Chapter: 9th Science : Applied Chemistry
Agricultural and Food Chemistry
Agricultural
and Food Chemistry
1. Agricultural Chemistry
Agricultural chemistry
involves the application of chemical and biochemical knowledge to agricultural
production, processing of raw materials into foods and beverages, and
environmental monitoring and remediation. It deals with scientific relation
between plants, animals, bacteria and environment.
(a) Role of agricultural chemistry
India is predominantly
an agricultural country. Its major source of food production is agriculture.
Indian agriculture began in 7000 BC and followed a traditional practice. After
independence, rapid growth of population and urbanization made threats to
agricultural production and it led to food scarcity.

Indian chemists and
biochemists applied their knowledge and developed modernized agricultural
practices which involve use of synthetic fertilizers, genetically modified
crops, and equipments.
(b) Goals of agricultural chemistry
The goals of
agricultural chemistry are to expand the understanding of the causes and
effects of biochemical reactions related to plant and animal growth, to reveal
opportunities for controlling those reactions, and to develop chemical products
that will provide the desired assistance or control. It aims at producing
sufficient nutritious food and feed the population in a sustainable way while
being responsible stewards of our environment and ecosystem. Based on the
issues and challenges in agricultural production, agricultural chemistry mainly
focusses to achieve the following:
• Increase in crop yield and livestock
• Improvement of food quality
• Reducing cost of food production
(c) Applications of Agricultural Chemistry
Chemical principles and
reactions are most widely used in agriculture in order to increase yield, to
protect crops from diseases and to simplify the practice of agriculture.
Various applications are give below.
Soil Testing: Crop lands may have
different kinds of soil with varying pH. Soil pH is one of the main
criteria to be considered for the selection of crop or remediation of soil.
Soil testing involve determination of pH, porosity and texture.
Chemical Fertilizers: Fertilizers are chemical
compounds added to crop field for supplying essential micro and macro
nutrients required for crop growth. Ammonium nitrate, calcium phosphate, urea,
NPK (Nitrogen, Phosphorous and Potassium), etc. are some of the fertilizers.
Depending on the nature of soil, these fertilizers are used singly or as
mixtures.

Pesticides and
Insecticides: Crops are prone to diseases caused by pests and insects.
Chemically synthesized pesticides and insecticides are used to solve these
issues. Chlorinated hydrocarbons, organophosphates and carbamates are used as
pesticides and insecticides.

2. Food Chemistry
Food is one of the basic
needs of human and animal. The food we eat also are made of chemicals. Any
human might require the following three kinds of food:
Body building foods: These are required for
physical growth of body. E.g. Proteins
Energy giving foods: These the foods that
supply energy for the functioning of parts human body. E.g. Carbohydrates
Protective
foods: These protect
us from deficiency diseases. E.g.
Vitamins and Minerals
Every human requires all
these three kind of foods in right proportion for the smooth functioning of the
body. The diet that contain all these three foods in right proportion is called
Balanced diet.
Food chemistry is
chemistry of foods which involves the analysis, processing, packaging, and
utilization of materials including bioenergy for food safety and quality.
(a) Goals of food chemistry
The main goal of food
chemistry is to cater the needs of quality food to the population in a
sustainable way. In basic research, food chemists study the properties of
proteins, fats, starches, and carbohydrates, as well as micro components such
as additives and flavourants, to determine how each works in a food system. In
application research, they often develop new ways to use ingredients or new
ingredients altogether, such as fat or sugar replacements.
(b) Chemicals in Food
Food we eat in our day
to day life contains natural or synthetic chemicals. They serve different
functions in human body.
Nutrients: They are the most
essential chemicals present in food. They are required for the growth,
physiological and metabolic activities of body. They are natural or synthetic.
E.g. Carbohydrates, proteins, vitamins and minerals
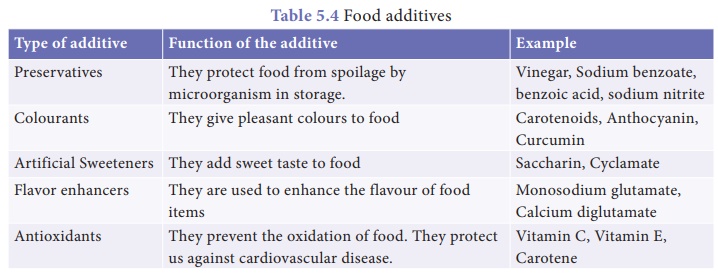
Food additives: These are the chemicals
added to food for specialized functions. The various types of additives of
foods are given in Table 5.4.
Food colouring or colour
additives are pigments-synthetic or natural-added to food to create a certain
colour, enhance a natural colour and improve the overall aesthetic appeal of a
dish. Food colouring can make food fun. Food colouring contains one or more of
the certified colour additives commonly known by their numbering system. Colour
additives are blended to create a brightness or intensity to the base colour.
The other basic ingredients of synthetic food colouring are propylparaben,
propylene glycol and water.

Related Topics