Chemistry Practical Laboratory Experiment - Organic Qualitative Analysis | 12th Chemistry : Practicals
Chapter: 12th Chemistry : Practicals
Organic Qualitative Analysis
Common Tests
1. Odour:
2. Test with litmus paper:
3. Action with sodium bicarbonate:
4. Action with Borsche’s reagent:
5. Charring test:
Tests for Aliphatic or Aromatic nature:
6. Ignition test:
Tests for an unsaturation:
7. Test with bromine water:
8. Test with KMnO4 solution:
TEST FOR SELECTED ORGANIC FUNCTIONAL GROUPS
Test For Phenol
9 Neutral FeCl3 test:
TEST FOR CARBOXYLIC ACIDS
10. Esterification reaction:
Test for aldehydes.
11. Tollen’s reagent test:
12. Fehling’s test:
Test for ketones
13. Legal’s test:
Test for an amine.
14. Dye test:
Test for diamide
15 Biuret test:
Test for carbohydrates
16 Molisch’s test:
17 Osazone test:
List of organic compounds for analysis:
1. Benzaldehyde
2. Cinnamaldehyde
3. Acetophenone
4. Benzophenone
5. Benzoic acid
6. Cinnamic acid
7. Urea
8. Glucose
9. Aniline
10. Salicylic acid
List of organic compounds for analysis:
1. Benzaldehyde
2. Cinnamaldehyde
3. Acetophenone
4. Benzophenone
5. Benzoic acid
6. Cinnamic acid
7. Urea
8. Glucose
9. Aniline
10. Salicylic acid

Report:
The given organic compound contains /is
(i) Aromatic / aliphatic
(ii) Saturated / unsaturated
(iii) __________ functional group
REASONING - ORGANIC QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS
3. Action with sodium bicarbonate:
Carboxylic acids react with sodium bi carbonate and liberate CO2. Evolution of carbon dioxide gives brisk effervescence.
2R-COOH+ 2NaHCO3 →2R-COONa+CO2 ↑ + H2O
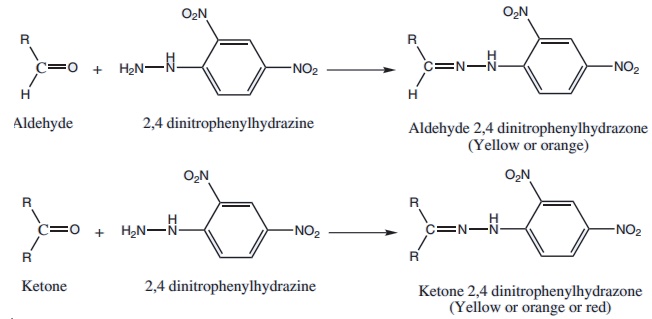
4. Action with Borsches reagent:
Borsches reagent is prepared by dissolving 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine in a solution containing methanol and little of conc sulphuric acid.
Aldehydes and ketones react with borsches reagent to form yellow, orange or red precipitate (dinitro phenylhydrazone)
Aliphatic carbonyl compounds give deep yellow precipitate.
Aromatic carbonyl compounds give red precipitate.
2,4-dinitrophenyl hydrazine can be used to qualitatively detect the carbonyl group of an aldehyde or ketone. A positive result is indicated by the formation of an yellow or orange-red precipitate of 2,4-dinitrophenyl hydrazone.
5. Charring test:
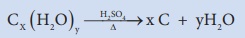
When carbohydrates are treated with concentrated sulphuric acid, dehydration of carbohydrates results in charring.
6. Ignition test
Aromatic compounds burn with a strong sooty yellow flame because of the high carbon–hydrogen ratio. Aliphatic compounds burn with non-sooty flame.
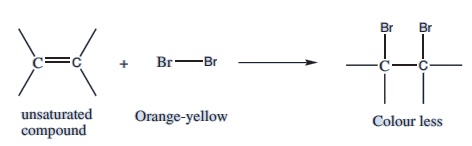
7. Test with bromine water:
In this test, the orange-red colour of bromine solution disappears when it is added to an unsaturated organic compound.
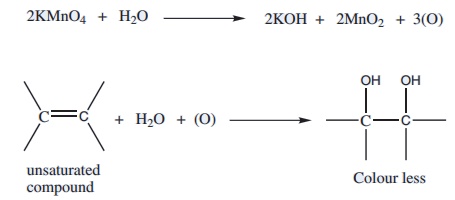
8. Test with KMnO4 (Baeyer’s Test )
In this test, pink colour of KMnO4 disappears, when alkaline KMnO4 is added to an unsaturated hydrocarbon. The disappearance of pink colour may take place with or without the formation of brown precipitate of MnO2.
9. Neutral FeCl3 test:
Phenol reacts with ferric ions to form violet coloured complex.
Aqueous solution Naphthols do not give any characteristic colour with neutral ferric chloride. But alcoholic solution of α and β naphtholsgiveblue-violet and green colouration respectively due to the formation of binaphthols.
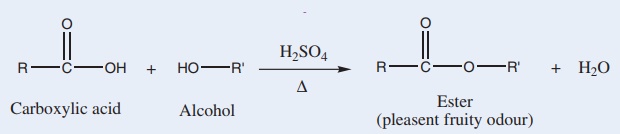
10. Esterification test:
Alcohols react with carboxylic acids to form fruity smelling compounds called esters. This esterification is catalysed by an acid such as concentrated sulphuric acid.
11. Tollen’s reagent test:
Aldehydes react with Tollen’s reagent to form elemental silver, accumulated onto the inner surface of the test tube. Thus silver mirror is produced on the inner walls of the test tube.
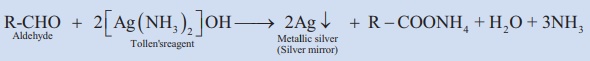
Tollen’s reagent preparation:
Tollen’s reagent is ammoniacal silver nitrate. It is prepared as follows. About 1 g of silver nitrate crystals are dissolved in distilled water in a clean dry test tube. To this aqueous solution of silver nitrate, add 2 ml of dilute NaOH solution to it. A brown precipitate of silver oxide is formed. This precipitate is dissolved by adding dilute ammonia solution drop wise.
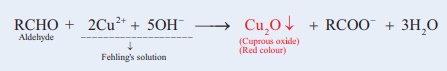
12. Fehling’s Test
Fehling’s solution A is an aqueous solution of copper sulphate.
Fehling’s solution B is a clear solution of sodium potassium tartrate (Rochelle salt) and strong alkali (NaOH).
The Fehling’s solution is obtained by mixing equal volumes of both Fehling’s solution A and Fehling’s solution B that has a deep blue colour. In Fehling’s solution, copper (II) ions form a complex with tartrate ions in alkali. Aldehydes reduces the Cu(II) ions in the Fehling’s solution to red precipitate of cuprous oxide(copper (I) oxide).
Note: Benzaldehyde may not give this test as the reaction is very slow.
13. Sodium nitroprusside Test
The anion of the ketone formed by a alkali reacts with nitroprusside ion to form a red coloured complex.this test is not given by aldehydes.
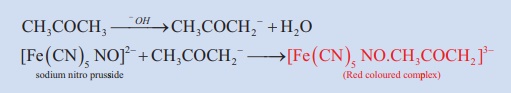
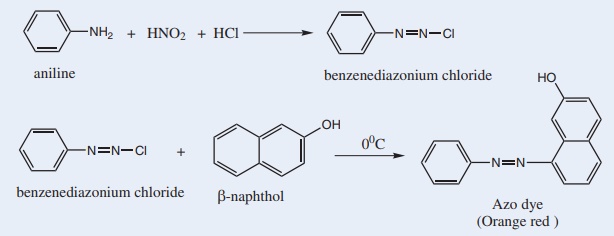
14. Azo-Dye Test
This test is given by aromatic primary amines. Aromatic primary amines react with nitrous acid to form diazonium salts. These diazonium salts undergo coupling reaction with β-naphthol to form orange coloured azo dye.
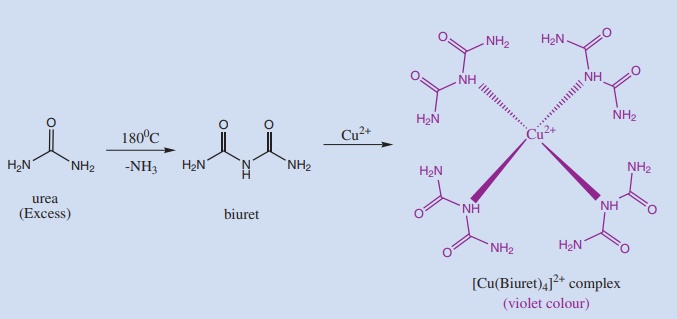
15. Biuret test
On strong heating Diamide (like urea) form biuret, which forms a copper complex with Cu2+ ions from copper sulphate solution. This copper –biuret complex is deep violet coloured.
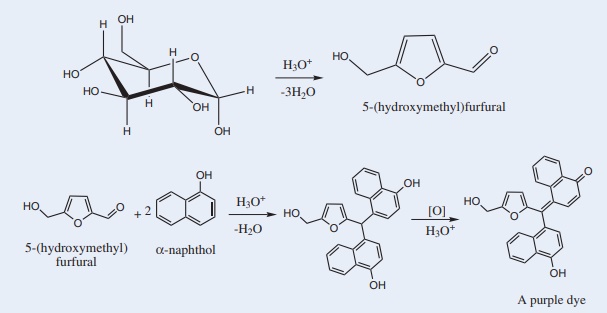
16. Molisch’s test:
Disaccharides, and polysaccharidesare hydrolysed to Monosaccharides by strong mineral acids. Pentoses are then dehydrated to furfural, while hexoses are dehydrated to 5-hydroxymethylfurfural. These aldehydes formed will condense with two molecules of α-Naphthol to form a purple-coloured product, as shown below.
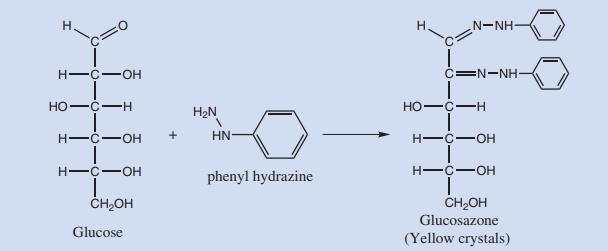
17. Osazone test:
Phenyl hydrazine in acetic acid, when boiled with reducing sugars forms Osazone. The first two carbon atoms are involved in this reaction. The sugars that differ in their configuration on these carbon atoms give the same type of Osazone. Thus glucose, fructose and mannose give the same needle type yellow crystals.
Related Topics