Characteristics, Sources, Types of Drugs - Pharmaceutical chemistry: Drugs | 9th Science : Applied Chemistry
Chapter: 9th Science : Applied Chemistry
Pharmaceutical chemistry: Drugs
Pharmaceutical
chemistry
People always want to
lead healthy life. But due to various reasons such as pollution, life style and
natural calamities they are always prone to diseases. So they need to fight
against diseases in order to lead healthy life. Do you know how our ancestors
treated diseases? There is a long history of plants being used to treat various
diseases. They figure in the records of early civilisations of Babylon, Egypt,
India and China.
When modern organic
chemistry evolved at the beginning of nineteenth century, chemists isolated
various alkaloids like morphine, quinine and atropine from plants and used them
for treatment of diseases. After 1860, many developments arose from synthesis
of medicinally important chemicals and were used for treatment of numerous
diseases.
When scientists started
using synthetic chemicals as medicines, they started to analyse the effects of
those chemicals in human and made necessary modifications. Then another new
branch of chemistry was evolved. It is called Pharmaceutical Chemistry.
Pharmaceutical chemistry
is the chemistry of drugs which utilizes the general laws of chemistry to study
drugs. Pharmaceutical chemistry deals with the preparation of drugs and study
of the chemical composition, nature, behavior, structure and influence of the
drug in an organism, condition of their storage and the therapeutic uses of the
drugs. Drug discovery is the core of pharmaceutical chemistry.
1. Drugs
Even though we use so
many chemicals in our daily life, the chemicals used for treating diseases are
termed as drug. The word drug is derived from the French word 'droque'
which means a dry herb.
According to World
Health Organisation, a drug is defined as follows: 'It is a substance or
product that is used or intended to be used to modify or explore physiological
systems or pathological states for the benefits of the recipient'.

2. Characteristics of drugs
Can we use all chemicals
as drugs? Definitely not. A drug must possess the following characteristics:
·
It should not be toxic.
·
It should not cause any side effects.
·
It should not affect the receptor tissues.
·
It should not affect the normal physiological activities.
·
It should be effective in its action.
Chemicals which satisfy
the above criteria only are preferred as drugs.
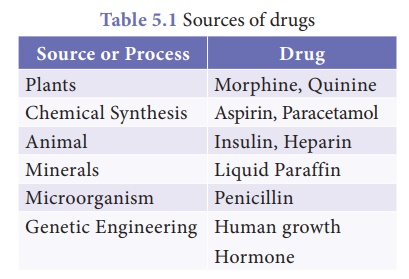
3. Sources of drugs
The main sources of
drugs are animals and plants. The modern manufacturers adopt many chemical
strategies to synthesize drugs for specialized treatments which are more
uniform than natural materials. The following table shows various
sources of drugs.
4. Types of Drugs
Drugs fall into two
general categories:
·
The drugs that are used in the treatment and cure of any specific
disease.
·
The drugs that have some characteristic effect on the animal
organism, but do not have any remedial effect for a particular disease. This class
includes, morphine, cocaine etc.
A. Anaesthetics
The drugs which cause
loss of sensation are called Anaesthetics. They are given to patients
when they undergo surgery.
(a) Types of Anaesthetics
When patients undergo a
major surgery in internal organs, some anaesthetics are given so that the they
lose sensation completely. But when they undergo a minor surgery in a specific
part of the body, anaesthetic is given to loose sensation around that
particular part. Based on this, there are two classes of anaesthetics as given
below.
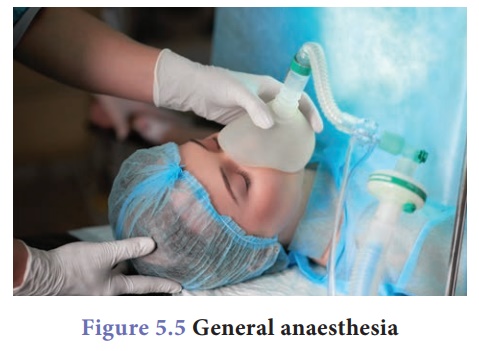
General anaesthetics: They are the agents,
which bring about loss of all modalities of sensation, particularly pain
along with ‘reversible’ loss of consciousness. For example, when a surgery is
carried out on internal organs, this anaesthetics are given. The patient loses
consciousness for specific period of time (depending on the duration of
surgery) and get it back later.
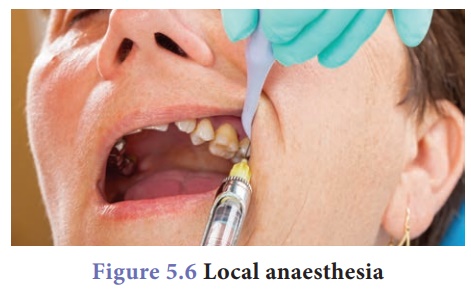
Local anaesthetics: They prevent the pain
sensation in localised areas without affecting the degree of consciousness.
For example, dentist give patients this kind of anaesthetics when carry out a
minor surgery in teeth.
(b) Chemicals as Anaesthetics:
There are three major
chemicals which are used as anaesthetics. They are:
Nitrous Oxide (N2O):
It is a colourless,
non-irritating, inorganic gas. It is the safest of the anaesthetic agents. This
is used after mixing general anaesthetics like ether.
Chloroform (CHCl3):
It is a volatile liquid.
It has pleasant smell and sweet taste. With oxygen it forms a toxic
carbonyl chloride. Hence it is not used now.
Ether: Diethyl ether or simply
ether (C2H5–O–C2H5) is a
volatile liquid. This is mixed with a stabilizer, 0.002% propyl halide. After
absorption by tissues it attacks the central nervous system and makes the
patient unconscious.
B. Analgesics
Analgesics are the
compounds which relieve all sorts of pains without the loss of consciousness.
These are also called as pain killer, or pain relievers.
These are effective in headaches, myalgia and arthralgia.

Aspirin and Novalgin are
the commonly used analgesics. Aspirin acts both as antipyretic as well as
analgesic. Certain narcotics (which produce sleep and unconsciousness) are also
used as analgesics. The analgesics are given either orally or applied
externally. In general, externally applicable pain killers come as “gels”.

C. Antipyretics
Antipyretics are the
compounds which are used for the purpose of reducing fever (lowering the body
temperature to the normal). They are taken orally as tablets and capsules. The
most common antipyretics are, aspirin, antipyrine, phenacetin, and paracetamol.

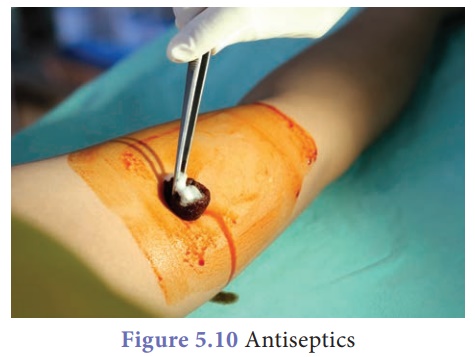
D. Antiseptics
Antiseptic is a
substance that prevents infections caused by disease causing microorganisms or
pathogens. Anticeptics either kill the microorganism or prevent their growth.
Anticeptics are used externally to cleanse wounds and internally to treat
infections of the intestine and bladder.
·
Iodoform (CHI3) is used as an antiseptic and its 1% solution is a
disinfectant.
·
0.2 percent solution of phenol acts as an antiseptic and its 1%
solution is a disinfectant.
·
Hydrogen peroxide is a minor antiseptic mainly used for
cleansing wounds.
E. Antimalarial
Malaria is a vector
borne disease which causes shivering and fever. It raises the body temperature
to 103-106°F. It causes physical weakness with the side-effects
in liver and also causes aneamia.
Extracts of roots and
stems of certain plants are extensively used as antimalarial. Quinine is a
natural antimalarial obtained from Cinchona bark. The last antimalarial
discovered in 1961 is pyrimethamine. However, quinine, primaquine and
chloroquine are some of the best antimalarials. Chloroquine is used specially
to control malarial parasites such as plasmodium ovale, plasmodium vivax etc.
It is not used in curing the disease. It is used as an additive with other
antimalarial drugs.

F. Antibiotics
Many microorganisms
(bacteria, fungi and molds) produce certain chemicals which inhibit the growth
or metabolism of some other disease causing microorganism. Such chemical
compounds are known as antibiotics. These need to be present only in
low concentration to be effective in their antibiotic action. The first
antibiotic 'penicillin' was discovered by Alexander Fleming in1929, from the
mould Penicillium notatum. Penicillin is extensively used for rheumatic fever,
narrowing of heart wall, bronchitis, and pneumonia etc.
There are three main
sources of antibiotics: (i) Bacteria (ii) Fungi and (iii) Actinomycetes. The
original antibiotics, like a lot of today’s antibiotics, are derived from
natural sources. Certain plant extracts, essential oils, and even foods have
antibiotic properties. Example: Honey, garlic, ginger, clove, neem and turmeric.

G. Antacids
Quite often, after
eating oily and spicy food, one may feel uncomfortable due to some burning
sensation in stomach / food pipe. This is due to imbalance in the acidity in
the stomach. Certain drug formulations provide relief from such burning
sensation. These are known as antacids. Antacids are available in tablet
as well as gel / syrup forms. These antacids contain magnesium and aluminium hydroxides,
in addition to flavouring agents and colour.

Related Topics