Universe and Space | Term 3 Unit 2 | 7th Science - Origin of the Universe | 7th Science : Term 3 Unit 2 : Universe and Space
Chapter: 7th Science : Term 3 Unit 2 : Universe and Space
Origin of the Universe
Origin of the Universe
You are a student who belong to a
particular class studying in VII std. In your school, there might me many
section for VII std.
Likewise, there are VI std class, VIII std class and so on. All of them
together make the school. Likewise, our Sun is a star with a planetary system.
Billions of such stars consitute a system called as galaxy. The name of our
galaxy is, Milky Way. Like Milky Way, there are at least hundreds of billions
of galaxies in the Universe.

How did all these come about? Where
they in existence always or was there a beginning?
When we observed other galaxies we
found a strange behavior. All the galaxies were appearing to move away from us.
Further, farther they are faster they appear to move. Cosmologists , scientists
who study the structure and evolution of universe that is cosmos, reason that
this imply at one point of time in the past all matter was confined in a single
point and since then it has started to expand.
The event when the matter confined
in a single point and began to expand is called ‘big bang’. This is considered
as the origin of our universe as we know it.
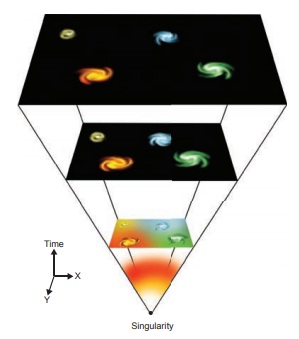
The Big Bang Theory is the
prevailing model of the evolution of the Universe. Under this theory, space and
time emerged together about 14 billions of years ago. At that time, the entire
Universe was inside a bubble that was thousands of times smaller than a
pinhead. It was hotter and denser than anything we can imagine. Then it
suddenly expanded. The present Universe emerged .Time, space and matter all
began with the Big Bang.
In a fraction of a second, the
Universe grew from smaller than a single atom to bigger than a galaxy. And it
kept on growing at a fantastic rate. It is still expanding today. Over the next
three minutes, the temperature dropped below 1 billion degrees Celsius. After
300 000 years, the Universe had cooled to about 3000 degrees. Atomic nuclei
could finally capture electrons to form atoms. At that stage of the evolution
of the Universe, it was filled with clouds of hydrogen and helium gas. Giant
clouds of hydrogen and helium were gradually drawn to the
places where dark matter was most dense, forming the first galaxies, stars, and
everything else seen today.
We cannot see anything that happened
during the first 300000 years of the Universe. Scientists try to work it out
from their knowledge of atomic particles and from computer models. The only
direct evidence of the Big Bang itself is a faint glow in space, called cosmic
microwave background.
As millions of years passed, the
dense areas pulled in material because they had more gravity. Finally, about
100 million years after the Big Bang, the gas became hot and dense enough for
the first stars to form. New stars were being born at a rate 10 times higher
than in the present-day Universe. Large clusters of stars soon became the first
galaxies.
The Hubble Space
Telescope and powerful ground-based telescopes are now beginning to find
galaxies that were created about one billion years after the Big Bang. These
small galaxies were much closer together than galaxies are today. Collisions
were common. Like two flames moving towards each other, they merged into bigger
galaxies. Our Milky Way galaxy came together in this way.

Building
Blocks Of Universe.
As stated above universe is
constituted of galaxies, just as lot of houses in our locality constitute a
village or a city. We have lot of things such as rooms, furniture etc. in our
homes.
Likewise lot of stellar objects such
as stars, planets, asteroids and meteors are the building blocks of our
universe.
More to know
Astronomical unit : The average distance between
the Earth and the Sun is called an astronomical unit. It is denoted by ‘au’.
1 au = 1.496 x 108 km
Light year : The distance travelled by light in
one year is called a light year. It is denoted by ‘ly’.
1 ly = 9.4607 x 1012 km
Parsec: A parsec is defined as the distance
at which one astronomical unit subtends an angle of one arc second.
It is denoted by ‘pc’
1 pc = 3.2615 ly = 3.09 x 1013
km
Related Topics