Chapter: 11th Nursing : Chapter 11 : Pharmacology
Pharmacodynamics
Pharmacodynamics
It covers all the
aspects relating to “what the drug does to the body”. It is the study of
biochemical and physiological effects of drug and their mechanism of action at
organ level as well as cellular level.
Types of Drug Action:
Different types of
drug actions are follows:
Stimulation: Some drugs act by increasing the activity of specialised cells, eg., catecholamine stimulate
heart to increase heart rate and force of contraction.
Depression: Some drugs act by decreasing the activity of specialised cells, eg., general anaesthetics
depress the central nervous system.
Irritation: Certain drugs on topical
application can cause irritation of the skin and the adjacent tissues, eg.,
eucalyptus oil.
Replacement: When there is a deficiency
of endogenous substances, they can be replaced by drugs, eg., Insulin.
Chemotherapeutic: Drugs are selectively toxic to infective organism or cancer cells, eg., antibiotics,
anticancer drugs.
Effects of Drugs on the Body
THERAPEUTIC EFFECTS: It is the
expected or predictable physiological response of medication. The drugs are
administered for the following purpose.
1.
TO PROMOTE HEALTH;- Drugs are given to the individual to
increase the resistance against diseases (e.g. vitamins).
2.
TO PREVENT DISEASES;- (e.g. vaccines and anti-toxins).
3.
TO DIAGNOSE DISEASE:- (e.g. barium used in the X-ray studies).
4.
TO ALLEVIATE
DISEASES:-Certain
drugs are given for the palliative effect or for the temporary relief of
distressing symptoms but does not remove the cause or cure the disease (e.g.
analgesics)
5.
TO TREAT OR CURE A
DISEASE:-
·
By restoring normal functions (e.g. digoxin).
·
By destroying the causative organisms (e.g. quinine in malaria.)
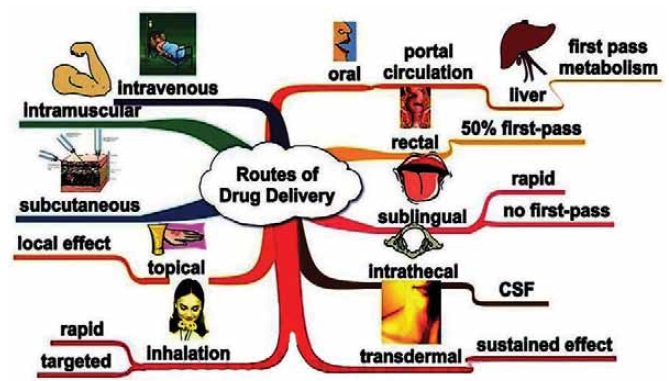
Local and Systemic effects
Local effects of a
drug are expected when they are applied topically to the skin or mucus
membrane.
A drug used for
systemic effect must be absorbed into the blood stream to produce the desired
effects in the various systems and parts of the body.
Adverse effects
Adverse effect is any
effect other than the therapeutic effect. These are generally considered severe
responses to medication.
Side effects
Side effect are the
minor adverse effects side effects can harmful or harmless.
Allergic Reactions
A client can react to
a drug as a foreign body and thus develop symptoms of allergic reaction.
Allergic reaction can be either severe or mild. A severe allergic reaction
usually occurs immediately after the administration of the drugs it is called anaphylactic reaction. A mild reaction
has a variety of symptoms. From skin rashes to diarrhoea. Such as:
SKIN RASHES:
(urticaria) Oedematous pink-ish elevation with itching .
PRURITIS: Itching of
the skin with or without a rash.
RHINITIS: Excessive
watery discharge from the nose.
LACRIMAL TEARING: Excessive
tears from the eyes.
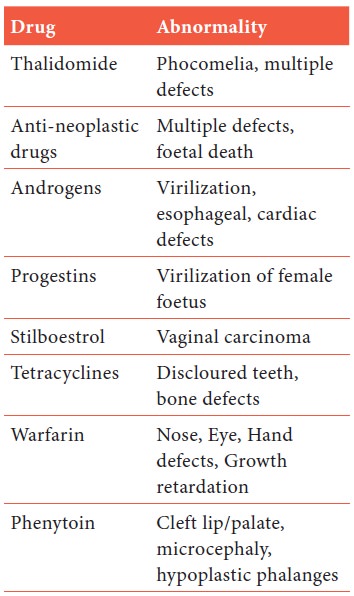
Proven Human Teratogens:
Related Topics