Chapter: Basic & Clinical Pharmacology : Antifungal Agents
Oral Systemic Antifungal Drugs for Mucocutaneous Infections
ORAL SYSTEMIC ANTIFUNGAL DRUGS FOR MUCOCUTANEOUS INFECTIONS
GRISEOFULVIN
Griseofulvin is a very
insoluble fungistatic drug derived from a species of penicillium. Its only use
is in the systemic treatment of dermatophytosis . It is administered in a micro-crystalline
form at a dosage of 1 g/d. Absorption is improved when it is given
with fatty foods. Griseofulvin’s mechanism of action at the cellular level is
unclear, but it is deposited in newly forming skin where it binds to keratin,
protecting the skin from new infec-tion. Because its action is to prevent
infection of these new skin structures, griseofulvin must be administered for
2–6 weeks for skin and hair infections to allow the replacement of infected
kera-tin by the resistant structures. Nail infections may require therapy for
months to allow regrowth of the new protected nail and is often followed by
relapse. Adverse effects include an allergic syn-drome much like serum
sickness, hepatitis, and drug interactions with warfarin and phenobarbital. Griseofulvin
has been largely replaced by newer antifungal medications such as itraconazole
and terbinafine.
TERBINAFINE
Terbinafine
is a synthetic allylamine that is available in an oral formulation and is used
at a dosage of 250 mg/d. It is used in the treatment of dermatophytoses,
especially onychomycosis . Like griseofulvin, terbinafine is a keratophilic
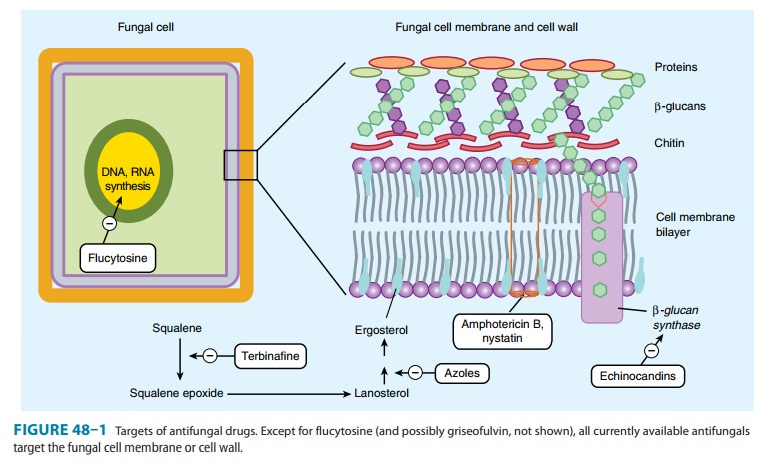
medi-cation, but unlike griseofulvin, it is fungicidal. Like the azole drugs,
it interferes with ergosterol biosynthesis, but rather than interacting with
the P450 system, terbinafine inhibits the fungal enzyme squalene epoxidase
(Figure 48–1). This leads to the accu-mulation of the sterol squalene, which is
toxic to the organism. One tablet given daily for 12 weeks achieves a cure rate
of up to 90% for onychomycosis and is more effective than griseofulvin or
itraconazole. Adverse effects are rare, consisting primarily of
gastrointestinal upset and headache. Terbinafine does not seem to affect the
P450 system and has demonstrated no significant drug interactions to date.
Related Topics