck
called a goiter (Figure 8-3). Goiter appears to be more common among women than
among men. A thyroid gland that doesn’t function properly causes myxedema
(hypo-thyroidism) in adults. The children of mothers lacking sufficient iodine
may suffer from cretinism (retarded physical and mental development).
Related Topics