Chapter: Organic Chemistry: Functional groups
Organic Chemistry: Recognition of functional groups
RECOGNITION OF FUNCTIONAL GROUPS
Key Notes
Definition
Functional
groups are portions of a molecule which contain atoms other than carbon and
hydrogen, or which contain bonds other than C–C and C–H.
Common functional groups
Some of
the most common functional groups in organic chemistry are alkenes, alkynes,
aromatics, nitriles, amines, amides, nitro compounds, alco-hols, phenols,
ethers, aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, acid chlorides, acid anhydrides,
esters, alkyl halides, thiols, and thioethers.
Definition
A functional group is a portion of an organic
molecule which consists of atoms other than carbon and hydrogen, or which
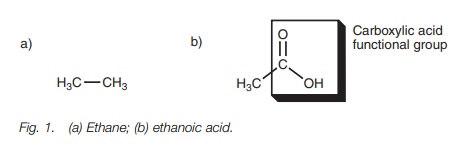
contains bonds other than C–C and C–H bonds. For example, ethane (Fig. 1a) is
an alkane and has no functional group. All the atoms are carbon and hydrogen
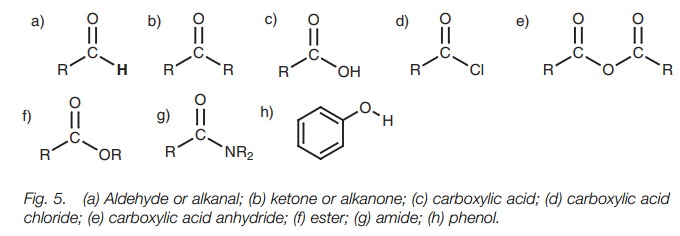
and all the bonds are C–C and C–H. Ethanoic acid on the other hand (Fig. 1b),
has a portion of the molecule (boxed portion) which contains atoms other than
carbon and hydrogen, and bonds other than C—H and C—C. This portion of the molecule is called a
functional group – in this case a carboxylic acid.
Common functional groups
The following are some of the more common
functional groups in organic chemistry.
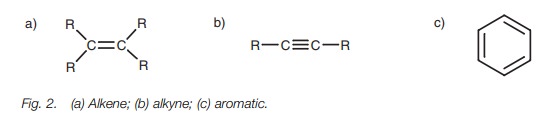
● functional groups which contain nitrogen (Fig. 3);
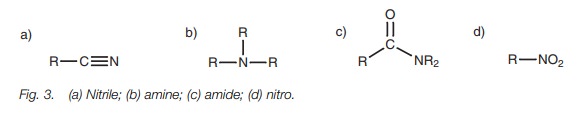
● functional groups involving single bonds and which contain oxygen (Fig. 4);
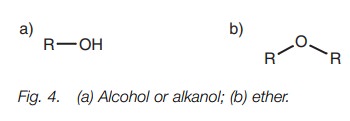
● functional groups involving double bonds and which contain oxygen (Fig. 5);
● functional groups which contain a halogen atom (Fig. 6);
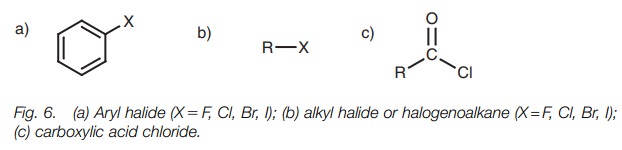
● functional groups which contain sulfur (Fig. 7).

Related Topics