Chapter: Basic & Clinical Pharmacology : Vasodilators & the Treatment of Angina Pectoris
Newer Antianginal Drugs
NEWER ANTIANGINAL DRUGS
Because
of the high prevalence of angina, new drugs are actively sought for its
treatment. Some of the drugs or drug groups currently under investigation are
listed in Table 12–6.
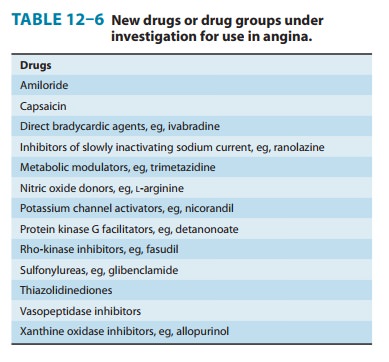
Ranolazine is a newer antianginal drug that appears to
act byreducing a late sodium current (INa) that facilitates calcium
entry via the sodium-calcium exchanger . The resulting reduction in
intracellular calcium concentration reduces cardiac contractility and work.
Ranolazine is approved for use in angina in the USA.
Certain metabolic modulators (eg, trimetazidine) are known as pFOX inhibitors because they partially inhibit the fatty acid oxida-tion pathway in myocardium. Because metabolism shifts to oxida-tion of fatty acids in ischemic myocardium, the oxygen requirement per unit of ATP produced increases.
Partial inhibition of the enzyme required
for fatty acid oxidation (long-chain 3-ketoacyl thiolase, LC-3KAT) appears to
improve the metabolic status of ischemic tis-sue. (Ranolazine was initially
assigned to this group of agents.). Trimetazidine is not approved for use in
angina in the USA. A much older drug, allopurinol,
represents another type of metabolic modifier. Allopurinol inhibits xanthine
oxidase , an enzyme that contributes to oxidative stress and endothelial
dysfunc-tion. A recent study suggests that high-dose allopurinol prolongs
exercise time in patients with atherosclerotic angina.
So-called
bradycardic drugs, relatively
selective If sodium chan-nel blockers (eg, ivabradine), reduce cardiac rate by inhibiting the
hyperpolarization-activated sodium channel in the sinoatrial node. No other
significant hemodynamic effects have been reported. Ivabradine appears to
reduce anginal attacks with an efficacy similar to that of calcium channel
blockers and β
block-ers. The lack of effect on gastrointestinal and bronchial smooth muscle
is an advantage of ivabradine, and Food and Drug Administration approval is
expected.
The
Rho kinases comprise a family of enzymes that inhibit vascular relaxation and
diverse functions of several other cell types. Excessive activity of these
enzymes has been implicated in coronary spasm, pulmonary hypertension,
apoptosis, and other conditions. Drugs targeting the enzyme have therefore been
sought for possible clinical applications. Fasudil
is an inhibitor of smooth muscle Rho kinase and reduces coronary vasospasm in
experimental animals. In clinical trials in patients with CAD, it has improved
performance in stress tests.
Related Topics