Size, Properties, Applications, Drawbacks of nanomaterials | chemistry - Nanochemistry | 9th Science : Applied Chemistry
Chapter: 9th Science : Applied Chemistry
Nanochemistry
Nanochemistry
We know that the size
and shape of materials influence their characteristics. Scientists found that
materials having size about 1/1,000,000,000 metre show special characteristics.
Then they started producing such kind of materials and studied the effect of
size on properties. Thus a new branch of chemistry called 'Nanochemistry' was
developed.
Nanochemistry is a
branch of nanoscience, that deals with the chemical applications of
nanomaterials in nanotechnology. It involves synthesis and manipulation of
materials at atomic and molecular level and the study of their physical and
chemical properties.
Nanotechnology is the application
of science to manipulate matter to atomic or molecular scale and making use of
them to develop specialized materials and devices for use in our day to day
life. It deals with the materials which are smaller than 100 nanometres and
hence it is so called.
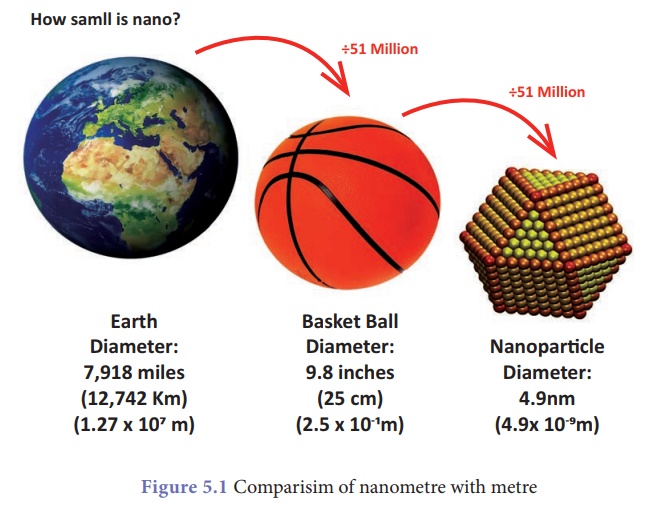
1. Size of Nanoparticles
The word, Nano has been
derived from the Greek word 'Nanos' which is designated to represent billionth
fraction of a unit. For instance, 1 Nanometre = 1/ 1,000,000,000 metre. Can you
imagine how small is a nanoparticle?
The following examples
may help to illustrate how small the nanoscale is.
·
One nanometre (nm) is 10−9 or 0.000,000,001 metre.
·
A nanometre and a metre can be understood as the same
size-difference as between golf ball and the Earth.
·
Our nails grow 1 nm each second.
·
The virus most usually responsible for the common cold has a diameter
of 30 nm.
·
One nanometre is about one twenty-five-thousandth the diameter of
a human hair.
· A cell membrane is around 9 nm across.
·
The DNA double helix is 2 nm across.
·
The diameter of one hydrogen atom is around 0.2 nm.
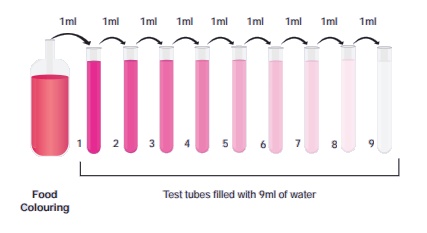
The method you have just
used is called a Serial dilution. You can notice that in each tube, the
food colouring is ten times more diluted than the previous tube. By the time
they reach tube 9, the original food colouring would have been diluted to the
level of one part of food colouring to a billion parts of water. At this stage,
the intensity of colour and smell would be extremely low.
In such a way, when
materials are broken down to nanoscale, they show some special surface
properties which make them to be used for special kinds of applications. This
type of manipulation of materials is done by nanotechnology.
How small is a nanoparticle? Visit the following link: https://www.youtube.com/ watch?v=38Vi8Dm0kdY
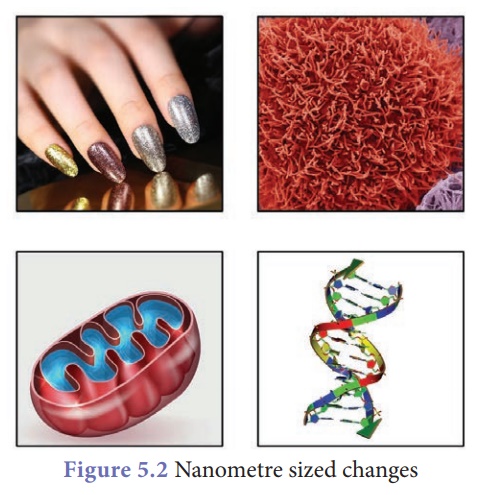
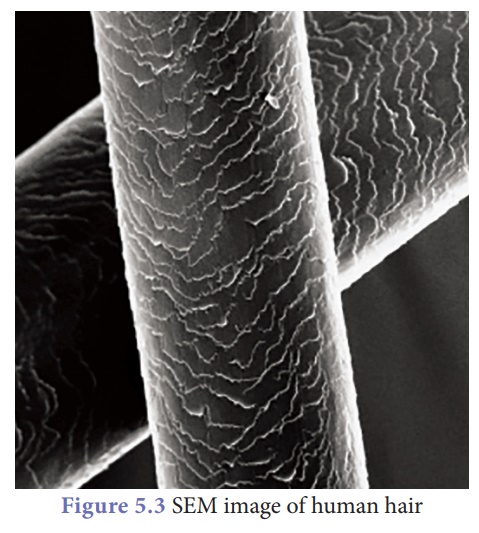
2. Properties of nanomaterials
Nanomaterials have the
structural features in between those of atoms and the bulk materials. The
properties of materials with nanometre dimensions are significantly different
from those of atoms and bulk materials. This is mainly because the nanometre
size of the materials render them, larger surface area, high surface energy,
spatial confinement and reduced imperfections, which do not exist in the
corresponding bulk materials. Due to their small dimensions, nanomaterials have
extremely large surface area to volume ratio, resulting in more 'surface
dependent' material properties. As the surface characteristics of nanoparticles
are the main criteria to be considered for applications, highly sophisticated
instruments like Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM), Tunneling Electron Microscope
(TEM) and Atomic Force Microscope (AFM) are used to analyse the surface
properties of a nanoparticle with high resolution.
3. Applications of Nanochemistry
The range of commercial
products available today is very broad, including stain-resistant and
wrinkle-free textiles, cosmetics, sunscreens, electronics, paints and
varnishes. Nanochemistry is applied in all these substance. Some of them are
given below.
·
The metallic nanoparticles can be used as very active catalysts.
·
Chemical sensors from nanoparticles and nanowires enhance the
sensitivity and sensor selectivity.
·
Nano coatings and nanocomposites are found useful in making
variety of products such as sports equipment, bicycles and automobiles etc.
·
These are used as novel UV-blocking coatings on glass
bottles which protect beverages from being damaged by sunlight.
·
Nanotechnology is being applied in the production of synthetic
skin and implant surgery.
·
Nanomaterials that conduct electricity are being used in
electronics as minute conductors to produce circuits for microchips.
·
Nanomaterials have extensive applications in the preparation of
cosmetics, deodorants and sun screen lotion and they are used to improve
moisturizers without making them too oily.
·
Nanoparticle substances are incorporated in fabrics to prevent the
growth of bacteria.
·
Biomedical devices like drug infusion pumps, microneedles and
glucometer are made from nanomaterials.
·
Nanochemistry is used in making space, defence and aeronautical
devices
4. Drawbacks of nanomaterials in chemistry
·
Nanoparticles are unstable when they contact with oxygen.
·
Their exothermic combustion with oxygen can easily cause
explosion.
·
Because nanoparticles are highly reactive, they inherently
interact with impurities as well.
·
Nanomaterials are usually considered biologically harmful and
toxic.
·
It is difficulty to synthesis, isolate and apply them.
·
There are no hard-and-fast safe disposal policies for
nanomaterials.
Related Topics