Chapter: Plant Biochemistry: Phenylpropanoids comprise a multitude of plant secondary metabolites and cell wall components
Flavonoids have multiple functions in plants
Flavonoids have multiple functions in plants
Chalcone is converted to flavanone by chalcone isomerase (Fig. 18.13). As a key enzyme of flavonoid synthesis, the synthesis of the enzyme protein of chalcone isomerase is subject to strict control. It is induced like PAL and CHS by elicitors. The middle ring is formed by the addition of a phenolic hydroxyl group to the double bond of the carbon chain connecting the two phenolic rings. Flavanone is the precursor for a variety of flavonoids; the details of the synthesis pathways of flavonoids will not be described here.
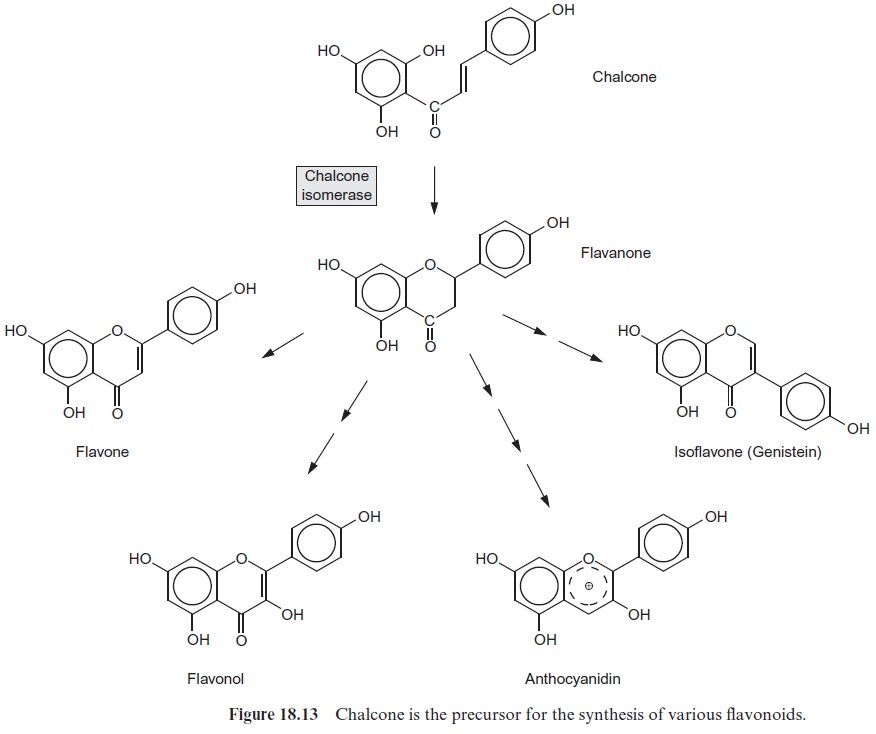
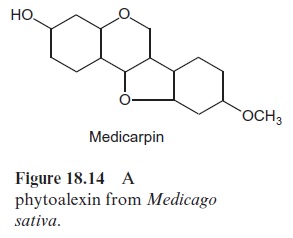
The flavonoids include protectants against herbivores and many are phytoalexins. An example of this is the poisonous isoflavone dimer roten-one, an inhibitor of the respiratory chain , which accumulates in the leaves of a tropical legume. Aboriginals in South America used to kill fish by flinging the leaves of these plants into the water. The isoflavone medicarpin from alfalfa (Medicago sativa) is a phytoalexin (Fig. 18.14). Flavonoids also serve as signals for interactions of the plant with symbi-onts. Flavones and flavonols are emitted from leguminous roots in order to attract rhizobia by chemotaxis and to induce in these the genes required for the nodulation.
Flavones and flavonols have an absorption maximum in the UV region. As protective pigments, they shield plants from the damaging effect of UV light. The irradiation of leaves with UV light induces a strong increase in flavonoid biosynthesis. Mutants ofArabidopsis thaliana, which, because of a defect in either chalcone synthase or chalcone isomerase, are not able to synthesize flavones, are extremely sensitive to the damaging effects of UV light. In some plants, fatty acid esters of sinapic acid can also act as protective pigments against UV light.
Many flavonoids are antioxidants in acting as radical scavengers for reactive oxygen species (ROS), thus preventing the peroxidation of lipids. As constituents of nutrients, they are assumed to be protectants against cardiovascular diseases and cancer. For this reason, nutrients containing flavonoids (e.g., green tea, soy sauce, and red wine) have been regarded as beneficial for health.
Recently, particular attention has been focused on certain isoflavones that are found primarily in legumes. It had been observed earlier that sheep became infertile after grazing on certain legumes. It turned out that these forage plants contained isoflavones, which in animals (and in humans) have an effect similar to that of estrogens. For this reason, they have been named phytoestrogens.Genistein, shown in Figure 18.13, has a strong estro-gen effect. Some of these phytoestrogens are used for medical purposes.
Related Topics