Chapter: Plant Biochemistry: Phenylpropanoids comprise a multitude of plant secondary metabolites and cell wall components
Phenylalanine ammonia lyase catalyzes the initial reaction of phenylpropanoid metabolism
Phenylalanine ammonia lyase catalyzes the initial reaction of phenylpropanoid metabolism
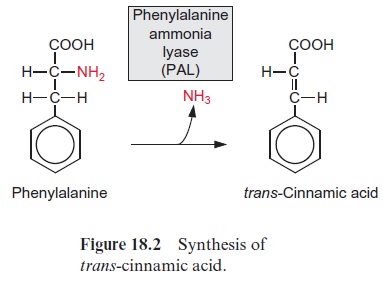
Phenylalanine ammonia lyase, abbreviated PAL, catalyzes a deamination of phenylalanine (Fig. 18.2): a carbon-carbon double bond is formed during the release of NH3, yielding trans-cinnamic acid. In some grasses, tyrosine is converted to 4-hydroxycinnamic acid in an analogous way by tyrosine ammonia lyase. The released NH3 is probably refixed by the glutamine syn-thetase reaction.
PAL is one of the most intensively studied enzymes of plant second-ary metabolism. The enzyme consists of a tetramer with subunits of 77 to 83 kDa. The formation of phenylpropanoid phytolalexins after fungal infection involves a very rapid induction of PAL. PAL is inhibited by its product trans-cinnamic acid. The phenylalanine analogue aminoxyphenyl-propionic acid (Fig. 18.3) is also a very potent inhibitor of PAL.

Related Topics